 PDF(1695 KB)
PDF(1695 KB)


塞罕坝自然保护区华北落叶松和樟子松人工林健康评价
赵金满, 韩馨悦, 程瑞明, 张志东
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 199-206.
 PDF(1695 KB)
PDF(1695 KB)
 PDF(1695 KB)
PDF(1695 KB)
塞罕坝自然保护区华北落叶松和樟子松人工林健康评价
Health assessment of Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii and Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in Saihanba Nature Reserve
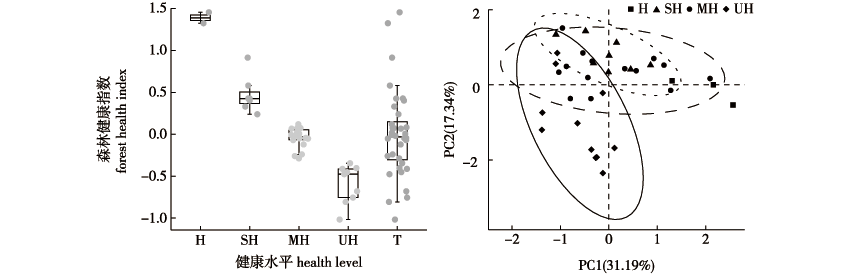
【目的】 了解自然保护区人工林健康状况,指导森林经营和保护区建设。【方法】 以河北省塞罕坝自然保护区华北落叶松(Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii)和樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)人工林为研究对象,基于分层随机取样法,设置36块样地,选取生产力、林分结构、物种多样性、土壤质量和稳定性等5个方面17个指标,建立森林健康评价指标体系。运用主成分分析法计算森林健康指数、K均值聚类法划分森林健康等级、Fisher判别分析法验证聚类结果的准确性。【结果】 研究区森林健康指数范围在-1.02~1.46;土壤质量和林分结构是影响研究区森林健康的最主要因素;森林健康等级所占面积比例从大到小依次为:中健康(50%)>不健康(25%)>亚健康(19%)>健康(6%);在中龄林(20~30 a)和近熟林(>30 a)中,华北落叶松林健康状况均优于樟子松林;随着林分密度的增加,华北落叶松林和樟子松林的森林健康指数呈降低趋势。【结论】 塞罕坝自然保护区人工林主要处于中健康和不健康状态,亟须采取有效经营活动改善森林健康状态。
【Objective】 The study aimed to understand the health status of plantations in nature reserves for forest management and the construction of nature reserves. 【Method】 A total of 36 sample plots were surveyed in the pure Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii and Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in the Saihanba Nature Reserve of Hebei Province using the stratified random sampling method. A total of 17 indicators, including the five aspects of productivity, stand structure, species diversity, soil quality, and stability, were selected to establish an indicator system for assessing forest health. The forest health index was calculated by principal component analysis, and the forest health grades were classified using the K-means clustering method. The accuracy of the clustering results was verified by Fisher’s discriminant analysis. 【Result】 The forest health index of the study area ranged between -1.02 and 1.46. The soil quality and stand structure were the most important indicators that influenced forest health in the study area. The proportionate areas were in the following order: mid-health (50%) > unhealthy (25%) > sub-health (19%) > healthy (6%). The health status of L. gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii forests was better than that of P. sylvestris var. mongolica forests for middle-aged (20-30 a) and near-mature (> 30 a) stands. The forest health indices of L. gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii and P. sylvestris var. mongolica forests tended to decrease with increasing stand density. 【Conclusion】 The plantations in the Saihanba Nature Reserve were primarily in the mid-health and non-health states. Therefore, the findings revealed that effective management strategies are urgently necessary for improving forest health in the study area.
森林健康 / 人工林 / 主成分分析 / 华北落叶松 / 樟子松 / 塞罕坝自然保护区
forest health / plantation / principal component analysis / Larix gmelinii var. prinoipis-rupprechtii / Prinus sylvestris var. mongolica / Saihanba Nature Reserve
| [1] |
刘建泉, 孙建忠. 东大河林区青海云杉林健康评价[J]. 草业科学, 2012, 29(4):624-628.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
刘世荣, 杨予静, 王晖. 中国人工林经营发展战略与对策:从追求木材产量的单一目标经营转向提升生态系统服务质量和效益的多目标经营[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(1): 1-10.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
郑学良, 陈丽华, 李洪洋, 等. 基于水源涵养功能的辽东防护林体系健康评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2020, 18(2): 102-110.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
董灵波, 刘兆刚. 森林健康评价及其多尺度转换方法[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(3): 206-216.
|
| [9] |
闫晋升, 王永东, 娄泊远, 等. 哈萨克斯坦首都努尔苏丹人工林健康评价[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(5): 1474-1483.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
赵勇钧, 谢阳生, 王建军, 等. 基于多元统计分析的马尾松人工林健康评价研究:以广西热带林业实验中心为例[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(7): 100-107.
|
| [12] |
谷鑫鑫, 司剑华. 基于层次分析法的西宁市油松人工林健康评价[J]. 青海大学学报, 2020, 38(3): 34-43.
|
| [13] |
王玮玮, 许彦红, 杨俊灵, 等. 纳板河流域国家级自然保护区主要森林植被类型健康评价研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(26): 32-39.
|
| [14] |
贾大鹏, 王新杰, 刘雨. 金沟岭林场森林健康评价[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2019, 47(8): 47-52,57.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
王秋燕, 陈鹏飞, 李学东, 等. 森林健康评价方法综述[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(2): 177-183.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
扈梦梅, 田龙, 吴亚楠, 等. 塞罕坝华北落叶松人工林间伐和混交改造对大型土壤动物群落结构的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(11): 153-162.
|
| [20] |
牛小云, 孙晓梅, 陈东升, 等. 辽东山区不同林龄日本落叶松人工林土壤微生物、养分及酶活性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(9):2663-2672.
|
| [21] |
鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000.
|
| [22] |
潘湘海. 塞罕坝樟子松人工林二元立木材积表的研制[J]. 河北林业科技, 2010(6): 20.
|
| [23] |
张菲, 张岩. 塞罕坝地区华北落叶松人工林二元立木材积表编制研究[J]. 河北林果研究, 2016, 31(2): 128-131.
|
| [24] |
杜秀芳, 汤孟平, 潘建勇, 等. 临安区不同森林类型竞争指数比较研究[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(12): 4064-4072.
|
| [25] |
潘磊磊,
|
| [26] |
喻泓, 杨晓晖. 地表火干扰时间序列上樟子松林竞争强度的变化[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(1): 79-85.
|
| [27] |
胡艳波, 惠刚盈. 优化林分空间结构的森林经营方法探讨[J]. 林业科学研究, 2006, 19(1): 1-8.
|
| [28] |
姜雨, 黄选瑞, 时田雨, 等. 不同间伐强度对自然保护区人工林植被多样性及分布格局的影响:以河北省塞罕坝机械林场为例[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(12):68-81.
|
| [29] |
徐梅, 关庆伟. 徐州侧柏人工林健康评价研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2014, 34(2):39-43,54.
|
| [30] |
曹小玉, 委霞, 赵文菲, 等. 基于结构方程模型的森林健康评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2635-2647.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
刘慧敏, 韩海荣, 程小琴, 等. 不同密度调控强度对华北落叶松人工林土壤质量的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(6): 50-59.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
刘怡青, 田育红, 宋含章, 等. 胸径和林分密度决定内蒙古东部落叶松林种内竞争[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(3):847-853.
|
| [37] |
董雪婷, 张静, 张志东, 等. 树种相互作用、林分密度和树木大小对华北落叶松生产力的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(8):2722-2728.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
王杰, 陆景星, 王相震, 等. 华北落叶松人工林间伐后9-10年林下天然更新研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(12):17-28.
|
| [40] |
徐雪蕾, 孙玉军, 周华, 等. 间伐强度对杉木人工林林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(3):1-12.
|
| [41] |
朱柱, 杨海龙, 黄乾, 等. 青海高寒黄土区典型水源涵养林健康评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(6):1166-1173.
|
| [42] |
安佳怡, 冯仲科, 马天天, 等. 基于GIS格网的重庆合川区森林火险等级区划[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(9):91-101.
|
| [43] |
常旭, 邱新彩, 刘欣, 等. 塞罕坝华北落叶松纯林和混交林土壤肥力质量评价[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(8): 50-59.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |