 PDF(3606 KB)
PDF(3606 KB)


 PDF(3606 KB)
PDF(3606 KB)
 PDF(3606 KB)
PDF(3606 KB)
城市绿地系统进化特征及驱动机制分析——以河南省许昌市为例
The evolution and driving mechanism of urban green space system: a case study of Xuchang City, Henan Province, China
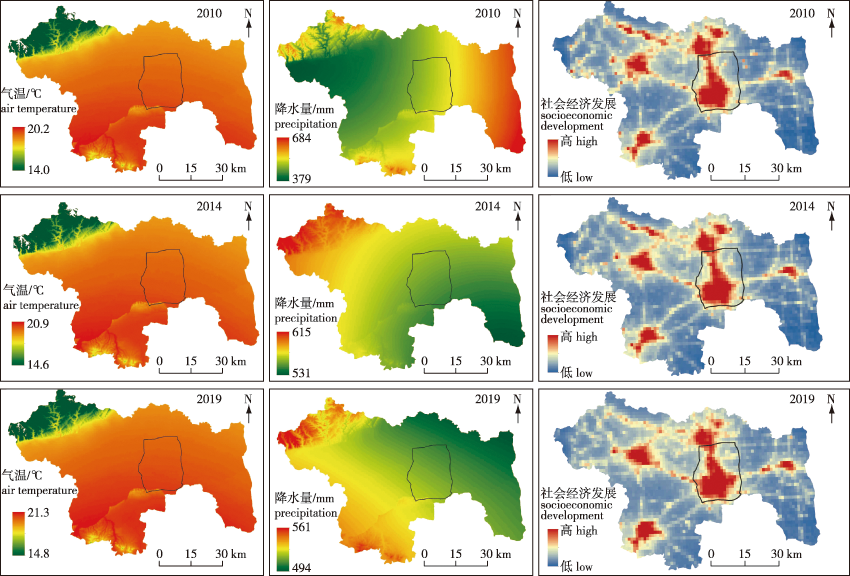
【目的】 基于资源约束趋紧、用地集约发展的现状,分析城市绿地系统的生态、社会和经济功能,探讨其进化特征及深层驱动机制,为城市用地的高效配置、城市建设的决策支持提供依据。【方法】 选择河南省许昌市为研究对象,以2010、2014、2019年为研究时间节点,采用回溯法镶嵌土地利用模拟模型,结合随机森林(RF)回归从政策因素、自然因素、社会经济因素等方面解析城市绿地系统进化的驱动机制。【结果】 ①2010—2019年,许昌市城市绿地系统的空间进化趋势与城市规划政策的引导基本保持一致,主要向东北和北方向发展。②规划政策对于城市绿地系统的影响机制可能是积极的保护,也可能是消极的侵蚀;基于未来土地利用变化模拟模型,可反馈规划政策的作用机制,并建立政策失效的分析框架。③社会经济因素对乡镇级别城市绿地系统的面积变化和景观格局指数变化影响较为显著,自然因素的影响较小,尤其对位于平原地区的许昌市而言,地形的影响最微弱;景观格局指数斑块密度(PD)能较好反映城市绿地景观格局与各驱动因素之间的相关性。【结论】 规划政策因素为城市绿地系统进化的导向驱动,社会经济因素为城市绿地系统进化的直接驱动,而自然环境因素的驱动作用相对较弱;城市绿地系统进化驱动机制的探讨是增强新国土空间规划体系下城市绿地系统专项规划科学性、前瞻性的必要途径。
【Objective】 Owing to tighter resource constraints and intensive land development, we analyzed the ecological, social, and economic functions of urban green space system (UGSS), and determined its evolutionary characteristics and driving mechanism. To provide a basis for efficient urban land allocation and decision-making support for urban construction. 【Method】 Xuchang City (Henan Province) was selected as a case study, using time nodes data from 2010, 2014 and 2019. We applied the backtracking method with a land use simulation model and random forest regression; driving factors such as policy, natural and socioeconomic factors were analyzed. 【Result】 (1) From 2010 to 2019, Xuchang’s UGSS developed from the northeast and north, which was consistent with the guidance of urban planning policies. (2) The impact of planning policy on UGSS could either be positive protection or negative erosion. The GeoSOS-FLUS model and the backtracking method could simulate the changes in the UGSS, which could then be used to determine the impacts of the planning policy and establish an analytical framework for policy failure. (3) Socioeconomic factors had a significant impact on changes in the areas of township-level UGSS and the landscape pattern index, whereas natural factors had lower impacts. In Xuchang, which located on a plain, topography, had the smallest impact on changes in UGSS. The patch density changes in the UGSS had a high goodness of fit with each driving factor, which reflects the correlations between the UGSS landscape pattern and its driving factors. 【Conclusion】 Planning policy is the guiding driver of changes in UGSS, whereas socioeconomic factors directly drive changes in UGSS and natural factors have relatively little impact. Determining the evolution law of UGSS is necessary for enhancing scientific and forward-looking planning for UGSS under the new territorial spatial planning system.
城市绿地系统 / 进化特征 / 驱动机制 / 社会经济因素 / 政策因素 / 许昌市
urban green space system / evolution characteristics / driving mechanism / socioeconomic factors / policy factors / Xuchang City, Henan Province
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
王如松, 欧阳志云. 社会-经济-自然复合生态系统与可持续发展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2012, 27(3):337-345,403.
|
| [4] |
张浪, 王浩. 城市绿地系统有机进化的机制研究:以上海为例[J]. 中国园林, 2008, 24(3):82-86.
|
| [5] |
张浪. 城市生态网络规划原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.
|
| [6] |
金云峰, 杨玉鹏, 王俊祺, 等. 《城市绿地规划标准》实施背景下上海市域绿地系统自组织演化动力机制研究[J]. 中国城市林业, 2019, 17(4):31-36.
|
| [7] |
张浪. 上海绿地系统进化的作用机制和过程[J]. 中国园林, 2012, 28(11):74-77.
|
| [8] |
张浪. 试论城市绿地系统有机进化论[J]. 中国园林, 2008, 24(1):87-90.
|
| [9] |
李方正, 解爽, 李雄. 基于PLSR模型的北京市中心城绿色空间演变驱动机制研究(1992—2016年)[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(4):116-126.
|
| [10] |
宋爽, 石梦溪, 胡珊珊, 等. 东北地区中心城市城区蓝绿空间演化及驱动机制研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(4):221-229.
|
| [11] |
尹上岗, 杨山. 长三角地区城市人口-绿地面积异速增长特征及驱动机制[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(10):2780-2795.
|
| [12] |
戴菲, 毕世波, 陈明, 等. 基于MSPA与混淆矩阵的绿地系统格局演化及其驱动因子研究:以伦敦为例[J]. 中国园林, 2020, 36(11):34-39.
|
| [13] |
史利江, 王圣云, 姚晓军, 等. 1994—2006年上海市土地利用时空变化特征及驱动力分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2012, 21(12):1468-1479.
|
| [14] |
罗文斌, 楚雪莲, 唐沛, 等. 城市公园用地增长的时空分异及其驱动因素:基于湖南省城市面板数据的实证分析[J]. 经济地理, 2021, 41(12):74-83.
|
| [15] |
唐明贵, 胡静, 吕丽, 等. 贵州省生态游憩空间时空演化特征及其驱动因素[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(21):8594-8604.
|
| [16] |
刘志强, 徐影秋, 洪亘伟, 等. 中国城区公园绿地面积与人口数量、建设用地面积演变的脱钩关系研究[J]. 中国园林, 2021, 37(2):54-59.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
许昌市人民政府. 许昌市“十四五”国土空间生态修复和森林许昌建设规划[Z]. 许昌: 许昌市人民政府, 2023-03-22.
|
| [24] |
柴子为, 王帅磊, 乔纪纲. 基于夜间灯光数据的珠三角地区镇级GDP估算[J]. 热带地理, 2015, 35(3):379-385.
|
| [25] |
郑渊茂, 何原荣, 王晓荣, 等. 夜光遥感数据应用述评与展望[J]. 遥感信息, 2020, 35(3):1-14.
|
| [26] |
郭伟. 夜间灯光数据和MODIS数据用于大尺度不透水面制图研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2015.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
| [29] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |