 PDF(2235 KB)
PDF(2235 KB)


无患子生殖生长物候期液流特征及其对枝叶修剪的响应
王冕之, 郑玉琳, 贾黎明, 李露, 罗水晶, 刘济铭, 刘俊涛
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6) : 13-22.
 PDF(2235 KB)
PDF(2235 KB)
 PDF(2235 KB)
PDF(2235 KB)
无患子生殖生长物候期液流特征及其对枝叶修剪的响应
The sap flow characteristics and responses to branch and leaf pruning during reproductive phenological periods in Sapindus saponaria
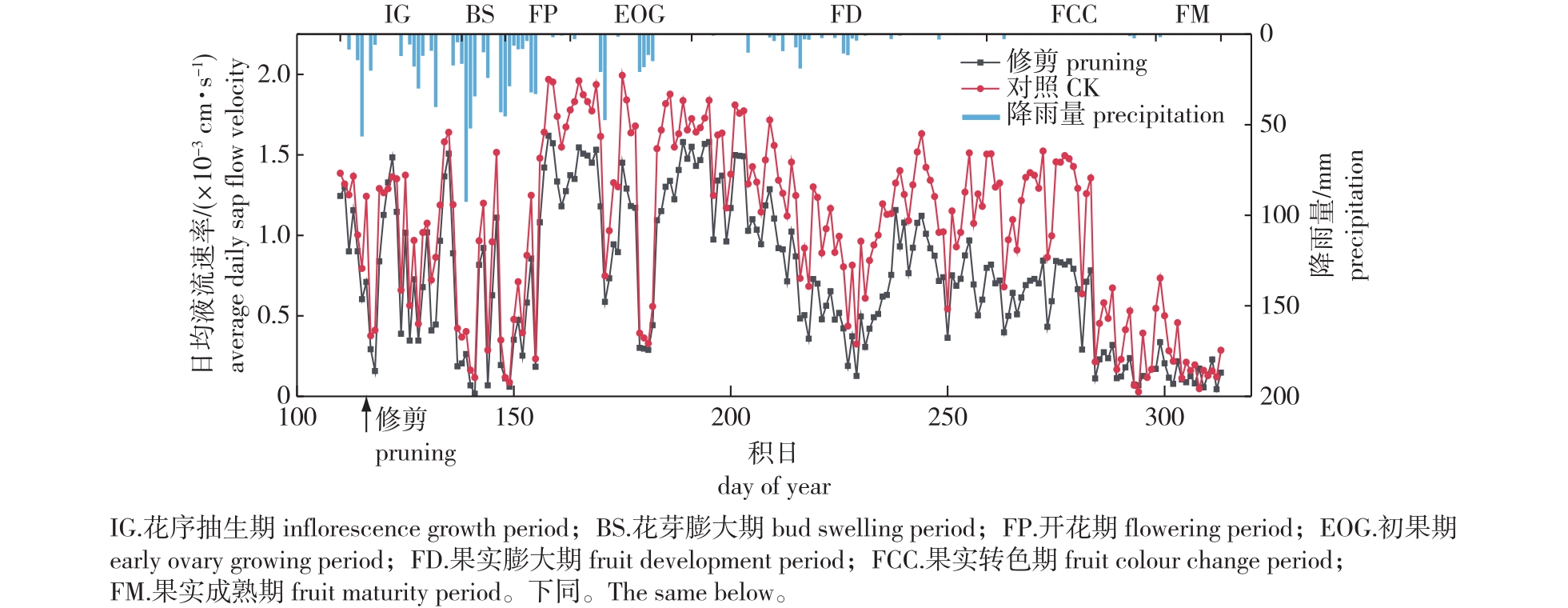
【目的】了解无患子(Sapindus saponaria)关键物候期液流速率特征及其对修剪和气象因子的响应规律,为无患子生殖生长各关键物候期水分的科学管理提供理论参考。【方法】在福建省三明市建宁县无患子国家林木种质资源库试验区,以5年生无患子新品种‘媛华’为试验材料,利用热扩散液流探针和自动气象站监测2021年4月20日—11月9日的树干液流和气象数据分析气象因子和枝叶修剪对无患子液流特征的影响。试验中探针安装于距地面约30 cm处以保证所有处理的探针都安装于第1分枝之下。修剪组样树在花序抽生期长出花序后进行一次性修剪,去掉遮蔽花序阳光的枝组和复叶。对照组样树不做修剪处理。【结果】①无患子日均液流速率随时间在7个生殖生长关键物候期尺度上呈现降低—升高—降低的趋势。在初果期蒸腾活动最强,日均液流速率高达(1.13±0.05)×10-3(修剪)和(1.48±0.05)×10-3cm/s(对照),在果实成熟期蒸腾活动最弱,日均液流速率低至(0.15±0.02)×10-3(修剪)和(0.26±0.03)×10-3 cm/s(对照)。除花芽膨大期外,修剪显著降低了无患子各物候期液流速率,降低作用在树体生长旺盛的晴天较明显、在果实发育末期最强。②太阳辐射、空气温度、风速和饱和水汽压亏缺是无患子液流速率的主要驱动因子,而降水量和空气相对湿度是主要限制因子。持续降水等气象因素是花芽膨大期至开花期前期和果实膨大期中期无患子蒸腾活动的主要限制因素,叶片老化、树体逐渐进入休眠是果实成熟期液流速率低的主要原因。【结论】修剪显著降低了树体蒸腾作用,降低效应随关键物候期向后发展而增强。无患子生殖生长全物候期液流速率波动明显,推测树木和果实生长对水分的需求与树体耗水行为密切相关,而花序生长发育时期持续过量降雨等气象因素不利于无患子蒸腾耗水。
【Objective】The present study aimed to investigate the characteristics of sap flow velocity of Sapindus saponaria and its response pattern to pruning and meteorological factors during the key phenological periods, and to provide a theoretical reference for scientific water management during key reproductive phenological periods of Sapindus.【Method】The present study was conducted in the experimental area of the Sapindus National Forest Germplasm Repository in Jianning County, Sanming City, Fujian Province. Using five-year-old S. saponaria ‘Yuanhua’. Thermal dissipation probes (TDPs) and automatic weather stations were utilized to monitor sap flow and meteorological data from April 20, 2021 to November 9, 2021. The probes were installed approximately 30 cm above the ground to ensure that all probes were installed under the first branch. Sample trees in the pruning group were pruned once after inflorescence growth at the inflorescence growth period to remove branches and leaves that shaded the inflorescence from sunlight. Trees in the control group were left unpruned for comparison.【Result】The average daily sap flow velocity of S. saponaria showed a decreasing-increasing-decreasing trend over time during the seven key reproductive phenological periods. The strongest transpiration activities were (1.13±0.05)×10-3 cm/s (pruning) and (1.48±0.05)×10-3 cm/s (CK) in the early ovary growing period, while the weakest transpiration activities were (0.15±0.02)×10-3 cm/s (pruning) and (0.26±0.03)×10-3 cm/s (CK) in the fruit maturity period. Pruning significantly reduced the sap flow velocity of S. saponaria in all phenological periods, except for the bud swelling period. This reduction effect was more pronounced on sunny days when the tree was actively growing and was strongest at the end of the fruit development period. In addition, solar radiation, air temperature, wind speed and vapor pressure deficit (VPD) were the main drivers of sap flow velocity, while precipitation and air humidity were the main limiting factors. Meteorological factors, such as persistent rainfall, were the main limitations of the transpiration activity of S. saponaria from the bud swelling period to the early flowering period and middle fruit development period. Leaf aging and gradual dormancy of the tree were the main reasons for low sap flow velocity during the fruit maturity period.【Conclusion】Pruning significantly reduced the transpiration, with the reduction effect becoming more pronounced as the phenological periods progressed. There were large fluctuations in sap flow velocity throughout the reproductive growth of S. saponaria. Thus, these findings suggested that the water demand for tree and fruit growth is closely related to the water consumption behavior of trees. Meteorological factors, such as persistent excessive rainfall, during inflorescence growth and development are not conducive to transpiration.
Sapindus saponaria / sap flow / pruning / phenological period / meteorological factor
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
吴佳伟, 李苇洁, 杨瑞, 等. 红阳猕猴桃生长发育期树干液流特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 果树学报, 2021, 39(3):1-25.
|
| [11] |
刘济铭, 孙操稳, 何秋阳, 等. 国内外无患子属种质资源研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2017, 30(6):12-18.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
刘诗琦, 贾黎明, 苏淑钗, 等. 林业生物质能源“林油一体化”产业高效可持续发展路径研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(12):96-107.
|
| [16] |
张赟齐, 刘晨, 刘阳, 等. 叶幕微域环境对无患子果实产量和品质的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(5):189-198.
|
| [17] |
高媛, 贾黎明, 高世轮, 等. 无患子树体合理光环境及高光效调控[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(11):29-38.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
孟秦倩. 黄土高原山地苹果园土壤水分消耗规律与果树生长响应[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2011.
|
| [26] |
刘俊涛, 仲静, 刘济铭, 等. 无患子初果期人工林土壤和叶片C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(4):67-75.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
高媛, 贾黎明, 苏淑钗, 等. 无患子物候及开花结果特性1)[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(6):34-40,123.
|
| [29] |
李广德, 张亚雄, 邓坦, 等. 树干液流及其主要影响因子对摘芽强度的响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(5):131-139.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
刘洋, 王烨, 王斐, 等. 宽窄行栽植下毛白杨不同方位树干液流的差异[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(10):95-105.
|
| [32] |
赵飞飞, 马煦, 邸楠, 等. 毛白杨茎干不同方位夜间液流变化规律及其主要影响因子[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(8):864-874.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
马长明, 袁玉欣, 翟明普. 基于物候期的核桃树干液流特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2008, 36(1):4-5,9.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
郑玉琳, 刘济铭, 史双龙, 等. 无患子果实成熟过程及其油脂、皂苷动态变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(4):76-82.
|
| [44] |
黄雅茹, 李永华, 辛智鸣, 等. 不同时间尺度气象因子与柽柳树干液流关系研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(11):149-154.
|
| [45] |
马文涛, 程平, 李宏, 等. 干旱绿洲区富士苹果树干边材茎流动态及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2020, 46(4):428-440.
|
| [46] |
王力, 王艳萍. 黄土塬区苹果树干液流特征[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(10):152-158,151.
|
| [47] |
党宏忠, 却晓娥, 冯金超, 等. 晋西黄土区苹果树边材液流速率对环境驱动的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(3):823-831.
|
| [48] |
麦合木提·图如普, 周伟权, 丁想, 等. 吐鲁番盆地杏树树干液流变化特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8):2378-2387.
Mahmoodt·Turup,
|
| [49] |
凡超, 邱燕萍, 李志强, 等. 荔枝树干液流速率与气象因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(9):2401-2410.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |