 PDF(2276 KB)
PDF(2276 KB)


基于InVEST模型的无锡市生境质量变化研究
赵晓雨, 王益明, 何旭, 刘小燕, 张佳敏, 邓懿, 冯耀, 初磊, 张增信
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 165-172.
 PDF(2276 KB)
PDF(2276 KB)
 PDF(2276 KB)
PDF(2276 KB)
基于InVEST模型的无锡市生境质量变化研究
Changing features of habitat quality in Wuxi City based on InVEST model
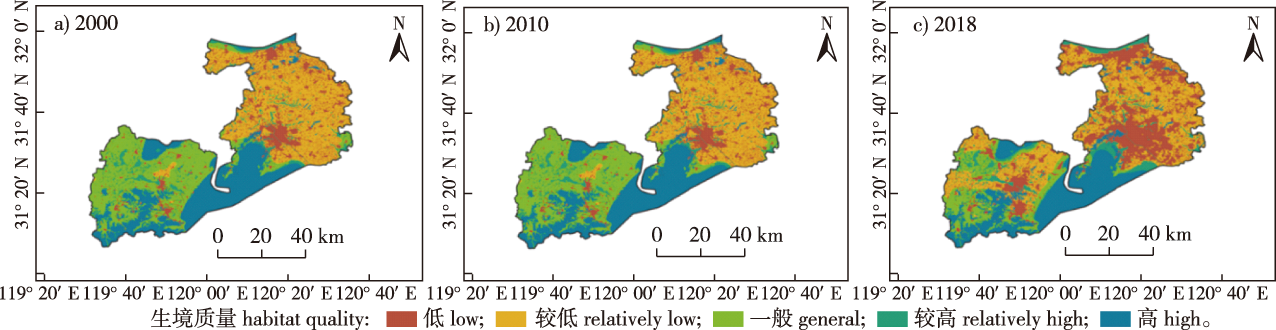
【目的】基于2000、2010和2018年无锡市30 m分辨率土地利用数据,利用生态系统服务与权衡的综合评估(InVEST)模型评估了无锡市生境质量及生境退化度演变规律,为无锡市的生态保护和修复提供依据。【方法】基于InVEST模型模拟了无锡3个不同时期的生境质量、生境退化度,并利用土地利用转移矩阵分析了土地利用与生境质量、生境退化度变化的关系。【结果】2018年无锡市高等级生境质量占全市面积约31.11%,一般等级比例较大,约占全市面积的40.60%;无锡市生境质量空间分布差异较大,高等级生境质量主要分布在宜兴市、滨湖区等地区,而低等级生境质量主要位于无锡市主城区及江阴市等地;过去20年,无锡市生境质量总体上有明显退化趋势,其中梁溪区等无锡主城区以及江阴市退化最明显,宜兴市退化度变化不大;无锡市生境质量变化与土地利用变化是密不可分的,其中,无锡市建设用地从2000年的717.40 km2增加至2018年的1 291.40 km2,增幅约12%,而建设用地增多的区域与生境质量下降比较明显的区域在空间上有较高的一致性。【结论】无锡市的生境质量退化与耕地面积减少及城市建设用地增多等密切相关,需合理利用土地,严格控制建设用地规模,保持生态用地规模,不断提高湿地保护和修复工作。
【Objective】 Based on 30 m of high-resolution land use data of Wuxi City in 2000, 2010 and 2018, the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Trade-offs (InVEST) model was used to reveal the changing features of habitat quality in Wuxi. Such information could provide a basis for ecological environment protection and restoration in Wuxi. 【Method】 Using the InVEST model, the habitat quality and habitat degradation degree of Wuxi during recent 20 years were simulated, and the relationship between the changes of land use, habitat quality and habitat degradation degree was analyzed by using the land use transfer matrix. 【Result】 In 2018, high-grade habitats in Wuxi accounted for approximately 31.11% of the city’s area, whereas the proportion of general grades was relatively higher, accounting for approximately 40.60% of the city’s area. The spatial distribution of habitat quality in Wuxi was various, with the high-grade habitats mainly distributed in Yixing City, Binhu District and other areas, while the low-grade habitats are predominantly located in the main urban area of Wuxi City and Jiangyin City. In the past 20 years, habitat quality in Wuxi has shown a significant degradation trend, of which the main urban areas of Wuxi such as Liangxi District and Jiangyin City have the most obvious degradation, whereas the degradation degree of Yixing City has not changed much. The changes of habitat quality and land use in Wuxi are inseparable, and among them, the construction land of Wuxi increased by approximately 12% from 717.40 km2 in 2000 to 1 291.40 km2 in 2018, and the area with increased construction land and the area where the quality of habitat decline is more obvious have good spatial consistency. 【Conclusion】 Degradation of habitat quality in Wuxi is closely related to the reduction of cultivated land area and the increase of urban construction land. Therefore, it is necessary to rationally use land, strictly control the scale of construction land, maintain the scale of ecological land use, and continuously improve the protection and restoration of wetlands.
土地利用 / 生态系统服务和权衡综合评估模型(InVEST模型) / 生境质量 / 生境退化度 / 建设用地 / 耕地面积 / 无锡市
land use / InVEST model / habitat quality / habitat degradation degree / land for construction / cultivated area / Wuxi City
| [1] |
张文静, 孙小银, 单瑞峰. 基于InVEST模型研究山东半岛沿海地区土地利用变化及其对生境质量的影响[J]. 环境生态学, 2019, 1(5):15-23.
|
| [2] |
杨园园, 戴尔阜, 付华. 基于InVEST模型的生态系统服务功能价值评估研究框架[J]. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(3):41-47.
|
| [3] |
霍思高, 黄璐, 严力蛟. 基于SolVES模型的生态系统文化服务价值评估:以浙江省武义县南部生态公园为例[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(10):3682-3691.
|
| [4] |
刘玮, 辛美丽, 周健, 等. 基于生境适宜性指数模型的俚岛海黍子生境层级分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(3):1061-1068.
|
| [5] |
包玉斌, 刘康, 李婷, 等. 基于InVEST模型的土地利用变化对生境的影响:以陕西省黄河湿地自然保护区为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2015, 32(3):622-629.
|
| [6] |
荣月静, 张慧, 王岩松. 基于Logistic-CA-Markov与InVEST模型对南京市土地利用与生物多样性功能模拟评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2016, 23(3):82-89.
|
| [7] |
吴季秋. 基于CA-Markov和InVEST模型的海南八门湾海湾生态综合评价[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2012.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
李明阳, 张称意, 吴军, 等. 扎龙湿地丹顶鹤繁殖生境变化驱动因素分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(6):76-80.
|
| [10] |
尹楠, 王俊. 西安市泾渭湿地自然保护区生境质量变化评估[J]. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(6):322-328.
|
| [11] |
杨洁, 谢保鹏, 张德罡. 黄河流域生境质量时空演变及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4):12-22.
|
| [12] |
赵晓冏, 王建, 苏军德, 等. 基于InVEST模型和莫兰指数的甘肃省生境质量与退化度评估[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(18):301-308.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
刘春芳, 王川. 基于土地利用变化的黄土丘陵区生境质量时空演变特征:以榆中县为例[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(20):7300-7311.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
李琴, 陈家宽. 长江流域的历史地位及大保护建议[J]. 长江技术经济, 2018, 2(4):10-13.
|
| [17] |
廖志丹, 付琳, 吴齐. 贯彻习近平生态文明思想与法治思想的立法实践:《长江保护法》解读[J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(4): 41-46.
|
| [18] |
高庆彦, 潘玉君, 刘化. 基于InVEST模型的大理州生境质量时空演化研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(3): 402-408.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
陈珊珊, 臧淑英, 孙丽. 基于InVEST模型的土地利用变化对生境质量的影响研究:以松嫩平原为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(3):74-80.
|
| [21] |
王燕, 高吉喜, 金宇, 等. 基于2005—2015年土地利用变化和InVEST模型的内蒙古巴林右旗农牧交错带生境质量研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(5):654-662.
|
| [22] |
许宝荣, 刘一川, 董莹, 等. 基于InVEST模型的兰州地区生境质量评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5):120-129.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
王培东, 马文杰, 文丰, 等. 基于InVEST模型的北京市土地利用变化对生境质量的影响研究[J]. 绿色科技, 2022, 24(4):173-176,180.
|
| [28] |
何清清, 何君. 基于InVEST模型的三峡库区(重庆段)生境质量时空演变分析[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 2022, 7(1):15-25.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |