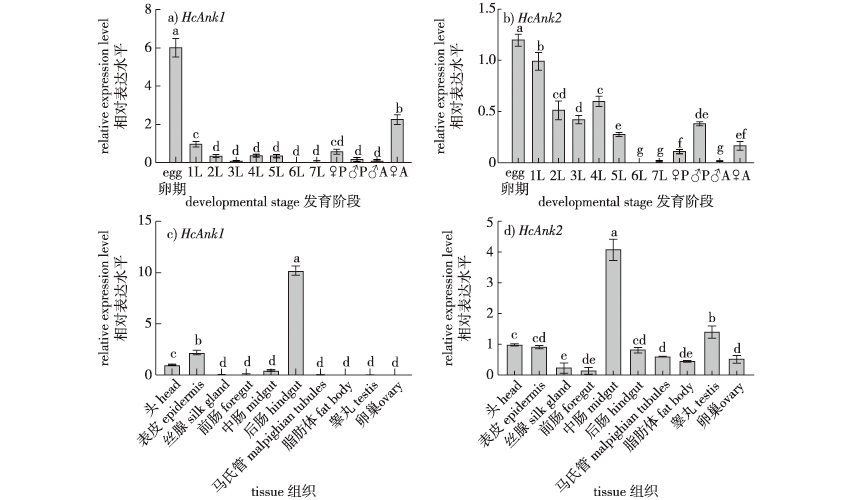
【目的】 锚定蛋白是连接细胞骨架与质膜的衔接蛋白家族。但昆虫中关于锚定蛋白基因功能研究甚少。笔者克隆美国白蛾(Hyphantria cunea)锚定蛋白基因,阐明该基因在其各发育期和组织中的表达特征及对美国白蛾核型多角体病毒(Hyphantria cunea nucleopolyhedrosisvirus, HcNPV)的敏感性,为进一步开发HcNPV增效剂提供理论依据。【方法】 通过转录组文库筛选出Ankyrin1(HcAnk1)和Ankyrin2(HcAnk2)基因,利用生物信息学分析基因特性,采用qRT-PCR检测不同发育阶段、不同组织以及不同HcNPV浓度胁迫下HcAnks的表达量,通过RNAi技术研究HcAnks基因沉默后美国白蛾对HcNPV的敏感性。【结果】 HcAnk1和HcAnk2基因开放阅读框依次为1 392和1 866 bp,分别编码463和621个氨基酸,蛋白质分子质量分别为59.18和69.19 ku,理论等电点分别为5.74 和 8.66;进化树分析显示HcAnk1与粉纹夜蛾(Trichoplusia ni)亲缘关系最近而聚为一类。HcAnks在各个发育阶段均有表达,卵期表达量最高,6龄表达量最低;HcAnks分别在中肠和后肠中表达量最高;在卵巢和精巢中未检测到HcAnk1,而HcAnk2主要在中肠和精巢中表达。在不同浓度HcNPV胁迫下,HcAnks转录水平表现为低浓度诱导,高浓度抑制。沉默HcAnks美国白蛾4龄幼虫的相对生长率(RGR)和食物转化效率(ECD)显著降低。此外,沉默HcAnks的美国白蛾4龄幼虫对HcNPV敏感性显著增加。【结论】 HcAnks在抵抗HcNPV侵染过程中发挥重要作用,HcAnks可作为HcNPV增效剂,用于美国白蛾无公害防治。
【Objective】 Ankyrin is a family of adaptor proteins that connect the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane. However, the functions of insect ankyrin are poorly understood. In this study, the Ankyrin genes of Hyphantria cunea were cloned and their expression characteristics were determined in different developmental stages and tissues of H. cunea. The mortality rate of H. cunea was measured under the stress of exposure to nucleopolyhedrosis virus, which provided a theoretical basis for further developing synergists for NPV-based control strategies. 【Method】 The Ankyrin1 (HcAnk1) and Ankyrin2 (HcAnk2) genes were screened by a transcriptome library, and the characteristics of the two Ankyrin genes were determined using bioinformatics. Using qRT-PCR, the expression of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 genes were determined at different developmental stages and in different tissues, and under different HcNPV concentrations. The survival rate of H. cunea larvae under HcNPV stress was investigated after the gene silencing of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 using an RNAi technique. 【Result】 The open reading frames of the HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 genes were 1392 and 1866 bp, encoding 463 and 621 amino acids, respectively. The molecular weights of the HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 proteins were 59.18 and 69.19 ku, respectively, and the theoretical isoelectric points were 5.74 and 8.66, respectively. A phylogenetic analysis showed that HcAnk1 was closely related to Trichoplusia ni and was clustered into one group. HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 were expressed at all developmental stages, with the highest expression in the egg stage and the lowest expression in the sixth instar larva. The highest expression of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 was observed in the midgut and hindgut, respectively, but HcAnk1 was not detected in the ovary or testis, while HcAnk2 was mainly expressed in the midgut and testis. In tests with different levels of HcNPV stress, the transcription levels of HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 were induced at low concentrations and inhibited at high concentrations. The relative growth rate and food conversion efficiency (ECD) were significantly decreased after silencing HcAnks in H. cunea larvae. Additionally, the H. cunea with HcAnks silencing were significantly less resistant to HcNPV. 【Conclusion】 HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 play an important role in the resistance to HcNPV. HcAnk1 and HcAnk2 can be used as HcNPV synergists for the pollution-free control of H. cunea.
 PDF(2364 KB)
PDF(2364 KB)


 PDF(2364 KB)
PDF(2364 KB)
 PDF(2364 KB)
PDF(2364 KB)