 PDF(1621 KB)
PDF(1621 KB)


 PDF(1621 KB)
PDF(1621 KB)
 PDF(1621 KB)
PDF(1621 KB)
欧洲鹅耳枥水培营养液适用效果比较研究
Comparative study on the effects of nutrient solution treatment in hydroponic cultivation of Carpinus betulus

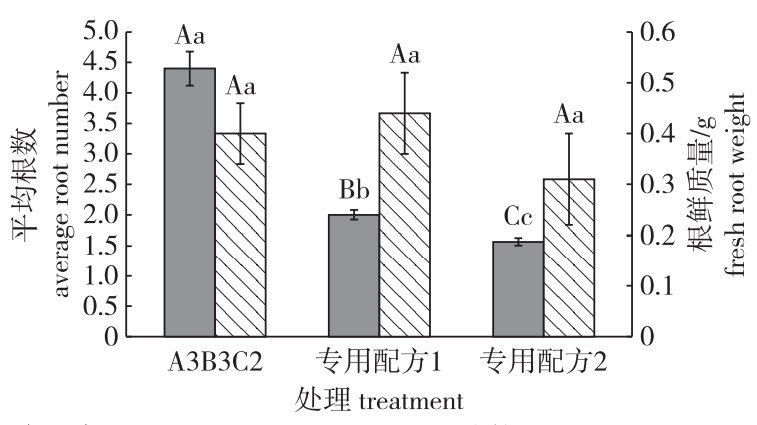
【目的】探究常用水培营养液的种类、浓度、pH,以及专用营养液对欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗生长的影响,筛选适合欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗生长的最佳营养液,为欧洲鹅耳枥的水培繁殖、生产应用及进一步生理生化研究提供理论依据。【方法】以欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗为试材,以存活率、叶片数、平均根数、平均二级根数和根鲜质量为形态指标,以可溶性糖、淀粉含量、可溶性蛋白含量、POD活性和根系活力为生理指标,采用3因素3水平正交试验研究了常用营养液种类及其浓度、pH对水培苗生长的影响。在筛选出最佳常用营养液的基础上,采用单因素试验研究了最佳常用营养液与自制专用营养液对欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗生长的影响。【结果】营养液正交试验表明,理论上适合欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗生长的常用营养液为1/4浓度的Hewitt通用配方(A3B3),在pH 6.5的该营养液中欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗存活率为85.71%,叶片数为1.60,平均根数为4.40,平均二级根数为25.90,根鲜质量为0.40 g,水培苗的可溶性糖含量、淀粉含量、可溶性蛋白含量和根系活力显著较其他处理高,POD活性显著较其他处理低。最佳常用营养液与专用营养液的对比试验表明,最适合欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗生长的营养液为作者自行配制的专用配方1,在该营养液中欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗存活率为93.33%,可溶性糖含量0.13 mg/g,淀粉含量2.55 mg/g,可溶性蛋白含量33.33 mg/g,根系活力49.75μg/(g·h)。【结论】最适合欧洲鹅耳枥水培苗生长的营养液为作者自行配制的专用配方1。
【Objective】To provide a theoretical basis for hydroponic breeding, production, and further physiological and biochemical studies of Carpinus betulus, the effects of type, concentration and pH of ordinary nutrient solution treatment and special nutrient solution for hydroponic seedling growth of C. betulus were examined, and the best nutrient solution for the growth of C. betulus seedlings was screened.【Method】We used C. betulus hydroponic seedlings as the test material. We analyzed the survival rate, number of leaves, average number of roots, average number of second roots and fresh root weight as morphological indexes; and soluble sugar content, starch content, soluble protein content, POD activity and root activity as physical indexes. Hydroponic seedling growth was examined by the type, concentration and pH value of nutrient solution treatment using three factors and three level orthogonal tests. To obtain the best ordinary nutrient solution, we tested hydroponic seedling growth treated with the best ordinary nutrient solutions and special nutrient solutions made by the authors using a single factor test.【Result】The orthogonal test of nutrient solution showed that the most suitable ordinary nutrient solution was the 1/4 Hewitt formula (A3B3). In this condition of pH 6.5, the survival rate was 85.71%, the number of leaves was 1.60, the average number of roots was 4.40, the average number of second roots was 25.90, and the fresh root weight was 0.40 g. The soluble sugar content, starch content, soluble proteins content, and the rooting activity were significantly higher than those in the other treatments, although the POD activity was significantly lower than that in the other treatment. The single factor test of the nutrient solutions showed that the most suitable nutrient solution for C. betulus growth was the special nutrient solution No. 1. Under this condition, the survival rate was 93.33%, the soluble sugar content was 0.13 mg/g, the starch content was 2.55 mg/g, the soluble proteins content was 33.33 mg/g, and the rooting activity was 49.75 μg/(g·h).【Conclusion】The most suitable nutrient solution for C. betulus was the special nutrient solution No.1 prepared by us.
欧洲鹅耳枥 / 水培 / 营养液 / 根生长 / 可溶性糖含量
Carpinus betulus / hydroponic culture / nutrient solution / roots growth / soluble sugav content
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
王华芳. 水培花卉[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002.
|
| [10] |
赵九洲, 陈洁敏, 陈松笔, 等. 无土基质与营养液EC值对切花菊生长发育的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 1999,26(5):327-330.
|
| [11] |
别之龙, 徐加林, 杨小峰. 营养液浓度对水培生菜生长和硝酸盐积累的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2005,21(S2):109-112.
|
| [12] |
祝遵崚, 火艳. 欧洲鹅耳枥水培专用营养液:中国, 201510102354.1[P]. 2017-11-14.
|
| [13] |
李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1999.
|
| [14] |
张志良, 瞿伟菁. 植物生理学试验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2003.
|
| [15] |
郑炳松. 现代植物生理生化技术研究[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2006.
|
| [16] |
张鸽香, 周丽琴. 水杨酸对水培风信子生长及开花的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,37(5):20-24.
|
| [17] |
许业洲, 杜超群, 许秀环, 等. 湿地松针叶束水培无性系生长特性遗传分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,37(5):25-30.
|
| [18] |
王瑞, 胡笑涛, 王文娥, 等. 张菠菜水培不同营养液浓度的产量、品质、 元素利用效率主成分分析研究[J]. 华北农学报, 2016,31(S) : 206-212.
|
| [19] |
丁文雅, 邬小撑, 刘敏娜, 等. 不同营养液配方对雾培生菜生物量和营养品质的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2012,38(2):175-184.
|
| [20] |
马太和. 无土栽培[M]. 北京: 北京出版社, 1980.
|
| [21] |
安娜, 须晖, 孙周平, 等. 雾培番茄不同营养液配方的生产效果比较[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2006,37(3):495-497.
|
| [22] |
石磊, 代红军. 不同浓度营养液处理对长寿花生长及形态指标的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2013(22):67-70.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
卢文晋. 枸杞水培根原机诱导基理研究[D]. 西宁:青海大学, 2014.
|
| [26] |
罗盼, 周兰英, 高宏梅, 等. 不同营养液水培对蟹爪兰的生长影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2011(16):86-88.
|
| [27] |
季延海, 武占会, 于平彬, 等. 不同营养液浓度对水培韭菜生长适应性的影响[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2017(11):53-56.
|
| [28] |
刘丹, 毕晓露, 郭腾, 等. 广东万年青在北方地区温室环境下水培营养液配方筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2015,52(4):667-674.
|
| [29] |
张仲新, 方正, 李英丽. 不同营养液水培对含羞草生长发育的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2007,34(4):1037-1040.
|
| [30] |
廖静. 三种观赏植物水培机制与技术研究[D]. 雅安:四川农业大学, 2006.
|
| [31] |
翁忙玲, 吴震, 李谦盛, 等. 营养液浓度及pH值对山葵生长及光合速率的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2004,31(1):101-102.
|
| [32] |
陈发棣, 房伟民, 余真霞, 等. 中国石竹无土栽培初步研究[J]. 上海农业学报, 1999,15(2):87-89.
|
| [33] |
宋立奕, 方升佐. 水培青檀幼苗对NaCl胁迫的生理响应[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2006,30(2):94-98.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |