 PDF(3857 KB)
PDF(3857 KB)


基于Biomod2组合模型的我国山杨潜在分布区研究
高明龙, 铁牛, 张晨, 李凤滋, 乌雅瀚, 罗奇辉, 王子瑞, 刘磊, 萨如拉
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (2) : 247-255.
 PDF(3857 KB)
PDF(3857 KB)
 PDF(3857 KB)
PDF(3857 KB)
基于Biomod2组合模型的我国山杨潜在分布区研究
Modelling the potential distribution area of Populus davidiana in China based on the Biomod2
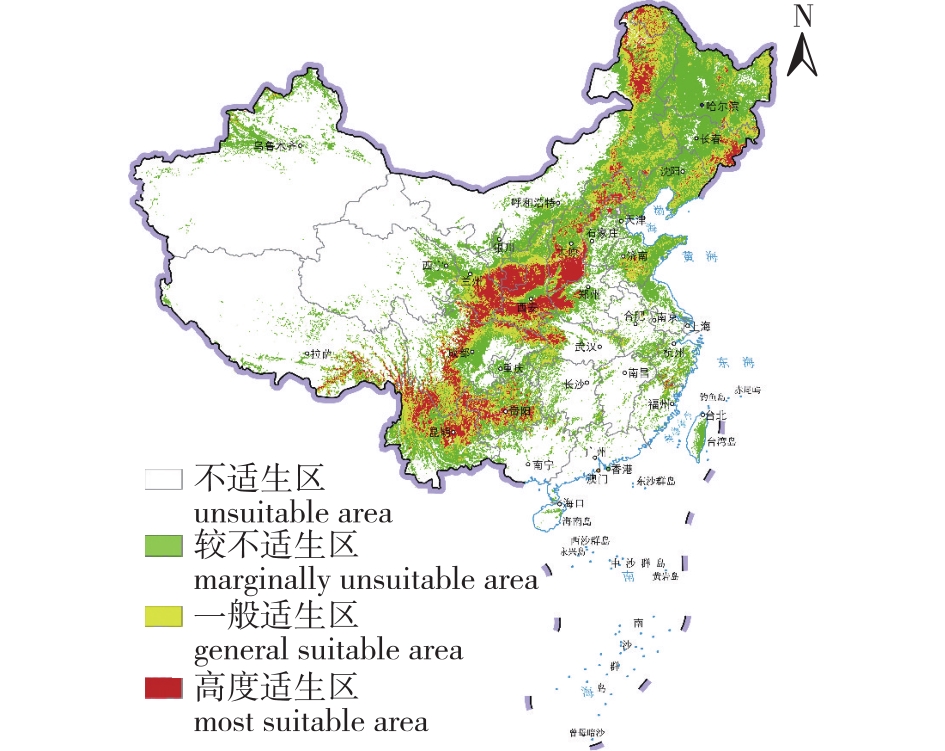
【目的】 通过探究环境变化对山杨(Populus davidiana)分布的影响,为山杨资源的保护和开发提供理论支撑。【方法】 根据山杨的134条地理分布数据,结合18个气候、土壤及地形因子,基于Biomod2软件包构建组合模型,模拟我国山杨潜在分布区在未来3种气候条件模式下的空间分布格局变化,并确定影响山杨分布的主要环境变量。【结果】 我国山杨当前潜在适生分布区主要位于400 mm等降水线两侧较高纬度或较高海拔地区,总面积约为1 560 340.9 km2,约占我国陆地面积的16.2%,其中大兴安岭、长白山、太行山、秦岭、祁连山南麓、横断山、云贵高原等地区为山杨高度适生区;在未来气候条件下,山杨适生区整体呈向西南方向收缩趋势,生境适宜度总体呈下降趋势;影响山杨分布主要环境变量为最热月最高气温、年降水量和海拔;基于5个最优单一模型构建的组合模型比单一模型对山杨适生区预测结果更好,训练集平均受试者工作特征曲线下面积和真实技巧统计值分布为 0.91和0.73,预测准确度较高。【结论】 我国山杨空间分布格局主要受水热条件影响,海拔也是影响山杨分布的重要因素。在未来气候条件下,山杨分布区面积将随气候变暖的程度逐渐减少。以山杨作为用材林和生态公益林树种进行造林时,造林地点应选择未来生境适宜度变化不大的地区,以降低未来由于气候变化造成的损失。
【Objective】 This study aims to investigate the effects of changes in environmental factors on the distribution of Populus davidiana, and to provide theoretical support for the conservation and development of P. davidiana resources. 【Method】 This study applied Biomod2 to simulate changes in the spatial distribution pattern of P. davidiana in China's potential distribution areas under three future climatic conditions based on 134 geographical distribution data points of P. davidiana in China, combined with 18 climatic, soil and topographic factors. Then a combinatorial model based on the Biomod2 package was consturcted and identified the main environmental variables affecting the distribution of P. davidiana were identified. 【Result】 The current potential distribution areas of P. davidiana in China were mainly located at higher latitudes or higher altitudes on both sides of the 400 mm precipitation line, with a total area of about 1 560 340.9 km2, of which the Greater Khingan Mountains, Changbai Mountains, Taihang Mountains, Qinling Mountains, southern foot of Qilian Mountains, Hengduan Mountains, Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and other areas are the highest suitable areas for P. davidiana. Under future climatic conditions, the overall trend of suitable areas for P. davidiana will shrink to southwest China, and the overall trend of suitable areas was decreasing. The ensemble model constructed based on the five optimal single models had better prediction results for suitable areas for P. davidiana compared to the single model, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and true skill statistics were distributed as 0.91 and 0.73, with higher prediction accuracy. 【Conclusion】 The spatial distribution pattern of P. davidiana in China was mainly influenced by water and heat conditions, while altitude was also an important factor affecting its distribution. Under future climatic conditions, the area of P. davidiana distribution will gradually decrease based on the degree of climate warming. When planting P. davidiana for timber forests and as an ecological public welfare forest species, planting sites should be selected in areas where habitat suitability will not change significantly in the future, to reduce future losses because of climate change.
山杨 / Biomod2软件包 / 组合模型 / 潜在分布区 / 气候变暖
Populus davidiana / Biomod2 / ensemble model / potential distribution area / global warming
| [1] |
曾建平, 代峰. 气候伦理是否可能[J]. 中国人民大学学报, 2011, 25(3):90-96.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
刘晓彤, 袁泉, 倪健. 中国植物分布模拟研究现状[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(4):273-283.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
赵光华, 崔馨月, 王智, 等. 气候变化背景下我国酸枣潜在适生区预测[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(6):158-168.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
吴晓萌, 叶冬梅, 白玉娥, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的中国白杄分布格局及未来变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(1):162-172.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
卫尊征, 郭丽琴, 张金凤, 等. 利用trnL-F序列分析杨属树种的系统发育关系[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2010, 32(2):27-33.
|
| [15] |
中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志-第二十卷, 第二分册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1984.
Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, Agendae Academiae Sinicae Edita. Flora reipublicae popularis sinicae tomus 20(2)[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1984.
|
| [16] |
翁宇威, 蔡闻佳, 王灿. 共享社会经济路径(SSPs)的应用与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(2):215-222.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
张天蛟, 刘刚. 提高生态位模型时间转移能力的方法研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2017, 22(2):98-105.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
吴艺楠, 马育军, 刘文玲, 等. 基于BIOMOD的青海湖流域高原鼠兔分布模拟[J]. 动物学杂志, 2017, 52(3):390-402.
|
| [22] |
郭恺琦, 姜小龙, 徐刚标. 薄片青冈潜在适生区及气候变化对其分布的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8):2563-2574.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
李易. 中国山杨群体历史动态初步研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2020.
|
| [25] |
郭彦龙, 赵泽芳, 乔慧捷, 等. 物种分布模型面临的挑战与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(12):1292-1305.
|
| [26] |
袁喆, 严登华, 杨志勇, 等. 1961—2010年中国400 mm和800 mm等雨量线时空变化[J]. 水科学进展, 2014, 25(4):494-502.
|
| [27] |
贺敏, 魏江生, 石亮, 等. 大兴安岭南段山杨径向生长和死亡对区域气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(11):3237-3244.
|
| [28] |
潘春芳, 赵秀海, 夏富才, 等. 长白山山杨种群的性比格局及其空间分布[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(2):297-305.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
白伟宁, 张大勇. 植物亲缘地理学的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 生命科学, 2014, 26(2):125-137.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
胡忠俊, 张镱锂, 刘林山, 等. 生物避难所及其识别方法评述[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(12):3397-3406.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |