 PDF(1721 KB)
PDF(1721 KB)


郑州市4种园林树木光合特性及其影响因素研究
李喜梅, 赵君静, 回祎, 黄鑫, 高春雨, 牛雅璇, 廖晓宇, 于晨一
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 105-112.
 PDF(1721 KB)
PDF(1721 KB)
 PDF(1721 KB)
PDF(1721 KB)
郑州市4种园林树木光合特性及其影响因素研究
A study on photosynthetic characteristics and influencing factors of four kinds of garden trees in Zhengzhou
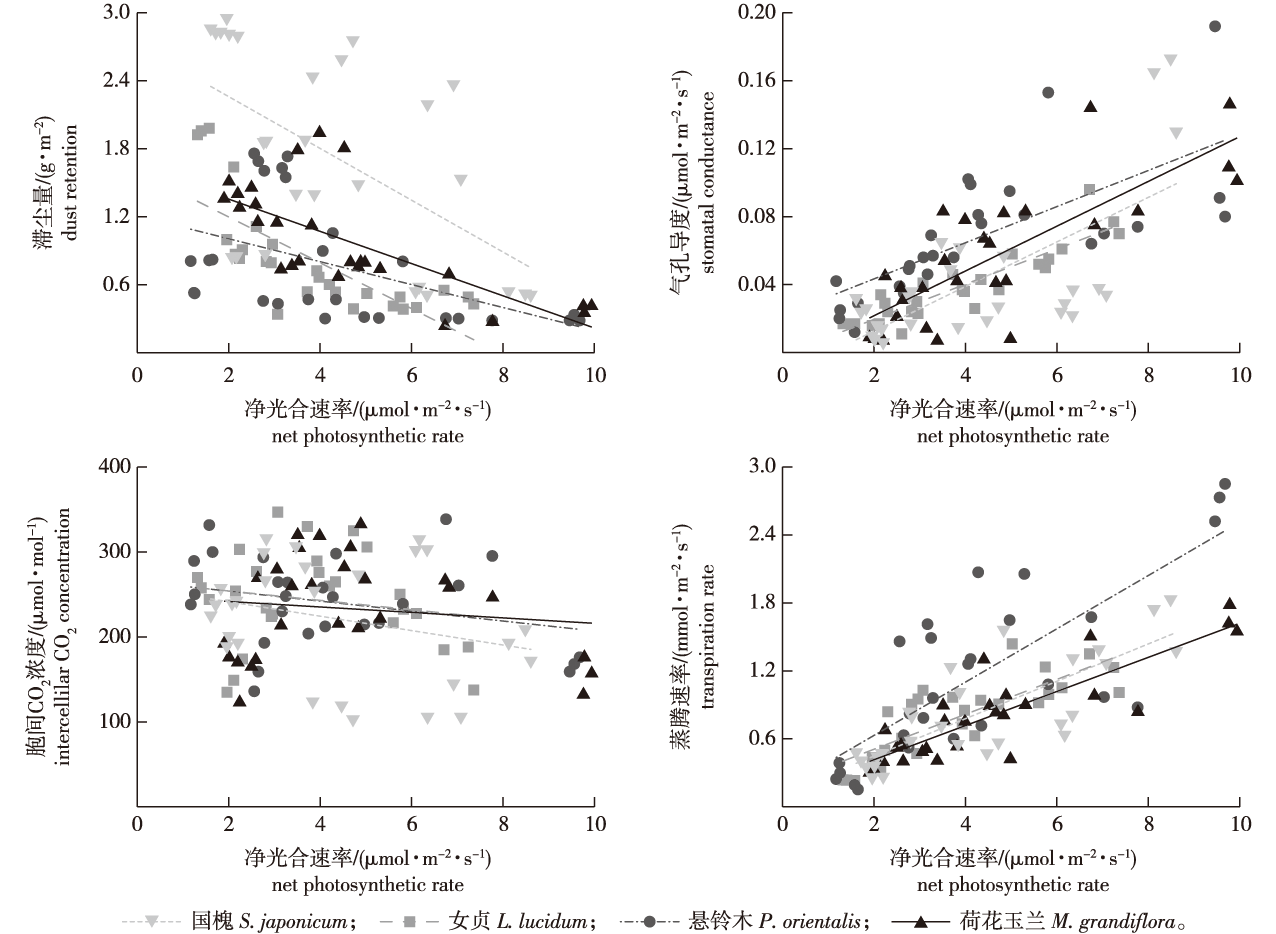
【目的】以女贞(Ligustrum lucidum)、荷花玉兰(Magnolia grandiflora)、悬铃木(Platanus orientalis)、国槐(Styphnolobium japonicum)等4种郑州市常见园林树木为研究对象,比较了生理及环境因子对树木净光合速率的影响,为郑州市绿地生态建设及优选树种提供理论依据。【方法】分别测量4种园林树木在不同季节的光合特性、叶表滞尘量及生长环境的温度和湿度,从生理环境的角度出发,使用双因素方差分析比较了不同季节各树种的光合特性差异,通过广义线性混合模型和结构方程模型探讨了不同因子之间的相互作用及其对树种光合速率的影响。【结果】4种园林树木净光合速率在不同季节均存在显著性差异(P<0.05),国槐的净光合速率显著高于其他树种,各树种夏季的净光合速率显著高于其他季节。生理因子(气孔导度和蒸腾速率)以及环境因素(滞尘量和湿度)与净光合速率有显著的相关关系(P<0.05)。湿度对植物的净光合速率有最显著的直接作用和间接作用,是影响植物光合作用的关键环境因素。【结论】国槐的净光合速率高于其他树种,女贞、荷花玉兰的光合特性与环境、生理因素之间的相关性较强。
【Objective】 Four common garden trees in Zhengzhou City, including Ligustrum lucidum, Magnolia grandiflora, Platanus orientalis and Styphnolobium japonicum, were selected as the study subjects. Our study provide a theoretical basis for the ecological construction of green space and the selection of tree species of Zhengzhou City from the perspective of physiological environment. 【Method】 Photosynthetic characteristics, leaf surface dust retention, and temperature and humidity of the growth environment were measured in different seasons to reveal the effects of physiological and environmental factors on net photosynthetic rate in the plants. Two-factor analysis of variance was used to compare the differences in photosynthetic characteristics of distinct species in different seasons. The interactions between different factors and their effects on plant photosynthetic rate were explored through generalized linear mixed models and structural equation models. 【Result】 There were significant differences in the net photosynthetic rate of the four garden trees in different seasons (P<0.05),and the net photosynthetic rate of Styphnolobium japonicum was significantly higher than that of other species. The net photosynthetic rate for each species was significantly higher in summer than in the other seasons. Physiological factors (stomatal conductance and transpiration rate) and environmental factors (dust retention and humidity) were significantly correlated with net photosynthetic rate (P<0.05). Humidity had the most significant direct and indirect effects on the net photosynthetic rate of plants and was the key environmental factor affecting plant photosynthesis. 【Conclusion】 The net photosynthetic rate of S. japonicum is higher than that of other tree species, and there is strong correlation between environmental and physiological factors of L. lucidum and M. grandiflora.
园林树木 / 光合特性 / 生理和环境因子 / 结构方程 / 郑州市
garden trees / photosynthetic characteristics / physiological and enviromental factors / structural modelling / Zhengzhou City
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
魏静, 谭星, 闫瑞, 等. 引种鸡爪槭光合特性及叶片呈色对异质生境的响应[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 46(2): 125-138.
|
| [3] |
宁朋, 王菲, 程小毛, 等. 川滇高山栎光合特性对不同海拔梯度的响应[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 41(6): 47-53.
|
| [4] |
张衷华, 唐中华, 杨逢建, 等. 两种主要油用牡丹光合特性及其微环境影响因子分析[J]. 植物研究, 2014, 34(6): 770-775.
|
| [5] |
汤文华, 窦全琴, 潘平平, 等. 不同薄壳山核桃品种光合特性研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(3): 81-88.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
孙安安, 智颖飙, 姜平平, 等. 西鄂尔多斯4种荒漠植物光合作用特征与差异性[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(13): 4944-4952.
|
| [8] |
杨建欣, 黄秋燕. 园林植物化感作用机理研究进展及展望[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(13): 90-97.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
吴统贵, 曾广泉, 肖杨根, 等. 湿地松林下6树种光合日变化及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(5): 135-138.
|
| [11] |
王月容, 谢军飞, 李薇, 等. 基于环境舒适度的8种园林植物光合特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(35): 124-130.
|
| [12] |
杨通文, 高秀梅, 韩维栋. 不同季节桃金娘光合特性与光系统PSⅡ活性研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(12): 2801-2810.
|
| [13] |
曾伟, 熊彩云, 肖复明, 等. 中亚热带常绿阔叶林优势树种幼树光合特性季节动态[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(5):157-160.
|
| [14] |
曹小林, 郝清玉, 王勇, 等. 干旱胁迫下6种海防林植物幼苗光合生理特性及抗旱性评价[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(10): 3424-3432.
|
| [15] |
张星, 王苗苗, 李国雷, 等. 栓皮栎和锐齿槲栎幼苗光合特性对高温胁迫的响应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(7): 25-35.
|
| [16] |
于晨一, 李镇江, 孙怡洁, 等. 太行山南麓锐齿槲栎-油松混交林竞争关系与空间格局[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 107-115.
|
| [17] |
路艳, 卞贵建, 季洪亮. 道路绿化树种滞尘的季节效应与叶片特征关系[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2020, 40(3): 269-275.
|
| [18] |
郭晖, 周慧, 张家洋. 郑州市15种常见园林树种固碳释氧能力分析研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2017, 32(4): 52-56.
|
| [19] |
林星宇, 李海梅, 李彦华, 等. 八种乔木滞尘效益及其与叶表面特征关系[J]. 北方园艺, 2019(17): 94-101.
|
| [20] |
胡梦玲, 阿丽亚·拜都热拉, 刘丽, 等. 果树叶片滞尘对其光合速率和耗水特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(11): 2032-2042.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
高冠龙, 冯起, 刘贤德, 等. 三种经验模型模拟荒漠河岸柽柳叶片气孔导度[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(10): 3486-3494.
|
| [23] |
赵辉, 吕良贺, 路鑫, 等. 杂种金叶银杏叶片光合特性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(1): 193-199.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
李计达, 张蔓蔓, 刘春鹏, 等. 败育雄性毛白杨优良无性系的生长性状特征和光合特性[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(10): 1-7.
|
| [26] |
袁颖红, 樊后保, 吴建平, 等. 不同年龄人工林尾巨桉(Eucalyptus urophylla×E.grandis)叶片光合特性及水分利用效率[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2016, 22(1): 58-63.
|
| [27] |
罗丹丹, 王传宽, 金鹰. 植物应对干旱胁迫的气孔调节[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(12): 4333-4343.
|
| [28] |
叶思源, 尚鹤, 陈展, 等. 不同浓度CO2对马尾松幼苗光合特性及单萜烯释放的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6): 71-78.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
宫江平, 高波, 努尔塔依·铁利汗, 等. 榆树秋季衰老叶光合特性研究[J]. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 34(3): 22-28.
|
| [31] |
刘振凡, 崔广强, 吴成华, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下园林植物再力花生长发育和光合特性的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2023, 55(12): 79-88.
|
| [32] |
张义, 谢永生, 郝明德, 等. 地表覆盖及生理生态因子对苹果树光合特性的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2010, 30(1): 125-130.
|
| [33] |
贺丹, 李海涛, 原江琴, 等. 郑州市7种园林植物滞尘能力与叶片生理及光合响应[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2023, 40(6): 1205-1214.
|
| [34] |
王书恒, 朱晓宇, 田如男, 等. 南京市6种常见园林植物滞尘效益的综合分析[J]. 中国园林, 2021, 37(6): 111-116.
|
| [35] |
李诗瑶, 王融融, 樊瑾, 等. 叶面滞尘对火电厂周边绿化树种叶片反射光谱及光合作用的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(1): 1-9,40.
|
| [36] |
胡新生, 刘建伟, 王世绩. 四个杨树无性系在不同温度和相对湿度条件下净光合速率的比较研究[J]. 林业科学, 1997(2): 12-21.
|
| [37] |
刘建锋, 叶建仁. 水分胁迫与植物侵染性病害的发生[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2004(2): 67-71.
|
| [38] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |