 PDF(1863 KB)
PDF(1863 KB)


 PDF(1863 KB)
PDF(1863 KB)
 PDF(1863 KB)
PDF(1863 KB)
长三角区域酸雨类型转变趋势研究
Changing trends of acid rain types in the Yangtze River Delta region

【目的】酸雨是人类面临的重要环境问题,而我国长三角区域已成为全球重要酸雨影响地区之一。目前,我国已对SO2排放进行了有效控制,但随着氮氧化物排放量显著增多,氮沉降问题逐渐加剧。为此,探究长三角区域的酸雨类型转变趋势,为现在及将来酸雨危害严重地区森林生态系统恢复和可持续经营发展提供理论依据。【方法】将长三角区域作为研究对象,以上海、南京、苏州和宁波4个城市为代表,通过分析4个城市降水及大气排放物特征,了解区域酸雨类型的特点。【结果】长三角区域多年平均降水pH和酸雨频率分别为4.87±0.28和(57.12±18.67)%,大气中SO2含量逐年显著下降,但是4个代表城市大气NO2含量变化趋势存在差异。其中,上海和南京地区NO2含量缓慢下降,而苏州和宁波地区NO2含量则仍然呈显著上升趋势。降水pH仍然受SO2含量变化的显著影响,降水中硫氮比( 与 含量比)从20世纪90年代的7.5左右下降到当前的2.0左右,区域酸雨类型已经转变为硫酸-硝酸混合型。【结论】长三角区域仍然受到酸雨影响,且酸雨中硫氮比正逐渐降低,酸雨类型发生了转变,这将对长三角区域生态系统提出更加严峻的考验。
【Objective】 Acid rain is an environmental problem of global concerns. The Yangtze River Delta region of China (YRD) has become one of the major acid rain regions in the world. Currently, SO2 emissions in China have decreased because of the implementation of a series of SO2 control measures. However, NO2 emissions have not decreased significantly, and this may lead to a progressive change in the type of acid rain. Exploring the changing trends of acid rain types in the YRD region will provide a theoretical basis for the restoration and sustainable management development of forest ecosystems stressed by acid rain. 【Method】 In this study, we explored the characteristics of acid rain in the YRD region by integrating the characteristics of precipitation and atmospheric emissions in major cities. 【Result】 The annual average pH values and frequency of acid rain were 4.87±0.28 and (57.12±18.67)% in the YRD region. The SO2 content in the atmosphere significantly decreased year by year. However, no consistent pattern of NO2 content was found in different cities. The NO2 content decreased slowly in Shanghai and Nanjing. In contrast, the NO2 content in the atmosphere clearly increased in Suzhou and Ningbo. The precipitation pH values were still mainly influenced by SO2 in the YRD region. However, the / in precipitation decreased from 7.5 in the 1990s to 2.0, which suggests that the type of acid rain has changed from sulfuric acid rain (SAR) to mixed acid rain (MAR) in the YRD region. 【Conclusion】 The Yangtze River Delta region experiences stress because of acid rain, and the / of acid rain has decreased year by year. In the future, the change in acid rain types from SAR to MAR, or to nitric acid rain (NAR), might complicate the ongoing challenge of ecosystem stability and increase the risks to ecosystem functioning in the YRD region.
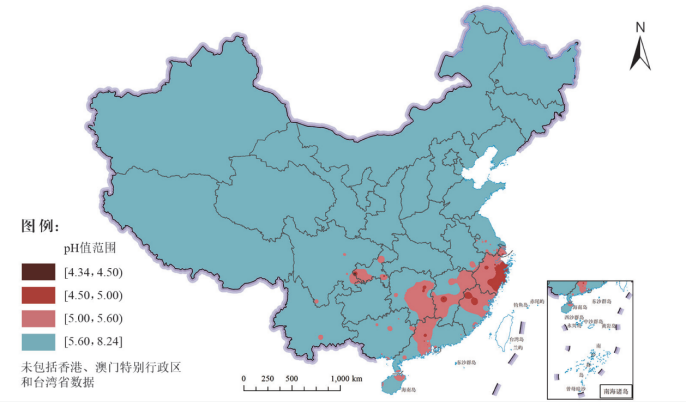
长三角地区 / 酸雨 / 二氧化硫 / 氮氧化物 / 硫氮比
Yangtze River Delta / acid rain / sulfur dioxide(SO2) / nitrogen oxide (NOx) /
| [1] |
Acidification of rain-water is identified as one of the most serious environmental problems of transboundary nature. Acid rain is mainly a mixture of sulphuric and nitric acids depending upon the relative quantities of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen emissions. Due to the interaction of these acids with other constituents of the atmosphere, protons are released causing increase in the soil acidity Lowering of soil pH mobilizes and leaches away nutrient cations and increases availability of toxic heavy metals. Such changes in the soil chemical characteristics reduce the soil fertility which ultimately causes the negative impact on growth and productivity of forest trees and crop plants. Acidification of water bodies causes large scale negative impact on aquatic organisms including fishes. Acidification has some indirect effects on human health also. Acid rain affects each and every components of ecosystem. Acid rain also damages man-made materials and structures. By reducing the emission of the precursors of acid rain and to some extent by liming, the problem of acidification of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem has been reduced during last two decades.
|
| [2] |
孙崇基. 酸雨[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2001.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
At present, acid rain or snow is falling on most of the northeastern United States. The annual acidity value averages about pH 4, but values between pH 2.1 and 5 have been recorded for individual storms. The acidity of precipitation in this region apparently increased about 20 years ago, and the increase may have been associated with the augmented use of natural gas and with the installation of particle-removal devices in tall smokestacks. Only some of the ecological and economic effects of this widespread introduction of strong acids into natural systems are known at present, but clearly they must be considered in proposals for new energy sources and in the development of air quality emission standards.
|
| [7] |
姚芳芳. 酸沉降类型和喷施方式对木荷和湿地松幼苗生理生态及生长的影响[D]. 上海:华东师范大学, 2016.
|
| [8] |
王丽红, 孙静雯, 王雯, 等. 酸雨对植物光合作用影响的研究进展[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017,17(2):775-780.
|
| [9] |
Facing challenges of increased energy consumption and related regional air pollution, China has been aggressively implementing flue gas desulfurization (FGD) and phasing out small inefficient units in the power sector in order to achieve the national goal of 10% reduction in sulfur dioxide (SO(2)) emissions from 2005 to 2010. In this paper, the effect of these measures on soil acidification is explored. An integrated methodology is used, combining emission inventory data, emission forecasts, air quality modeling, and ecological sensitivities indicated by critical load. National emissions of SO(2), oxides of nitrogen (NO(X)), particulate matter (PM), and ammonia (NH(3)) in 2005 were estimated to be 30.7, 19.6, 31.3, and 16.6 Mt, respectively. Implementation of existing policy will lead to reductions in SO(2) and PM emissions, while those of NO(X) and NH(3) will continue to rise, even under tentatively proposed control measures. In 2005, the critical load for soil acidification caused by sulfur (S) deposition was exceeded in 28% of the country's territory, mainly in eastern and south-central China. The area in exceedance will decrease to 26% and 20% in 2010 and 2020, respectively, given implementation of current plans for emission reductions. However, the exceedance of the critical load for nitrogen (N, combining effects of eutrophication and acidification) will double from 2005 to 2020 due to increased NO(X) and NH(3) emissions. Combining the acidification effects of S and N, the benefits of SO(2) reductions during 2005-2010 will almost be negated by increased N emissions. Therefore abatement of N emissions (NO(X) and NH(3)) and deposition will be a major challenge to China, requiring policy development and technology investments. To mitigate acidification in the future, China needs a multipollutant control strategy that integrates measures to reduce S, N, and PM.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
陈伟程, 吉喆, 肖寒, 等. 全国机动车保有量分析:《中国机动车环境管理年报(2017)》第Ⅰ部分[J]. 环境保护, 2017,45(12):33-34.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
There is an increasing concern over the impact of human-related emissions on the acid precipitation in China. However, few measurements have been conducted so far to clarify the acid-neutralization of precipitation on a regional scale. Under a network of 10 sites across Northern China operated during a 3-year period from December 2007 to November 2010, a total of 1118 rain and snow samples were collected. Of this total, 28% was acid precipitation with pH < 5.6. Out of these acid samples, 53% were found heavily acidic with pH value below 5.0, indicating significantly high levels of acidification of precipitation. Most of the acidity of precipitation was caused by H2SO4 and HNO3, their relative contribution being 72% and 28%, respectively. However; the contribution of HNO3 to precipitation acidity will be enhanced due to the increasing NO(x) and stable SO2 emissions in future. Neutralization factors for K+, NH4+, Ca2+, Na+, and Mg2+ were estimated as 0.06, 0.71, 0.72, 0.15, and 0.13, respectively. The application of multiple regression analysis further quantified higher NH4+ and Ca2+ contribution to the neutralization process, but the dominant neutralizing agent varied from site to site. The neutralization was less pronounced in the rural than urban areas, probably due to different levels of alkaline species, which strongly buffered the acidity. Presence of high concentrations of basic ions was mainly responsible for high pH of precipitation with annual volume-weighted mean (VWM) values larger than 5.6 at several sites. It was estimated that in the absence of buffering ions, for the given concentration of SO4(2-) and NO3-, the annual VWM pH of precipitation would have been recorded around 3.5 across Northern China. This feature suggested that emissions of particles and gaseous NH3 played very important role in controlling the spatial variations of pH of precipitation in the target areas.
|
| [18] |
邹晨, 欧向军, 孙丹. 长江三角洲城市群经济联系的空间结构演化分析[J]. 资源开发与市场, 2018,34(1):47-53.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
胡炳清, 易鹏, 段宁, 等. 影响精确界定我国酸雨区空间分布的因素探讨[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015,35(3):917-924.
|
| [21] |
黄银芝, 张明旭, 郑晓红. 上海市近16年湿沉降化学特征分析[J]. 城市环境与城市生态, 2008,21(6):1-3.
|
| [22] |
金鑫, 闻欣, 谢馨, 等. 南京市酸雨污染变化趋势分析[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2015,27(4):65-68.
|
| [23] |
罗益华, 励珍. 宁波市区近十年酸雨污染趋势分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011,34(S2):252-253,300.
|
| [24] |
杨龙誉, 于兴娜. 常州市酸雨化学特征及其与大气污染物的关系[J]. 城市环境与城市生态, 2010,23(5):30-33.
|
| [25] |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
张泽锋, 沈利娟, 朱彬, 等. 南京市降水化学特征及其来源研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 2015,38(4):473-482.
|
| [30] |
汤洁, 徐晓斌, 巴金, 等. 1992—2006年中国降水酸度的变化趋势[J]. 科学通报, 2010,55(8):705-712.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
吴福全, 薛媛媛, 郁蕾, 等. 苏州市十年酸雨变化趋势分析研究[J]. 环境监控与预警, 2013,5(4):40-42.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
With economic development and the increase of energy consumption, surface water acidification has been a potential environmental concern in China. Here, we analyzed variations and trends in surface water pH of 73 sites from ten river basins in China from 2004 to 2014 with nonparametric Seasonal Kendall test method. Our analysis showed that the variations of surface water pH in China ranged from 6.5 to 9.0 in the past decade (2004-2014), which satisfied the water quality criteria in pH for protection of aquatic ecosystems in China (6.0-9.0) and USA (6.5-9.0). However, significant decreasing trends in surface water pH were found in 31 monitoring sites, which were mainly located in Haihe River, Taihu Lake and Yangtze River, while the pH value showed significant increasing trends in 22 sites, which mainly were located in Songhua River and Pearl River. Our results suggested the increased potential acidification of susceptible water bodies in China. Besides the control policy of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, the emissions of nitrous oxides (NOx) should also be reduced to protect the aquatic systems in China.
|
| [35] |
As one of the most notorious atmospheric pollutants, NOx not only promotes the formation of ozone but also has adverse health effects on humans. It is therefore of great importance to study the sources of NOx and its effects on human health. The Comprehensive Air Quality Model (CAMx) modeling system and ozone source apportionment technology (OSAT) were used to study the contribution of NOx from different emission sources over southern China. The results indicate that heavy duty diesel vehicles (HDDVs) and industrial point sources are the two major local NOx sources, accounting for 30.8% and 18.5% of local NOx sources, respectively. In Hong Kong, marine emissions contributed around 43.4% of local NOx in 2011. Regional transport is another important source of this pollutant, especially in February and November, and it can contribute over 30% of ambient NOx on average. Power plant point emission is an significant regional source in Zhuhai, Zhongshan and Foshan. The total emission sources are estimated to cause 2119 (0-4405) respiratory deaths and 991 (0-2281) lung cancer deaths due to long-term exposure to NOx in the Pearl River Delta region. Our results suggest that local governments should combine their efforts and vigorously promote further reduction of NOx emissions, especially for those sources that make a substantial contribution to NOx emissions and affect human health: HDDV, LDGV, industrial point sources and marine sources.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
唐义华, 粟春青, 何通, 等. 酸雨处理对刨花润楠幼苗生长的影响[J]. 广西林业科学, 2019,48(2):213-217.
|
| [40] |
王寿超. 模拟不同类型酸雨对小白菜生长、生理及营养品质的影响研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2012.
|
| [41] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |