 PDF(2584 KB)
PDF(2584 KB)


岩土高效溶蚀菌株Bt NL-11发酵条件优化及应用效果分析
王凌剑, 贾赵辉, 张金池, 唐兴港, 孙昕, 孟苗婧, 刘鑫
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 71-80.
 PDF(2584 KB)
PDF(2584 KB)
 PDF(2584 KB)
PDF(2584 KB)
岩土高效溶蚀菌株Bt NL-11发酵条件优化及应用效果分析
Optimization for fermentation conditions and analysis of application effect for high efficiency dissolution strain Bt NL-11 from Bacillus thuringiensis
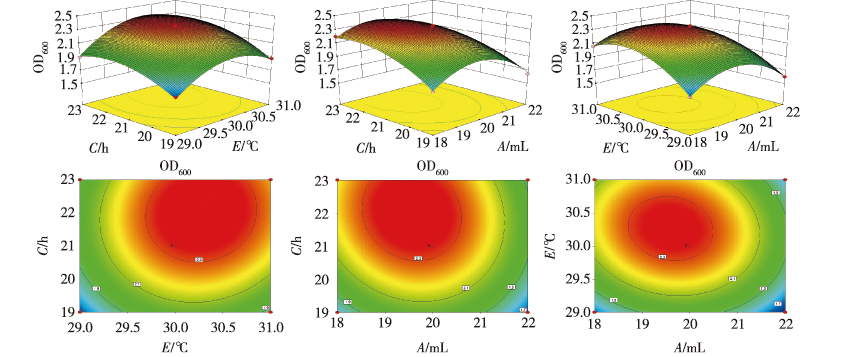
【目的】 为科学治理废弃矿山边坡,探究土壤细菌永久绿化法在生态修复中的应用与推广,对分离筛选出的高效溶蚀菌株进行发酵条件优化及应用效果分析。【方法】 从南京幕府山风化岩壁土壤中分离出多种溶蚀微生物,并从中挑选出1种表现突出的溶蚀细菌菌株NL-11[经16S rRNA鉴定为苏云金芽孢杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis,Bt)]进行发酵条件优化,利用盆栽试验观测其应用效果。首先利用单因素和Plackett Burman(PB)试验筛选出影响菌株生长的3个主要因素,即装液量、培养温度和时间;在此基础上使用最陡爬坡路径逼近最大响应区域;再利用Box-Behnken试验设计及响应面分析法进行回归分析;最后通过比较预测值与实测值验证模型可靠性。利用优化结果制备菌液,将制备好的菌液调节为低(10 cfu/mL)、中(1×105 cfu/mL)和高(1×109 cfu/mL)3种菌液浓度拌入基质(分别为T1、T2、T3处理)进行盆栽试验,设置不加菌液的处理为空白对照(CK),研究不同浓度菌液对矿物风化、植物和根系生长的促进作用。【结果】 模型准确可靠,菌株NL-11的最佳发酵培养条件为:装液量19.51 mL,接种量2%(体积分数),初始pH 7.0,培养温度30.30 ℃,培养时间22.07 h,在此优化条件下发酵液中活菌数达到1.47×1010 cfu/mL,是未优化前的2.03倍。盆栽试验结果表明,菌株NL-11能够促进矿物风化,以高浓度菌液效果最显著;NL-11能够促进矿质养分溶解,以高浓度菌液效果最显著;NL-11能够促进植物及根系生长,以中浓度效果最显著。【结论】 通过优化试验显著提高了菌株NL-11的发酵活菌产量,为菌株在边坡治理中的应用提供技术支持,综合评价菌株的应用效果并考虑生产成本等因素,喷播实践中的合适菌液浓度为1×105 cfu/mL。
【Objective】 This study aimed to scientifically manage abandoned mine slopes, explore the application and promotion of the soil bacteria permanent greening method in restoration, optimize the fermentation conditions, and analyze the application effect of the isolated and screened high-efficiency solubilizing bacteria.【Method】 A variety of solubilizing microorganisms were isolated from the weathered rock wall soil in Nanjing Mufu Mountain, and a prominent solubilizing strain, NL-11, identified as Bacillus thuringiensis by 16S rRNA, was selected to optimize fermentation conditions, and its application effect was observed with the potting test. The three main factors affecting the growth of the strain (liquid volume, temperature, and time), were screened using the univariate and Plackett Burman tests; on this basis, the steepest climbing path was used to approximate the maximum response area; then, the Box-Behnken experimental design was used and the response surface analysis method was used for regression analysis. Finally, model reliability was verified by comparing the predicted values with the measured values. The optimized results were used to prepare the bacterial solution, and then adjusted to low (10 cfu/mL), medium (1 × 105 cfu/mL), and high (1 × 109 cfu/mL) concentrations and mixed into the substrate (T1, T2, and T3 treatments, respectively) for the pot experiments, and the treatment without the bacterial solution was set as a blank control (CK) to study the effects of the different bacterial solution concentrations on mineral weathering and plant and root growth.【Result】 The model was accurate and reliable, and the optimal fermentation culture conditions for NL-11 were as follows: a liquid volume of 19.51 mL, an inoculum level of 2%, an initial pH of 7.0, a temperature of 30.30 ℃, and a time of 22.07 h. The number of viable bacteria in the fermentation broth under these optimized conditions reached 1.47 × 1010 cfu/mL, which was 2.03 times higher than that before optimization. The results of the pot tests showed that strain NL-11 could promote mineral weathering, and the effect of the high concentration of the bacterial solution was the most significant. Furthermore, strain NL-11 could promote the dissolution of mineral nutrients, and the effect of the high concentration of the bacterial solution was the most significant. Strain NL-11 could also promote plant and root growth, and the effect of the medium concentration was the most significant. 【Conclusion】 The optimization test significantly improved the production of fermentation of the live bacteria of strain NL-11 and provided technical support for the application of the strain in the management of slopes. The suitable concentration of the bacterial solution in spraying practice is 1 × 105 cfu/mL by the comprehensive evaluation of the application effect and consideration of the production cost and other factors.
生态修复 / 苏云金芽孢杆菌 / 发酵条件优化 / Box-Behnken设计
ecological restoration / Bacillus thuringiensis / fermentation process optimization / Box-Behnken design
| [1] |
关军洪, 郝培尧, 董丽, 等. 矿山废弃地生态修复研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2017, 36(2):193-200.
|
| [2] |
许晓明, 胡国峰, 邵雁, 等. 我国矿山生态修复发展状况及趋势分析[J]. 矿产勘查, 2022, 13(S1):309-314.
|
| [3] |
李海东, 沈渭寿, 贾明, 等. 大型露天矿山生态破坏与环境污染损失的评估[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(6):112-118.
|
| [4] |
周跃,
|
| [5] |
谢建华. 废弃采石场石质边坡植被重建与关键技术试验研究[J]. 亚热带水土保持, 2018, 30(3):11-13,70.
|
| [6] |
孙其河. 高陡石质边坡植被修复技术应用与效益评价[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
王世杰, 季宏兵, 欧阳自远, 等. 碳酸盐岩风化成土作用的初步研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 1999, 29(5):441-449.
|
| [10] |
李国保, 王秀英. 客土喷播技术在水库坝肩石质边坡处理中的应用[J]. 低碳世界, 2019, 9(7):69-70.
|
| [11] |
王广林, 黄玲玲, 张明, 等. 基于菌土技术的温湿地区困难立地快速绿化法[J]. 安徽林业科技, 2016, 42(3):7-9.
|
| [12] |
郎煜华. 土壤菌绿化法与普通喷播绿化的对比试验研究[C]// 第二届全国水土保持生态修复学术研讨会论文集.贵阳, 2010:211-237.
|
| [13] |
姚正学, 杨军. 岩石坡面土壤菌永久绿化法原理[J]. 甘肃科学学报, 2005, 17(4):37-39.
|
| [14] |
郎煜华, 邱茂国. 喷播绿化工程的失败经验与对策[J]. 建筑, 2011(17):73-74.
|
| [15] |
张金池, 王广林, 张波, 等. 一种石灰岩高效侵蚀细菌苏云金芽孢杆菌NL-11及其应用:CN103087954A[P]. 2013-05-08.
|
| [16] |
关雄. 苏云金芽孢杆菌研究回顾与展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2006, 8(6):5-11.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
杨静, 高泽鑫, 朱莉, 等. 产胞外多糖的苏云金芽孢杆菌的筛选及发酵工艺优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(24):124-131.
|
| [20] |
宋健, 张海剑, 丰硕, 等. 对韭菜迟眼蕈蚊高活性的苏云金芽胞杆菌JQD117发酵培养基及摇瓶发酵条件优化[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2022, 38(2):333-341.
|
| [21] |
闫洪雪, 刘露, 李丽, 等. 一株苏云金杆菌Bt02发酵条件的优化研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2015(23):127-128,130.
|
| [22] |
张路路, 朱朝华, 郭刚. 苏云金芽孢杆菌A322菌株发酵培养基和发酵条件的优化[J]. 热带生物学报, 2014, 5(3):253-259.
|
| [23] |
申烨华, 孙君, 周茂林, 等. 苏云金芽孢杆菌HD-1发酵工艺研究[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 31(5):396-398.
|
| [24] |
梁艳琼, 黄兴, 吴伟怀, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌TWC2发酵条件的优化[J]. 中国糖料, 2017, 39(6):17-22.
|
| [25] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [26] |
马欣娟, 吕慧威, 孙玉梅. 接种量对草莓酒发酵特性的影响[J]. 中国酿造, 2019, 38(5):123-126.
|
| [27] |
闫建芳, 赵柏霞, 刘秋, 等. 链霉菌组合ST-2发酵条件优化及对黄瓜枯萎病的防治效果[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2016, 32(4):531-538.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
张金池, 王广林, 庄家尧, 等. 一种石灰岩高效侵蚀细菌巨大芽孢杆菌NL-7及其应用:CN103087953A[P]. 2013-05-08.
|
| [35] |
张金池, 王广林, 王丽, 等. 一种石灰岩高效侵蚀放线菌嗜热一氧化碳链霉菌NL-1及其应用:CN103103151A[P]. 2013-05-15.
|
| [36] |
王广林, 张金池, 林杰, 等. 一种石灰岩高效侵蚀真菌卵形孢球托霉NL-15及其应用:CN103087926A[P]. 2013-05-08.
|
| [37] |
李莉, 张赛, 何强, 等. 响应面法在试验设计与优化中的应用[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2015, 34(8):41-45.
|
| [38] |
杨津, 杨霰霜, 段中余, 等. 化学试验设计及优化方法的发展与应用[J]. 广东化工, 2010, 37(10):67-68.
|
| [39] |
范玲, 王鑫, 胡风华, 等. 正交试验与响应面法优选六月雪-葎草药对提取工艺比较[J]. 中国药业, 2021, 30(10):40-44.
|
| [40] |
王瑞君, 袁欣. 响应面法优化产木聚糖酶耐热菌株的发酵条件[J]. 宜春学院学报, 2022, 44(3):83-89.
|
| [41] |
袁辉林, 康丽华, 马海滨. 响应曲面法及其在微生物发酵工艺优化中的应用[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(16):9498-9500,9502.
|
| [42] |
田泱源, 李瑞芳. 响应面法在生物过程优化中的应用[J]. 食品工程, 2010(2):8-11,53.
|
| [43] |
石子林, 李军乔, 王雅琼, 等. 密花香薷总皂苷提取工艺优化及其生物活性[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2021, 37 (1): 185-191.
|
| [44] |
白云洲, 赵前程, 吕东, 等. 纳豆芽孢杆菌发酵海参条件的响应面优化[J]. 农产品加工, 2022(5):7-11,15.
|
| [45] |
徐宇飞, 张晓敏, 朱佳美, 等. 具有杀线虫活性的郭霍氏芽孢杆菌发酵条件优化及稳定性评价[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(7):2612-2624.
|
| [46] |
孙承文, 赖迎迢, 巩华, 等. 基于响应面法的维氏气单胞菌灭活疫苗菌液发酵工艺优化及免疫效力比较[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2021, 36(4):546-553.
|
| [47] |
樊丹, 邓福容, 李绍戊, 等. 一株虹鳟源枯草芽孢杆菌产胞外蛋白发酵条件优化[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2022, 44(2):452-460.
|
| [48] |
白长胜. 禽用乳酸菌SR1发酵条件优化[J]. 发酵科技通讯, 2022, 51(1):15-18.
|
| [49] |
白雪, 李运杰, 孟冬冬, 等. 解纤维素热酸菌来源的耐热磷酸酶的酶学性质与应用[J]. 生物加工过程, 2021, 19(2):123-129.
|
| [50] |
王金萍. 肥料配施对微生物及土壤养分的影响研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2014.
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
王琦. 一株耐盐促生菌对植物的促生机制探讨[J]. 长治学院学报, 2021, 38(2):47-51.
|
| [60] |
王鹰翔. 不同土壤菌配置对紫穗槐幼苗生理生态学特性的影响[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2017.
|
| [61] |
王鹰翔, 张金池, 吴雁雯, 等. 喷播基质中土壤菌施用对紫穗槐幼苗光合特性和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(6):902-910.
|
| [62] |
刘晶晶, 孙合美, 岳胜天, 等. 不同溶磷菌菌液对盛花期大豆生长的影响[J]. 大豆科学, 2016, 35(2):275-279.
|
| [63] |
蒋晓玲. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌Y19微生物菌肥的研制及其生物效益研究[D]. 昆明: 云南农业大学, 2015.
|
| [64] |
占新华, 蒋延惠, 徐阳春, 等. 微生物制剂促进植物生长机理的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1999, 5(2):97-105.
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |