 PDF(2119 KB)
PDF(2119 KB)


不同性别南方型黑杨无性系叶片对土壤短期间歇性干旱的生理响应
马坛, 田野, 王书军, 李文昊, 段启英, 张庆源
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 172-180.
 PDF(2119 KB)
PDF(2119 KB)
 PDF(2119 KB)
PDF(2119 KB)
不同性别南方型黑杨无性系叶片对土壤短期间歇性干旱的生理响应
Sex-specific leaf physiological responses of southern-type poplar to short-term intermittent soil drought
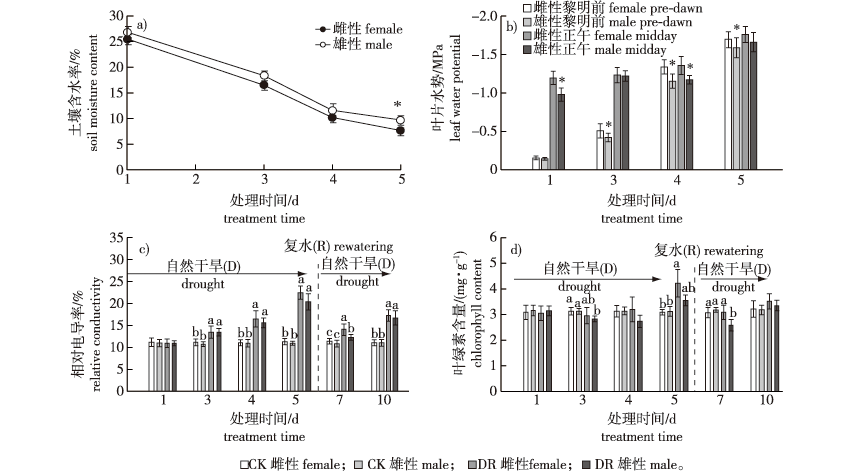
【目的】 全球气候变化背景下南方型黑杨(Populus spp.)栽培区的干旱问题日渐严重,限制了人工林的生产力提升。研究南方型黑杨应对土壤短期间歇性干旱的性别生理响应差异,探讨不同性别黑杨的干旱适应能力及策略,为基于性别的黑杨造林无性系选择提供参考。【方法】 以南方型黑杨栽培区重点推广的4种雌性和3种雄性黑杨无性系当年生扦插苗为研究对象,采用盆栽控水的方式进行土壤短期间歇性干旱(干旱—复水—干旱)处理,通过对比分析不同性别无性系在土壤短期间歇性干旱过程中叶片质膜稳定性、渗透调节、抗氧化系统,以及光合色素等生理指标的变化,分析南方型黑杨在叶片生理响应和干旱耐受性方面应对土壤短期间歇性干旱的性别差异。【结果】 受土壤干旱影响,雌、雄黑杨叶片均出现电导率上升、丙二醛和游离脯氨酸含量以及抗氧化酶活性升高、叶绿素含量下降等现象,表明叶片膜和光合系统受到一定损伤,而复水(解除干旱)后均恢复至正常水平。但雌、雄黑杨在生理响应的水平和模式方面存在一定差异:雌性黑杨在干旱胁迫时叶片抗氧化酶活性波动较大,叶绿素和脯氨酸含量维持较高的水平,而复水后叶绿素含量可以快速恢复,但膜脂过氧化程度维持较高水平;雄性黑杨在干旱胁迫时通过保持较高的细胞膜稳定性和稳定的抗氧化酶活性以提高抗旱性,同时降低叶绿素含量以减少水分损耗。表明在干旱条件下,雌性黑杨继续维持一定的光合和生长能力,但抗旱能力较低,而雄性黑杨相应具有较强的干旱耐受能力。此外,雄性黑杨无性系在应对干旱胁迫时表现出较为一致的生理响应,而雌性黑杨在无性系间存在较大差异。【结论】 雄性黑杨无性系整体上具有较高且稳定的抗旱能力,而雌性黑杨抗旱能力相对较弱,且无性系间差异较大,但复水后的干旱间歇期可以较快恢复至正常的叶片生理状态。
【Objective】 Climate change-induced drought restricts the distribution, growth and productivity of southern poplar plantations in the south of China. To explore adaptability to drought and provide reference for future sex-based poplar clone selection, we studied physiological responses to short-term intermittent soil drought between different sexes. 【Method】 Based on pot experiments by setting short-term intermittent soil water deficiency, four female and three male clones of southern-type poplar were used to compare sex-specific changes in physiological traits, including leaf plasma membrane stability, osmotic regulation, antioxidant system, and photosynthetic pigments. 【Result】 Short-term drought induced increases in electrical conductivity of leaves, malondialdehyde (MDA) and proline (Pro) contents, and antioxidant enzyme activities, but decreases in leaf chlorophyll content, for both male and female poplar clones, which indicated damage to leaf membranes and photosynthesis system with membrane lipid peroxidation. After drought relief by rewatering, these physiological traits all returned to substantially the same level as the (normal watering/non-drought) control treatment. Differences existed in the level and pattern of physiological responses to short-term soil drought between male and female clones. For female clones, the activity of antioxidant enzymes in leaves fluctuated greatly, and the contents of chlorophyll and proline remained at a high level under draught treatment; after drought relief by rewatering, chlorophyll content recovered rapidly, while membrane lipid peroxidation remained high. For male clones exposed to short-term drought, however, we detected stable POD activity and reduced chlorophyll content; this indicated higher drought resistance. Male clones, by maintaining membrane stability and reducing water loss. Therefore, female poplar clones showed relatively lower drought tolerance, but maintained a certain level of photosynthesis and growth, while male clones presented relatively higher drought tolerance. In addition, during short-term soil drought, three male clones showed relatively consistent physiological responses, while male clones had greater inter-clone variation. 【Conclusion】 Male poplar clones had relatively high and stable drought resistance, while female clones had generally weak but varied inter-clone drought resistance. However, female clones displayed rapid recovery of leaf physiological conditions after rewatering between short-term drought.
干旱胁迫 / 南方型黑杨 / 性别差异 / 抗旱策略 / 抗氧化酶系统
drought stress / southern-type poplar / sexual difference / drought resistance strategy / antioxidant enzyme system
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
常兆丰, 韩福贵, 仲生年. 甘肃民勤荒漠区18种乔木物候与气温变化的关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 2009, 33(2):311-319.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
徐建文, 居辉, 刘勤, 等. 黄淮海地区干旱变化特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(2): 460-470.
|
| [5] |
蔡运龙,
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
方升佐. 中国杨树人工林培育技术研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(10):2308-2316.
|
| [8] |
苏晓华, 黄秦军, 张冰玉, 等. 中国杨树良种选育成就及发展对策[J]. 世界林业研究, 2004, 17(1):46-49.
|
| [9] |
胥晓, 杨帆, 尹春英, 等. 雌雄异株植物对环境胁迫响应的性别差异研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(11):2626-2631.
|
| [10] |
陈小梅, 危晖, 林媚珍. 气候变化对雌雄异株植物影响的研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(11):3144-3149.
|
| [11] |
何梅, 施大伟, 胡玉安, 等. 干旱胁迫下银杏雌雄植株的生长及内源激素含量的差异[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2017, 39(6):1154-1162.
|
| [12] |
刘金平, 段婧. 营养生长期雌雄葎草表观性状对水分胁迫响应的性别差异[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(2):243-249.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
段启英, 田野, 鄂晓伟, 等. 南方型黑杨生长和生理特性对持续干旱和复水响应的性别差异[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(7):2140-2150.
|
| [16] |
李斌. 不同性别美洲黑杨幼苗生理生态特征对干旱胁迫的响应[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2021.
|
| [17] |
杨淑红, 宋德才, 刘艳萍, 等. 土壤干旱胁迫和复水后3个杨树品种叶片部分生理指标变化及抗旱性评价[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2014, 23(3):65-73.
|
| [18] |
张江涛, 杨亚峰, 刘艳, 等. 杨树品种2025及其2个芽变彩叶品种对土壤持续干旱胁迫的生理响应[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2014, 42(11):1-6.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
杨舒贻, 陈晓阳, 惠文凯, 等. 逆境胁迫下植物抗氧化酶系统响应研究进展[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 45(5):481-489.
|
| [21] |
沈燕. 欧美杂交杨(Populus deltoides × Populus nigra)雌雄植株对盐和干旱胁迫的生理生态响应[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2018.
|
| [22] |
裴斌, 张光灿, 张淑勇, 等. 土壤干旱胁迫对沙棘叶片光合作用和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(5):1386-1396.
|
| [23] |
张琳敏, 陈坚, 沈文涛, 等. 雌雄组合模式下青杨形态和生理特征对干旱的响应差异[J]. 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(4):325-331.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
刘瑞香, 杨劼, 高丽. 中国沙棘和俄罗斯沙棘叶片在不同土壤水分条件下脯氨酸、可溶性糖及内源激素含量的变化[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(3):148-151,169.
|
| [27] |
张净, 王锦霞, 郭萌萌, 等. 甜菜幼苗对干旱胁迫的适应机制[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(32):1-7.
|
| [28] |
唐学玺. 环境胁迫下雌雄异株植物的差异响应特征及研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(7):74-81.
|
| [29] |
韩瑞宏, 卢欣石, 高桂娟, 等. 紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa)对干旱胁迫的光合生理响应[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(12):5229-5237.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
常青山, 张利霞, 王建章, 等. 干旱和复水对4个芍药品种生理指标的影响及品种抗旱性评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(6):44-50.
|
| [35] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |