 PDF(2523 KB)
PDF(2523 KB)


转BpGLK白桦土壤酶活及根际土壤细菌、真菌群落组成分析
曹俐, 金冬雪, 姜静, 李天芳
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6) : 129-137.
 PDF(2523 KB)
PDF(2523 KB)
 PDF(2523 KB)
PDF(2523 KB)
转BpGLK白桦土壤酶活及根际土壤细菌、真菌群落组成分析
Analysis of bacterial and fungal community composition and soil enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of transgenic Betula platyphylla
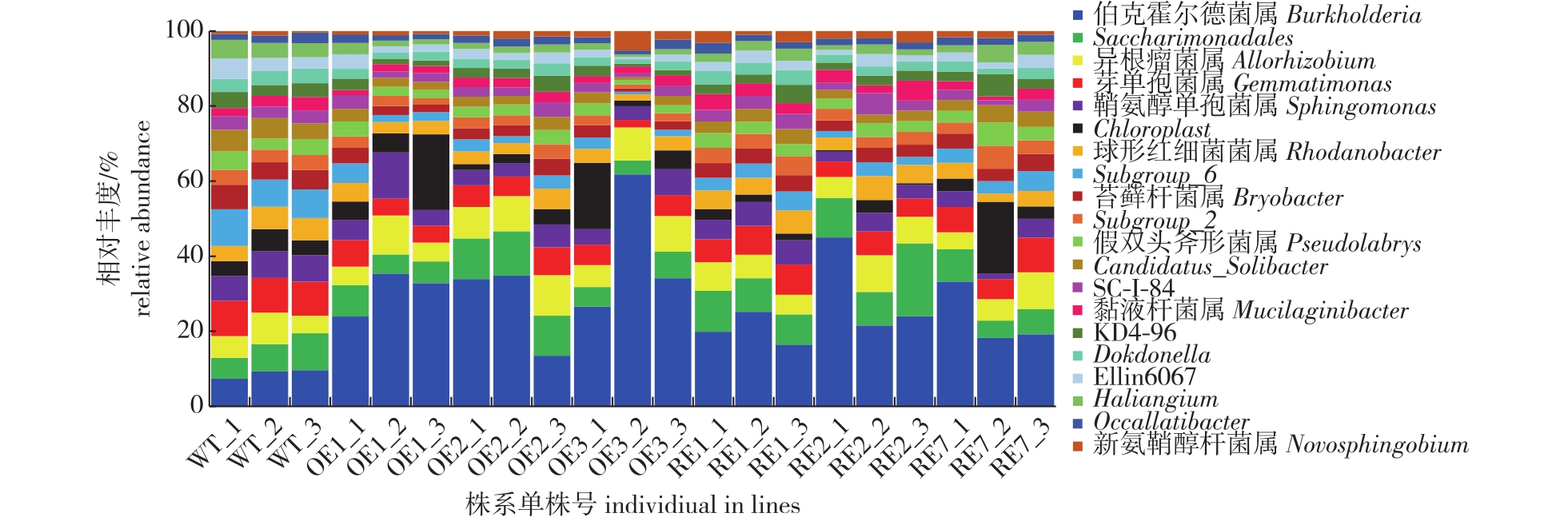
【目的】白桦(Betula platyphylla)BpGLK转录因子参与调控叶绿体发育及叶色,BpGLK抑制表达白桦在生长期内叶色呈黄绿色,在园林绿化中极具观赏价值。但作为转基因植物,大面积的推广应用是否会对环境产生不利影响引起研究者的重视。研究转BpGLK白桦对土壤酶活及根际土壤细菌、真菌群落组成的影响,为后续环境释放及商业化应用提供理论依据。【方法】以3年生转BpGLK白桦(OE株系及RE株系)及对照野生型(WT)白桦为材料,采用分光光度法测定土壤蔗糖酶、脲酶、中性蛋白酶、过氧化氢酶及纤维素酶的活性,利用 Illumina-Miseq 高通量测序平台对根际土壤微生物进行 16S rRNA 和 ITS 测序分析,对根际土壤细菌和真菌群落丰富度和多样性变化、结构差异性、群落组成进行分析,了解转基因活动对白桦土壤酶活性及根际土壤微生物组成的影响。【结果】在测定的4个时间点(6月15日、7月15日、8月15日和9月15日)转BpGLK白桦与WT株系的土壤脲酶、蔗糖酶、纤维素酶、中性蛋白酶活性均存在显著差异(P<0.05),而过氧化氢酶活性则呈现WT株系与部分转基因株系间存在显著差异,土壤脲酶和纤维素酶活性在8月中旬和9月中旬明显降低,而土壤中性蛋白酶活性在9月中旬明显升高,OE株系的土壤中性蛋白酶活性在4个时期均高于或显著高于WT株系(P<0.05)。根际土壤细菌群落属水平上,具有促生功能的伯克霍尔德菌属(Burkholderia)是转基因株系与WT株系的优势菌,该菌属在转基因株系根际土壤中的相对丰度显著提高;在根际真菌群落属水平上,棉革菌属(Tomentella)是转基因RE株系根际的优势类群,锁瑚菌属(Clavulina)是WT及转基因OE株系根际的优势类群,蜡蘑菌属(Laccaria)的相对丰度在OE株系和RE株系中显著降低(P<0.05);Alpha多样性分析显示,在细菌群落组成方面,转基因白桦的可观测物种数(observed species)、Chao1、香农(Shannon)及辛普森(Simpson)指数与WT株系间未达到显著差异;在真菌群落组成方面,RE株系的群落丰度、多样性均显著高于或高于WT株系,而OE与WT株系间差异未达到显著水平。韦恩图结果显示,转基因株系与野生型株系间的特征序列(ASV)差异显著;主成分分析结果显示,在细菌群落组成上,RE与WT株系的群落组成差异较小,而OE与WT株系差异相对较大;在真菌群落组成上,OE与WT株系的群落组成差异较小,而RE与WT株系差异相对较大。【结论】目标BpGLK基因的导入对白桦根际细菌、真菌群落丰度及多样性产生一定影响,并可能利于植物生长并提升自身抗逆性,但这种影响是否长期存在仍需后续试验验证。
【Objective】The BpGLK transcription factor of Betula platyphylla is involved in regulating chloroplast development and leaf color. The leaf color of B. platyphylla with inhibited BpGLK expression is yellow-green during the growth period, which holds great ornamental value in landscaping. However, as a genetically modified crop, concerns exist regarding the potential adverse environmental effects of widespread use. This study aims to examine the impact of transgenic BpGLK B. platyphylla on soil enzyme activity and the composition of rhizosphere soil bacterial and fungal communities, providing theoretical data for future environmental release and commercialization.【Method】Three-year-old transgenic B. platyphylla (OE and RE strains) and wild-type (WT) B. platyphylla are used as materials. Soil sucrase, urease, neutral protease, catalase, and cellulase activities were measured using the spectrophotometric method. In addition, 16S rRNA and ITS sequencing analyses of rhizosphere soil microorganisms were conducted using the Illumina-Miseq high-throughput sequencing platform. The richness and diversity of bacterial and fungal communities, structural differences, and community composition in rhizosphere soil were analyzed to understand the effects of transgenic activity on soil enzyme activity and microbial composition in the rhizosphere soil of B. platyphylla.【Result】Significant differences (P < 0.05) are observed in soil urease, sucrase, cellulase and neutral protease activities between BpGLK-transformed B. platyphylla and WT strains at four time points (June 15, July 15, August 15 and September 15). However, catalase activity showed significant differences between WT and some transgenic strains. Soil urease and cellulase activities decrease significantly in mid-August and mid-September. The activity of soil neutral protease in OE strains was higher than that of the WT strain at all four periods (P < 0.05). At the rhizosphere bacterial community level, Burkholderia, a growth-promoting function, was the dominant genus in transgenic and WT strains. The relative abundance of Burkholderia in the rhizosphere soil of transgenic strains significantly increased. At the rhizosphere fungal community level, Tomentella dominated the rhizosphere of transgenic RE strains, while Clavulina dominated the rhizosphere of WT and OE strains. The relative abundance of Laccaria was significantly lower in OE and RE strains (P < 0.05). The Observed, Chao1, Shannon and Simpson indices of transgenic B. platyphylla did not differ significantly from those of WT strains, while the community abundance and diversity of RE strains were significantly higher than those of WT strains. The difference between OE and WT strains was not significant. Venn diagram analysis revealed significant differences in ASV composition between transgenic and WT strains. In contrast, principal component analysis showed slight differences in community composition between RE and WT strains, while the difference between OE and WT strains was relatively larger. However, the difference between OE and WT strains remainsed smaller than that between RE and WT strains.【Conclusion】The results indicated that the introduction of the exogenous BpGLK gene had a specific effect on the abundance and diversity of rhizosphere bacterial and fungal communities in B. platyphylla. These changes can promote plant growth and enhance resistance. However, whether these effects persist over the long term remains to be confirmed in future experiments.
白桦 / 转基因 / 土壤酶活性 / 根际 / 细菌 / 真菌 / 群落组成
birch(Betula platyphylla) / transgenic / soil enzyme activities / rhizosphere / bacteria / fungi / community composition
| [1] |
李天芳, 姜静, 杨传平, 等. 我国白桦育种研究概况[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2008, 35(2):47-49.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
陆雅海, 张福锁. 根际微生物研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2006, 38(2):113-121.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
侯英杰, 苏晓华, 焦如珍, 等. 转基因银腺杂种杨对土壤微生物的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(5):148-153.
|
| [12] |
吕秀华. 转基因银中杨ABJ系列对土壤微生物类群的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2017, 36(5):1991-1996.
|
| [13] |
吕秀华. 转基因银中杨对根际土壤微生物的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2018, 37(5):1965-1970.
|
| [14] |
孙伟博, 魏朝琼, 马晓星, 等. 3类转基因南林895杨田间试验的安全性评估[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(10):53-62.
|
| [15] |
周培军, 李玲玲, 李红岩, 等. 转Bt基因‘南林895’杨时空表达及生物安全分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(5):1568-1580.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
王阳, 王伟, 姜静, 等. 转基因小黑杨根际土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(1):199-208.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
戴伟, 白红英. 土壤过氧化氢酶活度及其动力学特征与土壤性质的关系[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 1995, 17(1):37-41.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
林天, 何园球, 李成亮, 等. 红壤旱地中土壤酶对长期施肥的响应[J]. 土壤学报, 2005, 42(4):682-686.
|
| [22] |
杨宁, 杨满元, 雷玉兰, 等. 衡阳紫色土丘陵坡地土壤酶活性对植被恢复的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(4):575-580.
|
| [23] |
俞元春, 冷春龙, 舒洪岚, 等. 转基因抗虫棉对土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(5):21-24.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
冯翠莲, 万玥, 赵婷婷, 等. 抗虫转基因甘蔗对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 热带生物学报, 2020, 11(1):1-6.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
张珂飞, 钟永嘉, 孙丽莉, 等. 植物有益伯克霍尔德氏菌的研究进展及其在农业中的应用[J]. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(8):2205-2218.
|
| [32] |
刘佳琦, 宋逸欣, 成星川, 等. 转BpGLK1基因白桦叶色变异规律及生长特性分析[J]. 江西农业学报, 2021, 33(8):17-23.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
魏松坡, 宋怡静, 贾黎明, 等. 太行山片麻岩区栓皮栎外生菌根真菌多样性[J]. 菌物学报, 2018, 37(4):422-433.
|
| [41] |
杨岳, 闫伟, 魏杰. 黑里河和贺兰山自然保护区华北落叶松根区土壤中外生菌根真菌群落[J]. 菌物学报, 2019, 38(1):48-63.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
木兰. 白音敖包国家级自然保护区大型真菌资源调查兼中国蜡蘑属的分类学研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2015.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |