 PDF(3727 KB)
PDF(3727 KB)


 PDF(3727 KB)
PDF(3727 KB)
 PDF(3727 KB)
PDF(3727 KB)
基于生态空间识别的江苏省域自然风景体系构建
Construction of natural landscape system in Jiangsu Province based on spatial distribution characteristics and ecological space identification
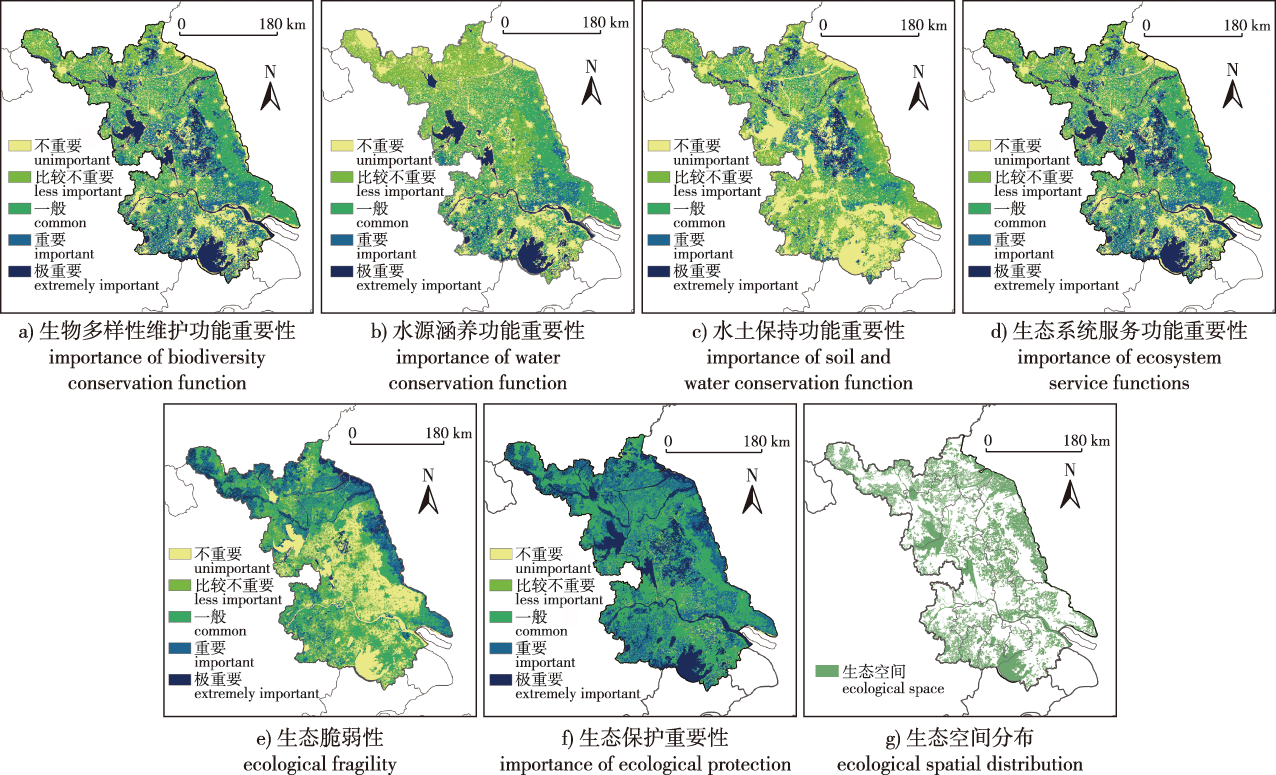
【目的】为了全面保护、合理开发和有效利用自然风景资源,缓解江苏省自然资源景观破碎化、孤岛化严重及资源分布不均衡的状况。【方法】运用ArcGIS平台空间分析技术,包括最邻近指数、核密度分析和可达性分析,揭示江苏省自然风景资源保护地的空间分布特征。结合国土空间规划下“双评价”依据,针对江苏省自然环境状况进行了以生态系统服务功能重要性评价和生态脆弱性评价为主导的生态保护重要性评价,根据评价的结果识别了江苏省的生态空间,将以上结果与江苏省相应的自然地理表征和人文地理表征等进行叠加分析。【结果】明确了江苏省自然风景资源保护地的分布规律和区域差异性,为自然风景斑块、廊道、优势区域的选择提供了现实依据。确定出江苏省9处自然风景斑块、7条自然风景廊道和2个自然风景优势区域,共同组成了以自然风景资源保护地为依托,以斑块、廊道、基质为主导的江苏省自然风景体系。【结论】该风景体系通过量化的方式,考虑江苏省自然地理特征,将空间概念运用到风景资源的研究中,有助于加强自然风景资源保护地之间的联系,优化资源整合,营造更适合江苏省自然风景资源保护地保护和发展的景观格局,实现对江苏省自然风景资源保护地建设的有效引导,并为其合理开发和利用提供科学依据。
【Objective】 This study aims to comprehensively protect, rationally develop as well as effectively utilize natural scenic resources and alleviate the fragmentation, islanding and uneven distribution of natural resource landscapes in Jiangsu Province.【Method】 Using ArcGIS spatial analysis technology, the spatial distribution characteristics of natural landscape resources in Jiangsu Province were obtained from the Nearest Neighbor Index (NNI) and results of the kernel density analysis and accessibility analysis. Also, based on the double evaluation' of the land and space planning and the natural environment of Jiangsu Province, an ecological protection evaluation, including evaluations of the ecosystem services and ecological sensitivity, was conducted. Based on the evaluation results, the ecological space of Jiangsu Province was delineated. The above results are superimposed with the corresponding physical and human geographical characterizations of Jiangsu Province. 【Result】 The distribution and regional differences of protected areas of natural landscape resources in Jiangsu Province were revealed, which provided a realistic basis for the selection of natural landscape patches, corridors and advantageous regions. Nine natural landscape patches, seven natural landscape corridors and two natural landscape dominant areas in Jiangsu Province were delineated. Also, a natural landscape system in Jiangsu Province was formed based on natural landscape resources dominated by patches, corridors and substrates. 【Conclusion】 The landscape system applied the spatial concept to the study of landscape resources. This approach helps to strengthen the connection between protected areas of natural landscape resources, improve the integration and optimization of resources, create a landscape pattern more suitable for the protection and development of natural landscape resources in Jiangsu Province, and provide effective guidance for the protection and construction of natural landscape resources in Jiangsu Province and a scientific basis for reasonable development and utilization.
自然风景资源保护地 / 空间分布特征 / 生态空间识别 / 自然风景体系 / 江苏省
protected area of natural landscape resources / spatial distribution characteristics / ecological space identification / natural landscape system / Jiangsu Province
| [1] |
屈茂辉, 唐莉. 自然风景资源管理机构法人化研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(社会科学版), 2017, 31(6):139-145.
|
| [2] |
战明松, 朱京海. 基于POI数据的特大城市生态空间廊道识别与空间布局优化研究:以沈阳市中心城区为例[J]. 中国园林, 2021, 37(10):112-117.
|
| [3] |
钟静玲, 李果, 胡文敏, 等. 风景资源整合视角下环洞庭湖区风景道体系构建[J]. 长沙大学学报, 2020, 34(2):129-135.
|
| [4] |
程茂吉, 陶修华, 张彦. 生态空间的系统化构建和差异化管控研究[J]. 规划师, 2020, 36(2):48-53.
|
| [5] |
赵毓芳, 祁帆, 邓红蒂. 生态空间用途管制的八大特征变化[J]. 中国土地, 2019(5):12-15.
|
| [6] |
王李睿, 邓西鹏, 王晨, 等. 基于生态系统服务重要性与生态敏感性的生态空间划设:以福建省永春县为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(1):166-173.
|
| [7] |
彭震伟, 高璟. 国土空间规划体系下生态敏感地区的乡村空间规划:以长白县为例[J]. 规划师, 2021, 37(3):58-63.
|
| [8] |
马明, 顾康康, 李咏. 基于生态安全格局的城乡生态空间布局与优化:以宣城市为例[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2019, 40(4):93-102.
|
| [9] |
颜文涛, 陈卉, 万山霖, 等. 省级次区域国土生态空间格局构建与管控政策:以川西北生态示范区为例[J]. 上海城市规划, 2021, 3(3):8-17.
|
| [10] |
王云才, 王琼萱. 城景融合的新城景观生态网络规划:以河南省汤阴县绿色生态新城为例[J]. 城市建筑, 2017(36):6-9.
|
| [11] |
段诗乐, 林箐. 城景互融:银川传统区域风景系统[J]. 中国园林, 2022, 38(1):38-43.
|
| [12] |
王越, 仝晖. 鲁运河影响下济宁古城风景体系特征解析[J]. 中国园林, 2021, 37(1):62-67.
|
| [13] |
张雪葳, 王向荣. 与天地参,居山水间:福州山水风景体系研究[J]. 风景园林, 2018, 25(9):34-39.
|
| [14] |
郝庆, 封志明, 袁国华. 省级国土空间规划编制的几点思考[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2018, 31(1):29-33.
|
| [15] |
唐晓岚, 夏茹雪, 胡刚, 等. 江苏省国家级风景名胜区游客感知形象:基于在线点评的内容分析[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2020(3):74-81.
|
| [16] |
申怀飞, 郑敬刚, 唐风沛, 等. 河南省A级旅游景区空间分布特征分析[J]. 经济地理, 2013, 33(2):179-183.
|
| [17] |
张晨钰, 王伟, 黄莉, 等. 高度城镇化背景下深圳市易涝点驱动因子分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2024, 40(2):35-45.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
李山, 王铮, 钟章奇. 旅游空间相互作用的引力模型及其应用[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(4):526-544.
|
| [20] |
马琪, 潘秋玲, 涂纯. 生物多样性维护功能评估及其空间尺度效应分析:以陕西省为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(8):1937-1948.
|
| [21] |
李露露, 曹玉红, 刘崇刚, 等. 基于MCR模型的皖江城市带建设用地适宜性评价[J]. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(3):280-286.
|
| [22] |
徐华连, 高伟龙, 陈思, 等. 基于GIS的苏南地区城市生态空间划定:以苏州市为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(2):614-624.
|
| [23] |
黄心怡, 赵小敏, 郭熙, 等. 基于生态系统服务功能和生态敏感性的自然生态空间管制分区研究[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(3):1065-1076.
|
| [24] |
刘思源, 唐晓岚, 孙彦斐, 等. 基于生态敏感性评价及景观格局分析的国家公园风景资源保育研究——以湖北神农架国家公园为例[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2021, 40(1):161-167.
|
| [25] |
颜磊, 许学工, 谢正磊, 等. 北京市域生态敏感性综合评价[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(6):3117-3125.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
马骏, 李昌晓, 魏虹, 等. 三峡库区生态脆弱性评价[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(21):7117-7129.
|
| [28] |
王丽霞, 邹长新, 王燕, 等. 基于GIS识别生态保护红线边界的方法:以北京市昌平区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(18):6176-6185.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |