 PDF(3155 KB)
PDF(3155 KB)


无锡市小微湿地演变特征及影响因素分析
张佳敏, 刘小燕, 邓懿, 冯耀, 朱斌, 初磊, 张增信
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (2) : 27-36.
 PDF(3155 KB)
PDF(3155 KB)
 PDF(3155 KB)
PDF(3155 KB)
无锡市小微湿地演变特征及影响因素分析
Changing features and influencing factors of small and micro wetlands in Wuxi City
【目的】 开展小微湿地时空演变特征及影响因素分析,可为湿地生态修复与保护提供数据基础和理论依据。【方法】 基于2000、2010和2020年Landsat系列卫星影像,利用支持向量机分类等方法,提取无锡市小微湿地斑块信息,结合气象、土地利用等数据,对无锡市小微湿地的时空演变特征及其影响因素进行分析。【结果】 ①近20年来无锡市湿地总面积呈下降趋势,由2000年的17.8万hm2减少至2020年的10.4万hm2,其中小微湿地总面积从2000年的1.9万hm2减少到2020年的1.5万hm2。②从空间分布来看,无锡市小微湿地主要分布在宜兴市,其面积占无锡市湿地面积的40.0%;从湿地类型来看,以自然湿地为主,比例高达61.0%;无锡市小微湿地具有明显的季节变化特征,2020年季节性小微湿地占小微湿地总面积的比例高达73.8%。③无锡市小微湿地受自然因素及人类活动影响,其动态变化与气温、降水呈正相关;人类活动对小微湿地面积下降影响显著,湿地和其他地类间的转化加速了湿地面积萎缩。【结论】 无锡市小微湿地资源丰富,但受季节和土地利用变化等影响,小微湿地的萎缩较为严重,亟须加强小微湿地的保护和修复工作。
【Objective】 Small and micro wetlands provide several important ecological functions, such as habitat support for key species, biological transfer, hydrological regulation and water purification, education and rest. Wuxi City in China contains numerous wetlands, of which most over 8 hm2 have been protected in recent years. However, not all small and micro wetlands have been protected in Wuxi City, and research regarding spatiotemporal changes in these habitats under various factors is lacking. Thus, analyzing the temporal and spatial characteristics and driving forces of small and micro wetlands can provide a theoretical basis for wetland ecological restoration and protection construction.【Method】 Based on Landsat satellite images in 2000, 2010 and 2020, patch information of small and micro wetlands in Wuxi City were extracted using support vector machine classification and other methods. Combined with meteorological and land use data, the spatiotemporal evolution of small and micro wetlands in Wuxi City and its influencing factors were analyzed.【Result】 (1) Within the past two decades, the total wetland area in Wuxi City has decreased from 178 000 hm2 in 2000 to 104 000 hm2 in 2020. Among them, the total area of small and micro wetlands has decreased from 19 000 hm2 in 2000 to 15 000 hm2 in 2020. (2) In terms of spatial distribution, small and micro wetlands in Wuxi were mainly distributed in the county-level city Yixing, which accounted for 40.0% of the area of Wuxi City. Small and micro wetlands in Wuxi City predominantly consisted of natural wetlands, accounting for up to 61.0% and displayed marked seasonal variation characteristics. In 2020, the proportion of seasonal small and micro wetlands in the total area of small and micro wetlands was as high as 73.8%. (3) The dynamic of small and micro wetlands in Wuxi City were positively correlated with temperature and precipitation due to natural factors and human activities. Specifically, human activities had a significant impact on the decline of small and micro wetland areas, and the transformation between wetland and other land types accelerated the decline of wetlands.【Conclusion】 Wuxi City is rich in small and micro wetland resources, which are in rapid decline due to seasonal and land use changes. Thus, the protection and restoration of small and micro wetlands must be enhanced to mitigate the negative impacts imposed by different factors.
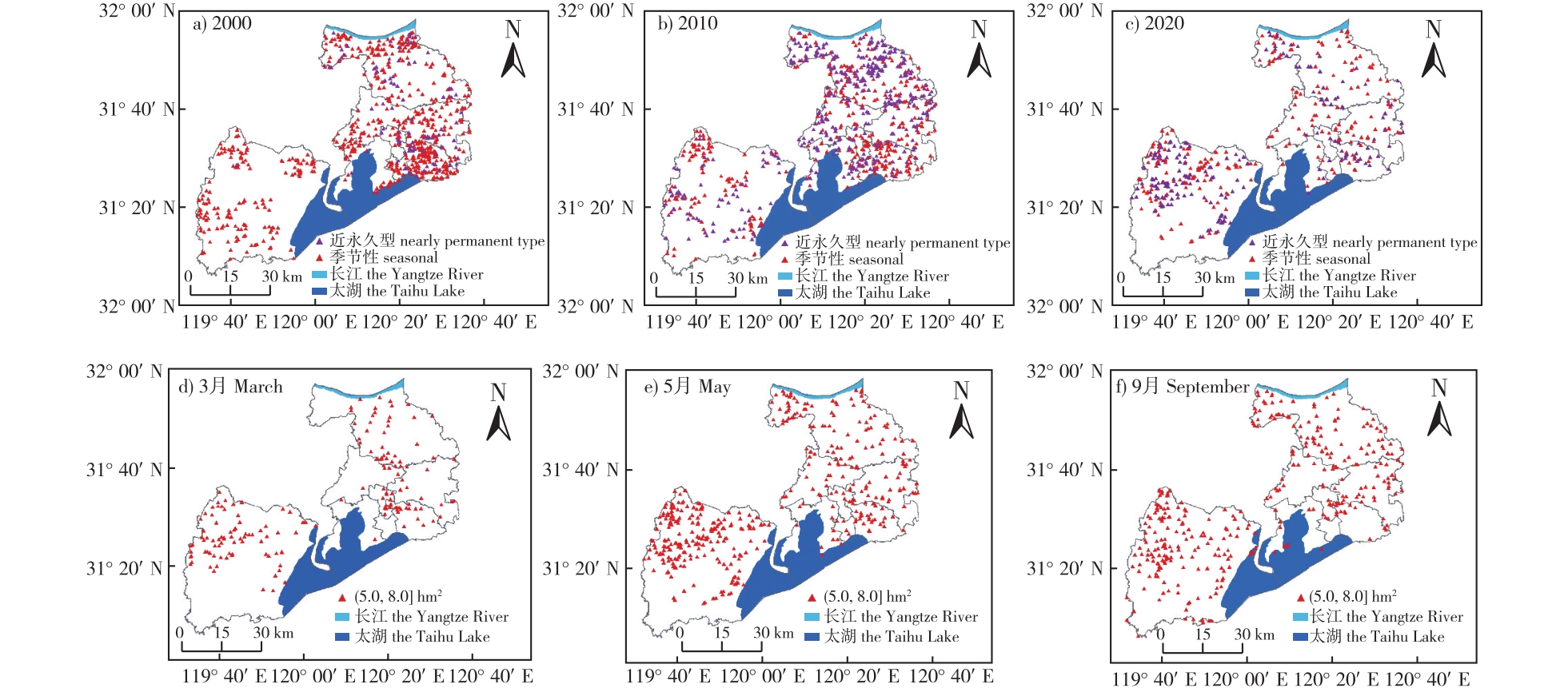
small and micro wetland / land use / spatial and temporal distribution / Wuxi City
| [1] |
宋长春. 湿地生态系统对气候变化的响应[J]. 湿地科学, 2003, 1(2):122-127.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
陈新芳, 冯慕华, 关保华, 等. 微地形对小微湿地保护恢复影响研究进展[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 2020, 16(4):62-65,70.
|
| [5] |
陈月庆, 武黎黎, 章光新, 等. 莫莫格国家级自然保护区地表水文连通性定量评估[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(11):3833-3841.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
周文莹, 张入匀, 李艳朋, 等. 粤港澳大湾区不同类型湿地水鸟群落物种多样性和越冬水鸟栖息地重要性评价[J]. 湿地科学, 2021, 19(2):178-190.
|
| [9] |
赵晖, 陈佳秋, 陈鑫, 等. 小微湿地的保护与管理[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 2018, 14(4):22-26.
|
| [10] |
崔丽娟, 雷茵茹, 张曼胤, 等. 小微湿地研究综述:定义、类型及生态系统服务[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(5):2077-2085.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
龙北辰, 杨景同. 小微湿地的环保功能及应用探究[J]. 环境与发展, 2019, 31(12):194,197.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
何奕忻, 蒋海波, 张运春, 等. 基于CiteSpace的小微湿地文献计量分析[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(13):5516-5530.
|
| [15] |
肖涛, 石强胜, 闻熠, 等. 湿地生态系统服务研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(6):1205-1212.
|
| [16] |
李玉凤. 基于SPOT5卫星影像的南四湖水体信息提取与土地覆被分类研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2008.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
邹青青, 戚晓明, 王晶, 等. 利用Landsat 8多光谱数据的湿地信息提取方法比较研究[J]. 湿地科学, 2018, 16(4):479-485.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
赵抗抗. 基于不同遥感影像的湿地信息分类方法研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2018.
|
| [24] |
李俊辉, 孙瑞, 许兰芳, 等. 无锡市区湿地空间范围监测技术方案与成果分析[J]. 现代测绘, 2020, 43(4):27-30.
|
| [25] |
欧阳玲. 基于遥感和SVM模型的松嫩平原南部耕地质量评价[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所), 2017.
|
| [26] |
高杰, 高敏, 赵志红, 等. 1987—2015年七里海潟湖湿地景观格局变化及驱动力分析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2018, 39(4):8-16.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
刘瑞, 朱道林. 基于转移矩阵的土地利用变化信息挖掘方法探讨[J]. 资源科学. 2010, 32(8): 1544-1550.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
陈钰, 雷琨, 杜尧, 等. 沉湖湿地近50年退化过程识别[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(2):661-670.
|
| [33] |
吴灵叶, 韩雨宸, 盛宇清, 等. 常熟市乡村小微湿地管护与可持续利用探讨[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 2021, 17(3):70-73.
|
| [34] |
吴梦红, 杨长保, 林楠, 等. 西辽河流域湿地动态变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 世界地质, 2016, 35(3):902-908.
|
| [35] |
王海云, 匡耀求, 郑少兰, 等. 粤港澳大湾区2010—2020年湿地时空变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2023, 39(4):126-134.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
董张玉, 刘殿伟, 王宗明, 等. 遥感与GIS支持下的盘锦湿地水禽栖息地适宜性评价[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(6):1503-1511.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |