 PDF(1886 KB)
PDF(1886 KB)


 PDF(1886 KB)
PDF(1886 KB)
 PDF(1886 KB)
PDF(1886 KB)
NO2胁迫下两种鹅耳枥的光合生理特性变化
Photosynthetic physiological characteristics of two kinds of hornbeam under NO2 stress

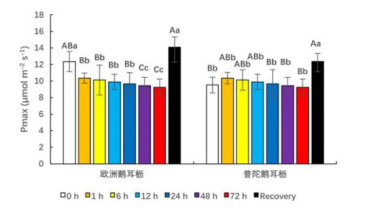
【目的】评价欧洲鹅耳枥和普陀鹅耳枥对NO2胁迫的耐受力,为选择抗大气污染的园林树种提供参考。【方法】以12.0 mg/m3的NO2对欧洲鹅耳枥和普陀鹅耳枥1年生幼苗进行熏气处理,熏气时间分别为胁迫零点(0 h,CK)、1、6、12、24、48、72 h,以及熏气后30 d测定两种鹅耳枥幼苗的光合生理指标和叶绿素荧光特性,分析不同NO2熏气时间与苗木光合生理响应特征的关系,比较两种鹅耳枥对NO2胁迫的适应性。【结果】NO2胁迫后欧洲鹅耳枥具有较高的最大净光合速率(Pn,max)和暗呼吸速率(Rd),较低的光补偿点(LCP)和较高的光饱和点(LSP),表明欧洲鹅耳枥在较宽泛的光照强度下能够正常生长;欧洲鹅耳枥与普陀鹅耳枥的NO2熏气1 h处理组最大PSⅡ光能转换效率(Fv/Fm)值增加,在6 h处理中仅欧洲鹅耳枥的Fv/Fm值增加,PSⅡ活性增强,用于光合电子传递的能量增多。【结论】推测认为欧洲鹅耳枥能够在NO2胁迫下有序适应外界不良环境,耐受性更强。这对城市道路树种选择与植物配置具有重要意义。
【Objective】This paper is to evaluate the tolerance of Carpinus betulus and Carpinus putoensis to NO2 stress, and to provide a reference for the selection of landscape tree species resistant to air pollution.【Method】The annual seedlings of C. betulus and C. putoensis were fumigated with 12.0 mg/m3 NO2 for stress zero point(0 h, CK), 1, 6, 12, 24, 48, 72 h, respectively, the photosynthetic physiological indexes and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of C. betulus and C. putoensis seedlings were measured 30 days after fumigation. The relationship between different NO2 fumigation time and photosynthetic physiological response characteristics was analyzed, and the adaptability of C. betulus and C. putoensis seedlings to NO2 stress was compared.【Result】The results showed that after NO2 stress, C. betulus had higher Pn,max and Rd, lower light compensation point (LCP) and higher light saturation point (LSP), which indicated that C. betulus could grow normally under a wide range of light intensity. It is increased that the maximum photosynthetical efficiency (Fv/Fm) of C. betulus and C. putoensis leaf treated by NO2 for 1 hour. Only Fv/Fm value of C. betulus increased, PSⅡ activity and energy for photosynthetic electron transfer increased at 6 h of NO2 stress.【Conclusion】It is suggested that C. betulus could adapt to the adverse environment in an orderly manner under NO2 stress, with stronger tolerance. The results of this study are of great significance to the selection and allocation of urban road species.
NO2胁迫 / 欧洲鹅耳枥 / 普陀鹅耳枥 / 光合特性指标 / 叶绿素荧光
NO2 stress / Carpinus betulus / Carpinus putoensis / photosynthetic characteristics index / chlorophyll fluorescence
| [1] |
张兴赢, 张鹏, 方宗义, 等. 应用卫星遥感技术监测大气痕量气体的研究进展[J]. 气象, 2007,33(7):3-14.
|
| [2] |
江文华, 马建中, 颜鹏, 等. 利用GOME卫星资料分析北京大气NO2污染变化[J]. 应用气象学报, 2006,17(1):67-72.
|
| [3] |
张兴赢, 张鹏, 张艳, 等. 近10年中国对流层NO2的变化趋势, 时空分布特征及其来源解析[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2007,37(10):1409-1416. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2007.10.013.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
任剑锋, 王增长, 牛志卿. 大气中氮氧化物的污染与防治[J]. 科技情报开发与经济, 2003,13(5):92-93.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
李明月, 王健, 王振兴, 等. 模拟氮沉降条件下木荷幼苗光合特性、生物量与C、N、P分配格局[J]. 生态学报, 2013,33(5):1569-1577.
|
| [8] |
衣艳君, 李芳柏, 刘家尧. 尖叶走灯藓(Plagiomnium cuspidatum) 叶绿素荧光对复合重金属胁迫的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2008,28(11):5437-5444.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
李泽, 谭晓风, 卢锟, 等. 干旱胁迫对两种油桐幼苗生长、气体交换及叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2017,37(5):1515-1524.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
潘文, 张卫强, 张方秋, 等. 红花荷等植物对SO2和NO2的抗性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2012,21(11):1851-1858.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
孙淑萍. 3种垂直绿化植物对污染物的富集及生理响应[D]. 南京:南京林业大学, 2011.
|
| [27] |
黄芳, 王建明, 徐玉梅. 二氧化硫污染对几种作物的伤害研究[J]. 山西农业科学, 2007,35(11):56-58.
|
| [28] |
马纯艳, 徐昕, 郝林, 等. 小白菜幼苗对二氧化氮胁迫的应答及过氧化氢的调节[J]. 中国农业科学, 2007,40(11):2556-2562.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
叶子飘. 光合作用对光和CO2响应模型的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010,34(6):727-740.
|
| [33] |
白伟岚, 任建武. 园林植物的耐荫性研究[J]. 林业科技通讯, 1999(2):12-15.
|
| [34] |
采列尼克尔. 木本植物耐荫性的生理学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986: 180-196.
|
| [35] |
刘云峰, 秦洪文, 石雷, 等. 水淹对水芹叶片结构和光系统Ⅱ光抑制的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2010,45(4):426-434.
|
| [36] |
耿东梅, 单立山, 李毅, 等. 土壤水分胁迫对红砂幼苗叶绿素荧光和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2014,49(3):282-291.
|
| [37] |
李鹏民, 高辉远,
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
冯志立, 冯玉龙, 曹坤芳. 光强对砂仁叶片光合作用光抑制及热耗散的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2002,26(1):77-82.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
吴文杰, 王文卿, 钱莲文, 等. 铝胁迫对常绿杨叶绿素荧光和叶绿体超微结构的影响[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2015,54(1):52-58.
|
| [42] |
梁英, 冯力霞, 尹翠玲, 等. 叶绿素荧光技术在微藻环境胁迫研究中的应用现状及前景[J]. 海洋科学, 2007,31(1):71-76.
|
| [43] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |