 PDF(2848 KB)
PDF(2848 KB)


基于EMD和CatBoost算法的改进时间序列模型——以大连市PM2.5预测为例
赵凌霄, 李智扬, 屈磊磊
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 268-274.
 PDF(2848 KB)
PDF(2848 KB)
 PDF(2848 KB)
PDF(2848 KB)
基于EMD和CatBoost算法的改进时间序列模型——以大连市PM2.5预测为例
Improved time series models based on EMD and CatBoost algorithms: taking PM2.5 prediction of Dalian City as an example
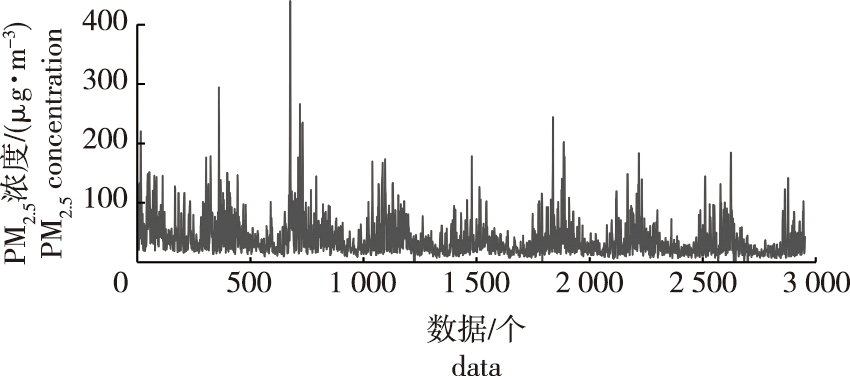
【目的】 解决传统大气PM2.5浓度时序预测时精度较低问题,减少PM2.5时间序列的非线性、高噪声、不平稳与波动性对预测的影响,从而更精确地预测PM2.5浓度。【方法】 以2014年1月1日至2022年1月31日大连市雾霾天气时PM2.5数据为例,提出了经验模态分解(EMD)、分类提升 (CatBoost)、自回归综合移动平均模型(ARIMA)组合的混合机器学习时间序列模型,并与传统自回归模型(AR)、ARIMA,以及只加入EMD方法后的混合模型进行比较。【结果】 混合模型EMD-CatBoost-ARIMA较原始序列均方根误差(RMSE)改进20.76%,平均绝对值误差(MAE)改进17.40%,希尔不等系数(TIC)改进29.17%。【结论】 对于高熵值的重构序列,EMD分解方法和CatBoost算法能够显著提升PM2.5时间序列模型的预测性能。相比较传统时间序列模型,EMD-CatBoost-ARIMA模型对大气PM2.5浓度预测性能较高。
【Objective】 The study aims to address the problem of low accuracy in traditional PM2.5 concentration time series prediction, and to reduce the impact of nonlinearity, high noise, instability and volatility on the prediction of PM2.5 time series, to predict PM2.5 concentration more accurately. 【Method】 The haze PM2.5 data of Dalian City from January 1, 2014 to January 31, 2022 was used as an example. In this study, a hybrid machine learning time series model with the combination of empirical modal decomposition (EMD), classification boosting (CatBoost) and autoregressive integrated moving average model (ARIMA) was proposed. It was compared with the traditional autoregressive model (AR), ARIMA and the hybrid model with only the EMD method. 【Result】 The hybrid model EMD-CatBoost-ARIMA improved the root mean square error (RMSE) of the original sequence by 20.76%, the mean absolute error (MAE) by 17.40%, and the theil inequality coefficient (TIC) by 29.17%. 【Conclusion】 For reconstructed sequences with high entropy values, the EMD decomposition method and CatBoost algorithm can significantly improve the prediction performance of PM2.5 time series models. Compared with the traditional time series models, the EMD-CatBoost-ARIMA model has higher performance in PM2.5 concentration prediction.
PM2.5浓度 / 经验模态分解(EMD) / 时间序列模型 / 混合模型 / CatBoost算法 / 机器学习 / 大连市
PM2.5 concentration / empirical modal decomposition(EDM) / time series model / hybrid model / CatBoost algorithm / machine learning / Dalian City
| [1] |
World health organization. Ambient air pollution:a global assessment of exposure and burden of disease[M]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
施婷婷, 王帅, 杨立娟, 等. 中国华东地区PM2.5浓度时空变化及与景观格局关联研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2024, 39(2): 435-446.
|
| [6] |
汪伟舵, 吴涛涛, 张子振. 基于ARIMA模型的杭州市PM2.5预测[J]. 哈尔滨师范大学自然科学学报, 2018, 34(3):49-55.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
杨茜雯, 朱萌. 基于ARIMA模型对扬州市PM2.5的分析和预测[J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2022, 35(1):35-37,40.
|
| [9] |
彭斯俊, 沈加超, 朱雪. 基于ARIMA模型的PM2.5预测[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2014, 21(6): 125-128.
|
| [10] |
严宙宁, 牟敬锋, 赵星, 等. 基于ARIMA模型的深圳市大气PM2.5浓度时间序列预测分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2018, 45(2):220-223,242.
|
| [11] |
谢心庆, 郑薇, 开璇, 等. 基于时间序列和多元方法的乌鲁木齐PM2.5浓度分析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(4):595-601.
|
| [12] |
余辉, 袁晶, 于旭耀, 等. 基于ARMAX的PM2.5小时浓度跟踪预测模型[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2017, 50(1):105-111.
|
| [13] |
吴明晖, 张广洁, 金苍宏. 基于多模态信息融合的时间序列预测模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(8):2326-2332.
|
| [14] |
何泽森. 移动APP日活跃用户量预测研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2018.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
张棋. 基于机器学习的中国气象干旱时空预测研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2021.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
王涯鑫, 李捷辉, 王健. 甲醇-柴油双燃料发动机甲醇泄漏故障预诊断研究[J]. 车用发动机, 2022(1):86-92.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |