 PDF(1789 KB)
PDF(1789 KB)


HPLC同时测定竹笋中8种酚酸类物质含量的方法研究及其应用
黄永健, 荀航, 张保, 尤俊昊, 姚曦, 汤锋
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 237-244.
 PDF(1789 KB)
PDF(1789 KB)
 PDF(1789 KB)
PDF(1789 KB)
HPLC同时测定竹笋中8种酚酸类物质含量的方法研究及其应用
Simultaneous determination of eight phenolic acids in bamboo shoots by HPLC and its applications
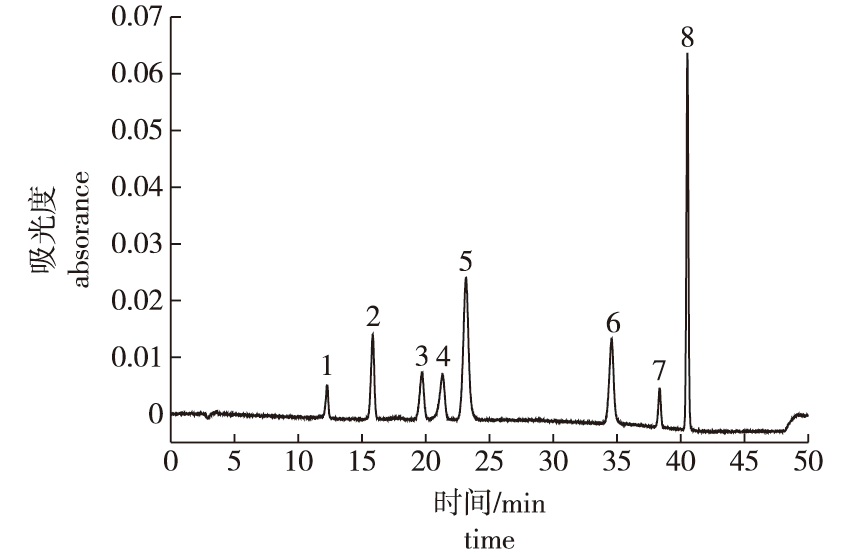
【目的】 为实现竹笋中3,4-二羟基苯乙酸、对羟基苯甲酸、香草酸、咖啡酸、对羟基苯甲醛、丁香醛、阿魏酸、3-羟基肉桂酸等8种酚酸类化合物的快速检测,建立一种基于高效液相色谱-二极管阵列(HPLC-PDA)检测方法。【方法】 采用Symmetry C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm)色谱柱,乙腈和乙酸-水(体积比0.5∶99.5)为流动相,在流速1.0 mL/min、进样量10 μL和柱温30 ℃的条件下梯度洗脱,检测波长275 nm。【结果】 8种酚酸的分离度均在1.5以上,在1.0~50.0 μg/mL的线性范围内,线性关系良好,相关系数R≥0.999 0,检出限[信号强度(S)与噪声强度(N)之比(S/N)为3]为0.12~0.69 μg/mL,定量限(S/N=10)为0.36~2.08 μg/mL,精密度、重复性、稳定性实验相对标准偏差(RSD)均小于5%,加标回收率为80.99%~129.12%,RSD均小于5%。应用该方法,检测了苦竹(Pleioblastus amarus)和苦篱竹(Arundinaria acerba)竹笋中酚酸类物质的含量,8种酚酸总量为(9.35±0.08)~(38.60±0.12) mg/kg;比较了自然生长和避光处理生长条件下苦竹笋中酚酸含量的变化,发现避光处理的竹笋中6种酚酸含量显著降低,总含量下降达46.2%。【结论】 HPLC-PDA检测方法简单方便,灵敏度高,准确可靠,适用于竹笋中酚酸类物质的测定;避光处理可以有效降低苦竹笋样品中酚酸类物质的含量。
【Objective】 Phenolic acids are present in almost all plant-derived foods, and are associated with the organoleptic and nutritional properties of foods. A high-performance liquid chromatography-photo-diode array (HPLC-PDA) method was established for the simultaneous detection of eight phenolic acids in bamboo shoots: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, caffeic acid, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, syringaldehyde, ferulic acid and 3-hydroxycinnamic acid. 【Method】 Eight phenolic acids were separated on a Symmetry C18 column (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm). Acetonitrile (phase A) and 0.5% acetic acid solution (phase B) were used as the mobile phase, the injection volume was 10 μL, and the detection wavelength was 275 nm. The analysis was performed at 30 ℃ with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. 【Result】 Eight phenolic acids were successfully separated (resolution>1.5), and had a good linear relationship (R ≥ 0.999 0) with a linear range of 1.0-50.0 μg/mL. The detection limits (S/N=3) were 0.12-0.69 μg/mL and the quantification limits (S/N=10) were 0.36-2.08 μg/mL. Precision, repeatability, and stability tests yielded relative standard deviations (RSD) of <5%. Additionally, the recoveries of phenolic acids were 80.99%-129.12%, and the RSD values associated with the recoveries were also <5%. The phenolic acid contents in the actual samples of Pleioblastus amarus bamboo shoots and Arundinaria acerba bamboo shoots were determined using an established method. The contents of eight phenolic acids in the actual bamboo shoots samples varied from (9.35±0.08) to (38.60±0.12) mg/kg. A comparative analysis of phenolic acids in P. amarus bamboo shoots grown under a shading treatment and normal conditions was conducted based on this method. Compared to the shoots grown under normal conditions, the contents of six phenolic acids in P. amarus bamboo shoots grown under the shading treatment were lower, and the content of total detected phenolic acids decreased by 46.2%.【Conclusion】 The method developed here is simple, sensitive, accurate and reliable, and is suitable for determining phenolic acids in bamboo shoots. The results showed that a shading treatment downregulated the accumulation of phenolic acids in P. amarus bamboo shoots.
竹笋 / 酚酸类物质 / 高效液相色谱 / 苦竹 / 苦篱竹 / 避光处理
bamboo shoots / phenolic acids / HPLC / Pleioblastus amarus / Arundinaria acerba / shading treatment
| [1] |
赵学敏. 本草纲目拾遗:十卷[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1963.
|
| [2] |
崔逢欣, 丁兴萃, 李露双, 等. 毛竹笋呈味物质种类、含量与辛辣味强度的关系[J]. 林业科学研究, 2017, 30(6):1041-1049.
|
| [3] |
章志远, 丁兴萃, 崔逢欣, 等. 感官评定方法确定麻竹笋苦涩味物质成分及与口感的关系[J]. 食品科学, 2017, 38(5):167-173.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
李露双, 董文慧, 丁兴萃, 等. 麻竹笋转录组测序及苦涩味物质合成基因差异表达分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2018, 31(4):38-46.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
乔丽萍, 傅瑜, 叶兴乾, 等. 酚酸生物活性研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报, 2013, 13(10):144-152.
|
| [9] |
陈清艳. HPLC法同时测定荞麦中8种酚酸类成分[J]. 食品工业, 2022, 43(2):279-282.
|
| [10] |
赵希娟, 庞雯辉, 谭涛, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-HRMS技术结合SWATH采集方法同时测定柠檬果实中26种生物活性成分的含量[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 48(23):306-314.
|
| [11] |
方鑫, 杨峥, 王晨旭, 等. 丹参DnaJ基因的鉴定及胁迫响应分析[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2022, 45(1):94-102.
|
| [12] |
李明良, 陈双林, 郭子武, 等. 覆土栽培对高节竹笋呈味氨基酸的影响[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2015, 35(2):54-57.
|
| [13] |
童龙, 张磊, 李彬, 等. 覆土栽培对绿竹笋品质与适口性的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2018, 40(3):487-493.
|
| [14] |
王晓娟, 马光良, 陈洪, 等. 不同覆盖措施对梁山慈竹出笋和竹笋适口性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2):143-149.
|
| [15] |
徐圣友, 曹万友, 宋曰钦, 等. 不同品种竹笋蛋白质与氨基酸的分析与评价[J]. 食品科学, 2005, 26(7):222-227.
|
| [16] |
苏玉, 李璐, 黄亮, 等. 超微化雷竹笋膳食纤维对高脂血症小鼠的影响[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(15):203-210.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
何乐, 王大成, 吴立军, 等. 苦味西葫芦化学成分研究[J]. 中国现代中药, 2007, 9(7):10-12.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
李雪蕾, 丁兴萃, 张闪闪, 等. 不同光强下麻竹笋不同部位苦涩味物质含量的变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(3):161-166.
|
| [25] |
朱玉燕, 邬波龙, 赵宇瑛, 等. 绿竹笋苦味物质成分分析[J]. 食品科技, 2015, 40(8):77-80.
|
| [26] |
董春凤, 赵一鹤. 储藏时间和温度对甜龙竹笋采后品质的影响[J]. 竹子学报, 2021, 40(4):80-86.
|
| [27] |
李倩, 梁宗锁, 董娟娥, 等. 丹参品质与主导气候因子的灰色关联度分析[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(10):2569-2575.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
陈勤操, 戴伟东, 蔺志远, 等. 代谢组学解析遮阴对茶叶主要品质成分的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(6):1066-1077.
|
| [30] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |