 PDF(1862 KB)
PDF(1862 KB)


毛竹林下植被演替过程中土壤颗粒组成与水分入渗特征
谢燕燕, 郭子武, 林树燕, 左珂怡, 杨丽婷, 徐森, 谷瑞, 陈双林
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 108-116.
 PDF(1862 KB)
PDF(1862 KB)
 PDF(1862 KB)
PDF(1862 KB)
毛竹林下植被演替过程中土壤颗粒组成与水分入渗特征
Soil particle distribution and water infiltration characteristics during vegetation succession in Phyllostachys edulis stands
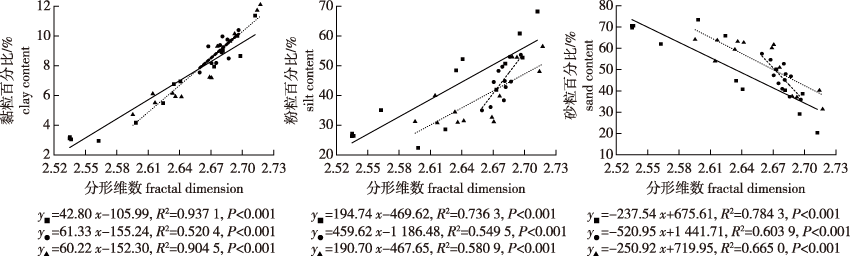
【目的】 测定毛竹(Phyllostachys edulis)林地不同土层土壤粒径组成、分布和水分入渗性能,揭示土壤粒径分布及水分入渗性能对林下植被演替的响应规律,为毛竹林地土壤生态管理与植被更新提供依据。【方法】 以林下植被演替年限分别为0、9及21 a的毛竹林为研究对象,测定了林地不同土层,即[0, 10) cm、[10, 20) cm和[20, 30) cm层土壤颗粒组成、土壤颗粒体积分形维数,采用Kostiakov、Philip和Horton模型模拟分析土壤水分入渗性能,解析土壤分形特征与颗粒组成、水分入渗性能的关系。【结果】 同一演替年限毛竹林土壤黏粒、粉粒含量、分形维数和水分入渗性能均随土层深度增加而降低,而砂粒含量逐渐增加。随林下植被演替年限延长,[0, 10) cm土层黏粒、粉粒含量及分形维数逐渐下降,砂粒含量逐渐增加,[10, 20) cm和[20, 30) cm土层黏粒、粉粒含量及分形维数呈先升高后下降的趋势,砂粒含量则与之相反;不同土层土壤初渗率和稳渗率总体呈升高的变化趋势;土壤分形维数与黏粉粒含量、初渗率和稳渗率均呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05),与砂粒含量呈显著负相关关系(P<0.05);Kostiakov与Horton模型更适用于试验毛竹林土壤水分入渗过程模拟。【结论】 毛竹林下植被演替能够显著改善土壤粒径结构,提高土壤水分入渗性能,且呈现明显的演替时间效应,植被演替21 a毛竹林的土壤水分入渗性能明显优于植被演替9 a毛竹林和毛竹纯林的。
【Objective】 The particle size composition, distribution, and water infiltration capability of soil in different soil layers of Phyllostachys edulis stands were measured. The response of soil particle size distribution and water infiltration capability to understory vegetation succession was revealed, which provides guidance for soil ecological management and vegetation renewal of P. edulis stands.【Method】 The understory vegetation successional ages of 21, 9 and 0 years in P. edulis stands were chosen for research. Soil particle size composition and fractal dimension of soil particle volume in different soil layers, as [0, 10) cm, [10, 20) cm, [20, 30) cm of stands land were measured. Soil water infiltration capability was simulated by using Kostiakov, Philip and Horton models. The relationships among soil fractal characteristics, particle composition, and water infiltration capability were analyzed. 【Result】 For P. edulis forests with the same understory successional years, soil clay content, silt content, fractal dimension, and water infiltration capability decreased with the increase of soil depth, while sand content increased gradually. With the extension of vegetation succession years, the content of clay and silt as well as fractal dimension decreased gradually in the [0, 10) cm soil layer, while the sand content increased gradually. The clay and silt contents and fractal dimension in [10, 20) cm and [20, 30) cm soil layers increased first and then decreased, but the sand content changed in the opposite direction. The initial infiltration rate and stable infiltration rate of all soil layers showed an increasing trend with the extension of successional age. Soil fractal dimension was positively correlated with clay particle content, initial infiltration rate, and stable infiltration rate (P<0.05), but negatively correlated with sand particle content (P<0.05). The Kostiakov and Horton models are more suitable for the simulation of soil water infiltration process in experimental P. edulis stands. 【Conclusion】 Vegetation succession under P. edulis stands can significantly improve soil water particle structure and enhance soil water infiltration capability, and the succession time effect is obvious. Soil water infiltration capability of P. edulis in the older 21-year successional understory age was better than that of the younger 9-year and pure bamboo stands.
毛竹 / 植被演替 / 土壤粒径 / 分形特征 / 土壤水分入渗性能
Phyllostachys edulis / vegetation succession / soil particle size / fractal characteristic / soil water infiltration capability
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
朱梦雪, 赵洋毅, 王克勤, 等. 中亚热带不同演替森林群落土壤结构分形特征对大孔隙的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 202(2):67-77.
|
| [3] |
程杰, 王欢元, 解建仓, 等. 不同配比下复配土的土壤颗粒组成、分形维数与质地变化特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(2):30-34.
|
| [4] |
常美蓉, 庞奖励, 张彩云, 等. 关中东部不同土地利用方式对土壤质地影响探讨[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2009, 25(1):50-53.
|
| [5] |
张立欣, 段玉玺, 王伟峰, 等. 毛乌素沙地不同植被类型的土壤颗粒分形与土壤碳氮变化特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2016, 44(8):55-60.
|
| [6] |
彭舜磊, 由文辉, 沈会涛. 植被群落演替对土壤饱和导水率的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(11):78-84.
|
| [7] |
马任甜. 子午岭植被恢复过程中土壤团聚体稳定性提升的内力作用机制[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021.
|
| [8] |
高传友, 赵清贺, 刘倩. 北江干流河岸带不同植被类型土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2016, 23(3):37-42.
|
| [9] |
王俊, 郭金龙, 张永旺, 等. 黄土高原自然植被恢复过程中土壤温度和水分的相关性[J]. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(2):130-137.
|
| [10] |
战海霞, 张光灿, 刘霞, 等. 沂蒙山林区不同植物群落的土壤颗粒分形与水分入渗特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2009, 7(1):49-56.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
梁士楚, 董鸣, 王伯荪, 等. 英罗港红树林土壤粒径分布的分形特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(1):11-14.
|
| [14] |
王飞, 郭树江, 张卫星, 等. 干旱荒漠区不同演替阶段白刺灌丛沙堆土壤粒度特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(1):15-20,44.
|
| [15] |
张冠华, 易亮, 丁文峰, 等. 三峡库区苔藓生物结皮对土壤水分入渗的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(7):1835-1842.
|
| [16] |
李卓, 刘永红, 杨勤. 土壤水分入渗影响机制研究综述[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2011, 30(5):124-130.
|
| [17] |
张金武, 王立. 白龙江上游不同演替阶段森林土壤入渗和持水特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(4):41-47.
|
| [18] |
姚淑霞, 赵传成, 张铜会. 科尔沁不同沙地土壤饱和导水率比较研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2013, 50(3):469-477.
|
| [19] |
阿茹·苏里坦, 常顺利, 张毓涛. 天山林区不同群落土壤水分入渗特性的对比分析与模拟[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(24):9111-9118.
|
| [20] |
陈双林. 毛竹林地覆盖竹笋早出技术应用的问题思考[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2011, 28(5):799-804.
|
| [21] |
李玉敏, 冯鹏飞. 基于第九次全国森林资源清查的中国竹资源分析[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2019, 17(6):45-48.
|
| [22] |
陈双林, 杨伟真. 我国毛竹人工林地力衰退成因分析[J]. 林业科技开发, 2002, 16(5):3-6.
|
| [23] |
黄昌勇. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [24] |
常海涛, 赵娟, 刘佳楠, 等. 退耕还林与还草对土壤理化性质及分形特征的影响:以宁夏荒漠草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7):14-25.
|
| [25] |
王国梁, 周生路, 赵其国. 土壤颗粒的体积分形维数及其在土地利用中的应用[J]. 土壤学报, 2005, 42(4):545-550.
|
| [26] |
刘顺, 盛可银, 刘喜帅, 等. 赣南毛竹林土壤的渗透性特征[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2018, 45(2):252-257.
|
| [27] |
王德, 傅伯杰, 陈利顶, 等. 不同土地利用类型下土壤粒径分形分析:以黄土丘陵沟壑区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(7):3081-3089.
|
| [28] |
袁希. 江西东南部山地森林土壤入渗及其影响因素研究[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2020.
|
| [29] |
赵盼盼, 李国旗, 邵文山, 等. 封育对荒漠草原苦豆子群落土壤粒径分形特征的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2017, 37(6):1234-1241.
|
| [30] |
张希彪, 上官周平. 人为干扰对黄土高原子午岭油松人工林土壤物理性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(11):3685-3695.
|
| [31] |
王韵, 王克林, 邹冬生, 等. 广西喀斯特地区植被演替对土壤质量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2007, 21(6):130-134.
|
| [32] |
张海廷, 时延庆. 山东省不同土地利用方式土壤颗粒组成及其分形维数特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(1):126-131,138.
|
| [33] |
李敏, 李毅. 土壤颗粒数量分布的局部分形及多重分形特性[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(11):216-222.
|
| [34] |
吕圣桥. 黄河三角洲滩地土壤颗粒分形特征及其与土壤性质的相关性研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2012.
|
| [35] |
蒋嘉瑜, 刘任涛, 张安宁. 干旱与半干旱荒漠草原区柠条灌丛土壤分形维数与理化性质对比分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(4):54-61,69.
|
| [36] |
李平, 王冬梅, 丁聪, 等. 黄土高寒区典型植被类型土壤入渗特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(5):1610-1620.
|
| [37] |
胡阳, 邓艳, 蒋忠诚, 等. 岩溶坡地不同植被类型土壤水分入渗特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3):597-604.
|
| [38] |
陈家林, 郭二辉, 杨果果, 等. 太行山低山丘陵区不同水土保持林地土壤渗透性能及其影响因素研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2016, 36(10):34-40.
|
| [39] |
吕渡, 杨亚辉, 赵文慧, 等. 不同恢复类型植被细根分布及与土壤理化性质的耦合关系[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(11):3979-3987.
|
| [40] |
李广文. 黑河上游八宝河流域土壤特性及入渗模拟研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2016.
|
| [41] |
王意锟, 金爱武, 方升佐, 等. 浙西南不同经营强度下毛竹林土壤渗透性研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2015, 22(2):41-46.
|
| [42] |
张昌顺, 范少辉, 官凤英, 等. 闽北毛竹林的土壤渗透性及其影响因子[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(1):36-42.
|
| [43] |
赵西宁, 吴发启. 土壤水分入渗的研究进展和评述[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2004, 19(1):42-45.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |