 PDF(3686 KB)
PDF(3686 KB)


基于生态环境质量评价的酒泉市生态空间网络优化
仇实, 于强, 刘泓君, 王慧媛, 李松, 岳德鹏
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (2) : 199-208.
 PDF(3686 KB)
PDF(3686 KB)
 PDF(3686 KB)
PDF(3686 KB)
基于生态环境质量评价的酒泉市生态空间网络优化
The optimization of ecological spatial network in Jiuquan City based on the evaluation of ecological environment quality
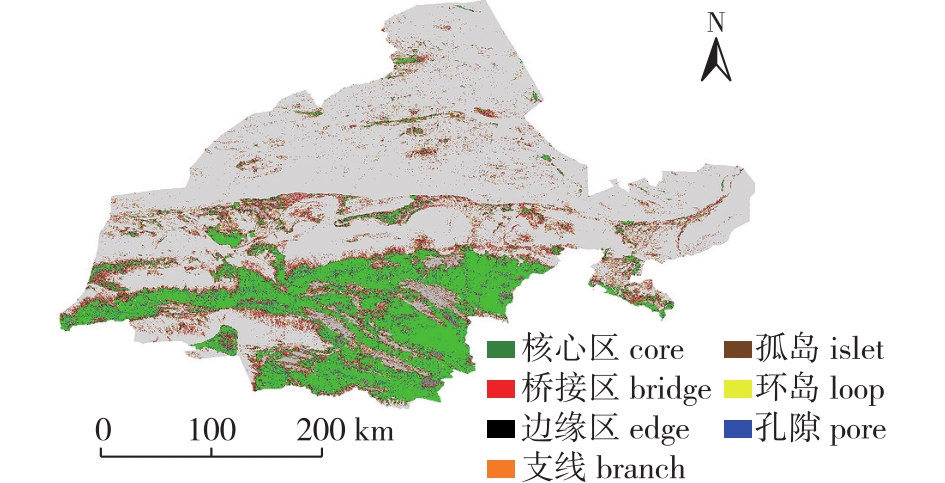
【目的】 构建并优化酒泉地区生态空间网络,提升生态环境质量,发挥区域生态作用,防止沙漠扩张。【方法】 将遥感生态指数(RSEI)与生态空间网络结合,评估酒泉地区景观格局空间,基于复杂网络理论确定薄弱生态源地,提出优化策略。【结果】 ①酒泉市RSEI呈现北部地区低,中南部地区高的空间格局。②酒泉市潜在生态空间网络由332个生态节点,656条生态廊道组成,依照RSEI最低的区域进行增边优化,模拟增边242条,增加生态踏脚石9个。③增边优化后,网络的节点鲁棒性和连接鲁棒性有明显的提升,网络边的鲁棒性略有提升但不明显。【结论】 对生态环境质量弱节点采取增边以及增加踏脚石的优化策略,可使酒泉市生态空间网络的稳定性和生态恢复能力得到一定程度的提升。针对新增生态廊道开展建设,增强源地间的连接,有利于发挥区域生态效益,为酒泉市未来生态工程建设提供策略。
【Objective】 The objective of this study is to construct and optimize the ecological spatial network in Jiuquan City, aiming to enhance the quality of the ecological environment, harness regional ecological functions, and prevent desert expansion. 【Method】 By integrating remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) with the ecological spatial network, this study assessed the spatial pattern of landscape in Jiuquan City. By using complex network theory, the study identified weak ecological source areas and proposed optimization strategies. 【Result】 (1) The RSEI exhibited a spatial pattern in the Jiuquan City, with low values in the northern region and high values in the central and southern regions. (2) The potential ecological spatial network in Jiuquan City comprised 332 ecological nodes and 656 ecological corridors. Through the simulation of additional edges based on the region with the lowest RSEI, 242 edges were added, resulting in the inclusion of nine ecological stepping stones. (3) After the addition of edges, there was a noticeable improvement in the robustness of network nodes and connections, while the improvement in edge robustness was slight and not significant. 【Conclusion】 The optimization strategies of adding edges and stepping stones to weak ecological areas can enhance the stability and ecological restoration capacity of the ecological spatial network in Jiuquan City. The construction of new ecological corridors to enhance connectivity between source areas would facilitate regional ecological benefits and provide strategies for future ecological engineering projects in Jiuquan City.
遥感生态指数(RSEI) / 生态质量评价 / 生态空间网络 / 增边优化 / 鲁棒性
remote sensing ecological index(RSEI) / ecological quality evaluation / ecological spatial network / edge-increasing optimization / robustness
| [1] |
徐涵秋. 城市遥感生态指数的创建及其应用[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(24):7853-7862.
|
| [2] |
孙桂凯, 王国帅, 魏义熊, 等. 基于改进遥感生态指数的岩溶山区生态质量评价:以澄碧河流域为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(2):230-239,F0003.
|
| [3] |
王小宇. 基于遥感生态指数的石漠化地区生态环境质量评价:以贵州花江示范区为例[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2019.
|
| [4] |
彭燕, 何国金, 张兆明, 等. 赣南稀土矿开发区生态环境遥感动态监测与评估[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(6):1676-1685.
|
| [5] |
于强, 张启斌, 牛腾, 等. 绿色生态空间网络研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(12):1-15.
|
| [6] |
于强, 岳德鹏, 张启斌, 等. 磴口县景观格局演变特征及生态网络构建[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3):601-609.
|
| [7] |
马仲武, 王新源, 王小军, 等. 甘肃省酒泉市土地沙漠化现状及动态分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(3):141-147.
|
| [8] |
刘凌冰, 李世平. 西北荒漠化地区土地生态安全评价:以酒泉市为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 2014, 21(4):190-194,202.
|
| [9] |
牛腾, 岳德鹏, 张启斌, 等. 潜在生态网络空间结构与特性研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(8):166-175.
|
| [10] |
王戈, 于强,
|
| [11] |
裴燕如, 孙炎浩, 于强, 等. 黄河流域典型矿区生态空间网络优化:以鄂榆地区为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(5):1541-1554.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
王雪然, 万荣荣, 潘佩佩. 太湖流域生态安全格局构建与调控:基于空间形态学-最小累积阻力模型[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(5):1968-1980.
|
| [16] |
张启斌. 乌兰布和沙漠东北缘生态网络构建与优化研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
| [17] |
王戈, 于强,
|
| [18] |
王戈. 京津冀生态空间网络与区域热环境关系研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
| [19] |
周东东. 城市存量开发中生态空间优化策略研究——“生态踏脚石”在存量生态空间的应用模型[C]// 持续发展理性规划——2017中国城市规划年会论文集(08城市生态规划). 2017:232-241.
|
| [20] |
周涛, 柏文洁, 汪秉宏, 等. 复杂网络研究概述[J]. 物理, 2005, 34(1):31-36.
|
| [21] |
张娟, 文广超, 王恩营, 等. 基于遥感生态指数的焦作市生态环境动态监测与评价[J]. 水土保持通报, 2020, 40(6):107-114.
|
| [22] |
张亚球, 姜放, 纪梦达, 等. 基于遥感指数的区县级生态环境评价[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(6):1598-1605.
|
| [23] |
褚馨德, 贾伟, 张峻豪, 等. 基于RSEI模型的祁连山自然保护区生态环境质量评价[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2022, 34(1):38-42.
|
| [24] |
胡其玉, 陈松林. 基于生态系统服务供需的厦漳泉地区生态网络空间优化[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(2):342-355.
|
| [25] |
卢杰, 王戈, 马骏, 等. 基于复杂网络理论的西藏巴宜区森林景观空间结构研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(4):152-158.
|
| [26] |
张启舜, 李飞雪, 王帝文, 等. 基于生态网络的江苏省生态空间连通性变化研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(8):3007-3020.
|
| [27] |
潘竟虎, 刘晓. 疏勒河流域景观生态风险评价与生态安全格局优化构建[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3):791-799.
|
| [28] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |