 PDF(2684 KB)
PDF(2684 KB)


 PDF(2684 KB)
PDF(2684 KB)
 PDF(2684 KB)
PDF(2684 KB)
东北温带森林不同材性树种木质部解剖和水力性状
Xylem anatomical and hydraulic traits of trees with different wood properties in a temperate forest in northeast China
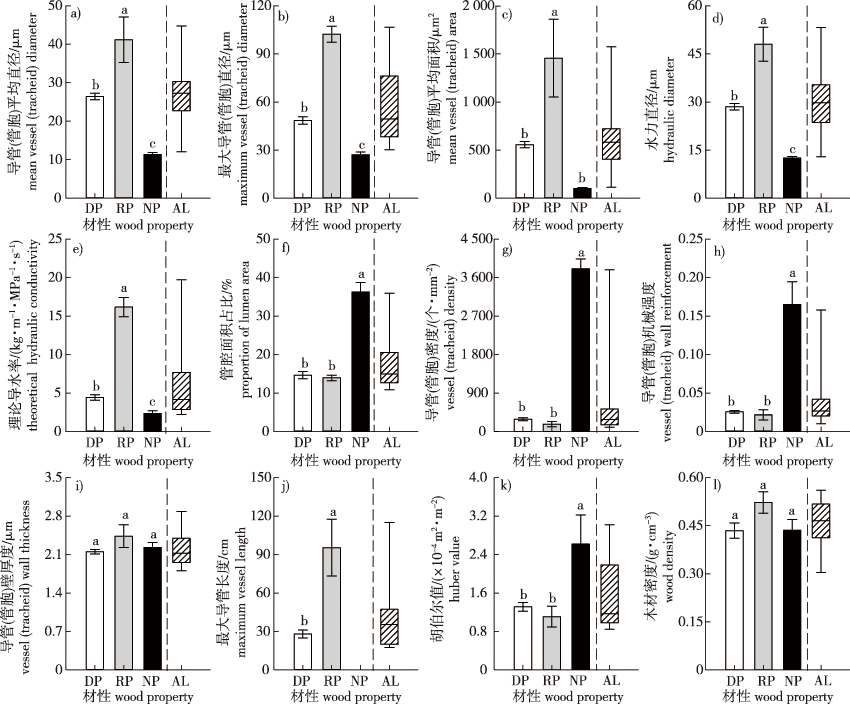
【目的】 木质部解剖结构影响树木水分运输效率和抗旱能力,进而影响树木的生长和生存,因此,研究木质部解剖和水力性状有利于阐明树木应对环境变化的响应和适应机制。【方法】 以东北温带森林20种主要树种(11种散孔材、5种环孔材和4种无孔材)为研究对象,比较不同材性树种茎解剖性状和水力性状的差异,并分析水力性状与解剖性状之间的关系。【结果】 不同材性树种的解剖性状[导管(管胞)平均直径、最大导管(管胞)直径、导管(管胞)密度、平均导管(管胞)面积、管腔面积占比]和水力性状[理论导水率、水力直径、导管(管胞)机械强度、胡伯尔值(边材面积/叶面积)]均差异显著(P<0.05)。环孔材树种理论导水率显著高于散孔材和无孔材(P<0.05),而无孔材树种管胞机械强度显著高于散孔材和环孔材树种的导管机械强度(P<0.05)。理论导水率与所有解剖性状均呈显著相关关系(P<0.05);除导管(管胞)壁厚度和最大导管长度以外,胡伯尔值与其他解剖性状均显著相关(P<0.05),但木材密度与所有解剖性状(导管长度除外)的关系均不显著。【结论】 木材密度不能反映东北温带森林树木的水力性状,树木茎导水能力依赖于木质部解剖结构和树木水分供需平衡关系。
【Objective】 Xylem anatomy affects the water transport efficiency and drought resistance of trees, which in turn affects tree growth and survival. Therefore, studying xylem anatomical and hydraulic traits will enable a better understanding of the response and adaptation mechanisms of trees to environmental changes. 【Method】 Here, we measured xylem anatomical and hydraulic traits in 20 tree species with three different wood properties (11 diffuse-porous, 5 ring-porous, and 4 non-porous) in a temperate forest in northeastern China. Our aim was to examine the differences in stem anatomical and hydraulic traits of tree species with three different wood properties and explore the potential relationships between stem hydraulic and anatomical traits. 【Result】 We found that there were significant differences in the anatomical traits (mean vessel (tracheid) diameter, maximum vessel (tracheid) diameter, vessel (tracheid) density, mean vessel (tracheid) area, proportion of lumen area), and hydraulic traits (theoretical hydraulic conductivity, hydraulic diameter, vessel (tracheid) mechanical strength, Huber value) among the tree species with different woody properties (P<0.05). The ring-porous trees had the highest theoretical hydraulic conductivity, whereas the non-porous trees had the highest tracheid mechanical strength. Theoretical hydraulic conductivity was significantly correlated with all anatomical traits. Huber values (sapwood area/leaf area) were significantly correlated with all anatomical traits (P<0.05), except vessel (tracheid) wall thickness and maximum vessel length. However, there were no significant correlations between wood density and all anatomical traits (except vessel length). 【Conclusion】 We concluded that wood density cannot better reflect the hydraulic traits of trees in temperate forests in northeastern China and that their water transport capacity is dependent on the xylem anatomical structure and the balance between a tree’s supply and demand for water.
木质部解剖 / 水力性状 / 木材密度 / 胡伯尔值 / 木材材性
xylem anatomy / hydraulic traits / wood density / Huber values / wood property
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
荆烁, 孙慧珍. 东北东部山区主要树种枝条及其组分水力特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(4): 159-166.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
徐茜, 陈亚宁. 胡杨茎木质部解剖结构与水力特性对干旱胁迫处理的响应[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(8): 1059-1065.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
李吉跃, 翟洪波. 木本植物水力结构与抗旱性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2000, 11(2): 301-305.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
李媛媛. 东北主要树种关键物候期木质部水力结构变化特征[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
殷笑寒, 郝广友. 长白山阔叶树种木质部环孔和散孔结构特征的分化导致其水力学性状的显著差异[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(2): 352-360.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
黄恺翔, 俞重阳, 钱海蓉, 等. 鸡公山国家级自然保护区散孔材、环孔材树种木质部结构和功能的关系[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(2): 244-251.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
赵乐文, 陈梓熠, 邹滢, 等. 九种维管植物水力性状的演化趋势[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(2): 220-228.
|
| [40] |
李泽东. 山东低山丘陵区不同类型树种木质部与叶片解剖特征及水力特性分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2020.
|
| [41] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |