 PDF(2075 KB)
PDF(2075 KB)


C源与NP添加对Cd胁迫下林地土壤呼吸作用的影响
孙劲伟, 王圣燕, 范弟武, 朱咏莉
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 140-146.
 PDF(2075 KB)
PDF(2075 KB)
 PDF(2075 KB)
PDF(2075 KB)
C源与NP添加对Cd胁迫下林地土壤呼吸作用的影响
Effects of C, N and P additions on soil respiration in woodland under Cd stress
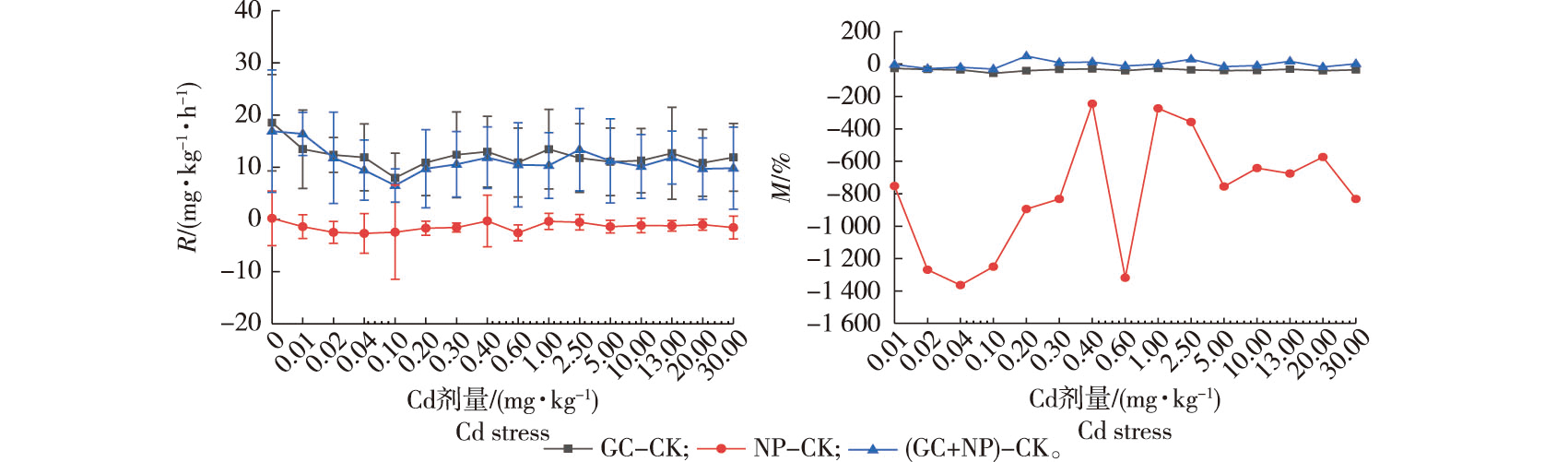
【目的】研究C源与矿质营养氮磷(NP)添加对土壤呼吸作用毒物兴奋效应(Hormesis)的影响。【方法】以模式土壤为对象,接种杨树林地土壤微生物,设置单独添加葡萄糖(GC)、单独添加矿质营养NP(NP)、同时添加葡萄糖和NP(GC+NP),以及二者均无添加的对照(CK)4个处理,研究Cd胁迫下土壤呼吸作用潜在的Hormesis效应。【结果】①NP和GC+NP处理,林地土壤呼吸速率在Cd剂量为0.02、0.10、0.40、2.50、13.00 mg/kg时均显著高于对照,且表现出显著的多重Hormesis效应交替出现的现象,刺激幅度变化在66.6%~262.6%。②土壤中不添加Cd时,GC与NP处理土壤呼吸速率之和大于GC+NP处理,土壤呼吸对二者的添加表现为拮抗效应;当Cd剂量在0.01~0.20 mg/kg区间时,GC与NP处理土壤呼吸速率之和小于GC+NP处理,C源与NP添加对土壤呼吸的影响表现为协同效应;Cd剂量>0.20 mg/kg时,二者之间表现为协同与拮抗效应的交替出现。【结论】外源添加N、P条件下,Cd诱导林地土壤呼吸表现出显著的Hormesis效应。当面临逐渐增加的Cd胁迫时,C源与NP添加对土壤呼吸的交互作用表现为由拮抗向协同效应转变。
【Objective】 Artificial standard soil was used to investigate the potential stimulatory effects of low-dose C, N, and P additions on soil respiration and Hormesis under heavy metal stress. 【Method】The four treatments were: GC (glucose), NP (nitrogen and phosphorus), GC+NP (glucose, nitrogen and phosphorus), and, no additions (CK). The soil samples were inoculated with soil microorganisms from forest land to determine the potential Hormesis effect of exogenous addition of glucose, N and P on soil respiration under Cd stress. 【Result】In the case of the NP and GC+NP treatments, the soil respiration rate was significantly higher than that of the control at Cd doses of 0.02, 0.10, 0.40, 2.50, and 13.00 mg/kg, respectively. There was a significant alternating phenomenon of multiple hormetic effects with stimulation amplitudes between 66.6% and 262.6%. When there was no Cd added to the soil, the sum of the soil respiration rates in the GC and NP treatments was greater than that in the GC+NP treatment. The interaction between C source and NP addition on soil respiration showed an antagonistic effect. When the Cd dose was 0.01 to 0.20 mg/kg, the sum of soil respiration rates in GC and NP treatments was lower than the corresponding rates in GC+NP treatments, and the effects of C source and NP additions on soil respiration showed a synergistic effect. Synergistic and antagonistic effects appeared alternately when the Cd dose was over 0.20 mg/kg. 【Conclusion】The Cd-induced soil respiration rate had a significant Hormesis effect under exogenous NP addition. With increasing Cd stress, the interaction between the C source and NP addition on soil respiration changed from antagonistic to synergistic effects.
土壤呼吸 / Cd胁迫 / 毒物兴奋效应 / 模式土壤 / 葡萄糖 / 氮磷添加
soil respiration / cadmium stress / hormesis / artificial standard soil / glucose / nitrogen and phosphorus addition
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan. Environmental quality standards for soil pollution[S].[2022-04-18]. www.env.go.jp/en/water/soil/sp.html, 2011.
|
| [20] |
王国庆, 邓绍坡, 冯艳红, 等. 国内外重金属土壤环境标准值比较:镉[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2015, 31(6):808-821.
|
| [21] |
王小庆, 马义兵, 黄占斌. 痕量金属元素土壤环境质量基准研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2013, 44(2):505-512.
|
| [22] |
USEPA United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ecological soil screening levels[R/OL]. [2022-04-18]. http://www.epa.gov/ecotox/ecossl, 2011.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
周涵君, 于晓娜, 秦燚鹤, 等. 施用生物炭对Cd污染土壤生物学特性及土壤呼吸速率的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2017, 23(6):61-68.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |