 PDF(2573 KB)
PDF(2573 KB)


雅长保护区老龄林不同林层功能性状多样性及其影响因素分析
王耀仪, 王宏翔, 王永强, 曾文豪, 叶绍明
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 28-38.
 PDF(2573 KB)
PDF(2573 KB)
 PDF(2573 KB)
PDF(2573 KB)
雅长保护区老龄林不同林层功能性状多样性及其影响因素分析
Affecting factors analysis of functional diversity at different forest strata in an old growth forest community in Yachang Natural Reserve
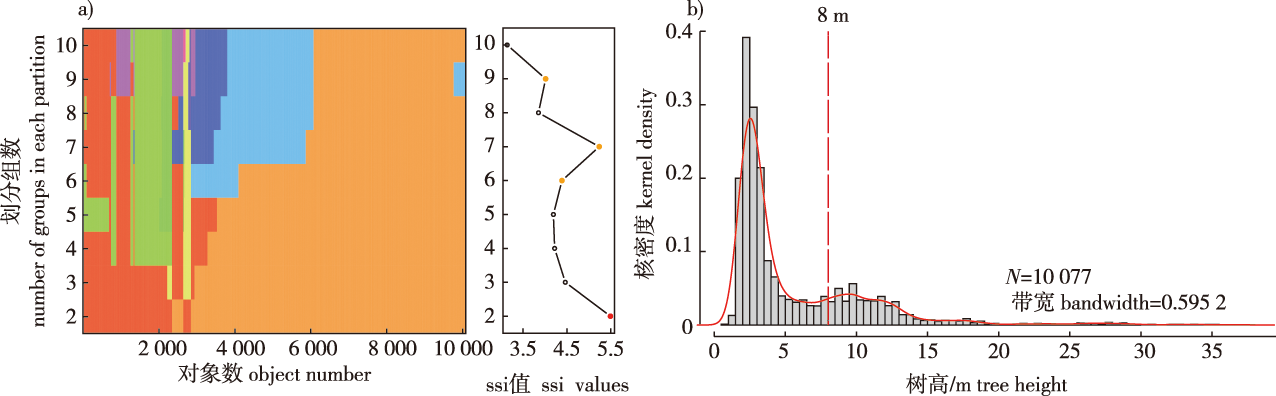
【目的】功能性状多样性对森林生物多样性保护及生态系统功能稳定性的维持具有重要意义。探究不同林层的功能多样性特征及其形成原因,有助于深入理解生物多样性维持机制和植物群落构建过程。【方法】以广西雅长兰科植物国家级自然保护区1.6 hm2常绿阔叶天然老龄林监测样地植被调查数据为基础,运用K-means非层次聚类与高斯核密度估计方法划分林层,采集植物叶片性状和环境因子数据,通过结构方程模型揭示不同林层物种多样性与环境因子(地形、土壤和光照)对功能多样性的直接、间接影响。【结果】①林下层多样性指数显著高于林冠层(P<0.05)。②林下层物种多样性对4个功能多样性指数均有显著的直接影响,而林冠层物种多样性仅对功能丰富度指数(FRic)与功能二次熵指数(RAOQ)有显著的直接影响(P<0.05)。③林冠开度对林下层FRic指数有极显著的间接效应(β= 0.278,P<0.01),对林下层功能均匀度指数(FEve)有极显著的直接效应(β= -0.593,P<0.01)。④地形因子主要影响林冠层功能多样性。其中,坡向对林冠层FEve指数(β= -0.420,P<0.01)与RAOQ指数(β= -0.300,P<0.05)均有显著的直接效应。⑤土壤因子主要通过物种多样性间接影响各林层的功能多样性。其中,林下层功能多样性主要受全磷、有效磷、碱解氮、有效钾含量的影响,而全钾含量对林冠层FRic与RAOQ指数有一定的影响。【结论】研究区内各林层功能多样性存在较大差异。林下层功能多样性主要受物种多样性、林冠开度和土壤养分的影响,而地形因子则是林冠层功能多样性的主要影响因素。本研究结果揭示了不同林层内功能性状多样性对生物及非生物环境变化的响应,拓展了以往对于林分垂直分层多样性的认识,为天然林生物多样性保护提供更进一步的参考依据。
【Objective】 Functional diversity is crucial for forest biodiversity protection and maintenance of ecosystem stability. Exploring the characteristics and causes of functional diversity variation at different stratum levels will assist in understanding the maintenance mechanisms of biodiversity and plant community assembly processes. 【Method】 Leaf traits and environmental factors were collected from forest plot data from an 1.6 hm2 evergreen broadleaved forest in Guangxi Yachang Orchidaceae National Natural Reserve. K-means partitioning and Gaussian kernel density estimation were used for stratification. The direct and indirect effects of species diversity and environmental factors (light, topography, and soil) on functional diversity were explored in different forest strata using structural equation models. 【Result】 The diversity indices of the understory were greater than those of the canopy (P<0.05). Species diversity had a significant direct impact on all four functional diversity indices in the understory layer, whereas only the functional richness index (FRic) and quadratic entropy (RAOQ) indices were affected directly by species diversity in the canopy layer (P<0.05). A significant indirect effect (β = 0.278, P<0.01) of canopy openness on FRic index and a direct effect (β = -0.593, P<0.01) of canopy openness on functional evenness index (FEve) were found for understory trees. Topographic factors affected canopy functional diversity. Specifically, there was a relatively significant direct effect of aspect on FEve (β = -0.420, P<0.01) and RAOQ (β = -0.300, P<0.05) indices for canopy trees. Soil factors mainly affected the functional diversity of different forest layers through species diversity. Soil total phosphorus, available phosphorus, alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen, and available potassium content had a greater effect on the functional diversity of the understory, whereas soil total potassium content affected the FRic and RAOQ indices of the canopy. 【Conclusion】 There were marked differences in the characteristics of functional diversity at different forest stratum in the study area. Functional diversity was mainly affected by species diversity, canopy openness, and soil nutrients of understory plants, whereas topographic factors determined the functional diversity of the canopy layer. This study reveals the effects of biological and abiotic environmental factors on functional diversity across different forest layers and expands the understanding of the diversity of vertical stratification. The findings provide a further reference for biodiversity protection in natural forests.
老龄林 / 林冠层 / 林下层 / 功能性状多样性 / 结构方程模型(SEM)
old-growth forest / canopy / understory / functional diversity / structural equation model (SEM)
| [1] |
马克平. 生物多样性科学的热点问题[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1):1-2.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
何芸雨, 郭水良, 王喆. 植物功能性状权衡关系的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(12):1021-1035.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
韩涛涛, 唐玄, 任海, 等. 群落/生态系统功能多样性研究方法及展望[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(8):3286-3295.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
许驭丹, 董世魁, 李帅, 等. 植物群落构建的生态过滤机制研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(7):2267-2281.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
盘远方, 李娇凤, 姚玉萍, 等. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落植物功能多样性和环境因子与坡向的关联研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11):4484-4492.
|
| [16] |
李杰, 李远发, 陆道调, 等. 南盘江流域松栎混交林的分层多样性特征[J/OL]. 生态学杂志:1-13[2022-06-21].
|
| [17] |
桂旭君, 练琚愉, 张入匀, 等. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直结构及其物种多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6):619-629.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
李艳朋, 倪云龙, 许涵, 等. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林植物功能性状变异与不同垂直层次个体生长的关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9):1186-1197.
|
| [20] |
吴昊, 肖楠楠, 林婷婷. 秦岭松栎林功能多样性与物种多样性和环境异质性的耦合关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(6):1090-1100.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
楼一恺, 范忆, 戴其林, 等. 天目山常绿落叶阔叶林群落垂直结构与群落整体物种多样性的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(21):8568-8577.
|
| [23] |
张田田, 王璇, 任海保, 等. 浙江古田山次生与老龄常绿阔叶林群落特征的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10):1069-1080.
|
| [24] |
李述万. 广西雅长兰科植物国家级自然保护区维管束植物物种多样性研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2017.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
柯娴氡, 贺立静, 苏志尧. 南方4种木本植物相对叶绿素指标及其分布[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2010, 30(8):82-86.
|
| [28] |
熊映杰, 于果, 魏凯璐, 等. 天童山阔叶木本植物叶片大小与叶脉密度及单位叶脉长度细胞壁干质量的关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(2):136-147.
|
| [29] |
鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000:1-336.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
濮毅涵, 徐丹丹, 王浩斌. 基于数码相片的林冠郁闭度提取方法研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(6):153-160.
|
| [32] |
唐丽丽, 陈国平, 冯小梅, 等. 基于系统发育的燕山东麓植物群落的构建机制[J]. 植物研究, 2017, 37(6):807-815.
|
| [33] |
马克平, 刘玉明. 生物群落多样性的测度方法 Ⅰ:α多样性的测度方法(下)[J]. 生物多样性, 1994, 2(4):231-239.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
石亚飞, 石善恒, 黄晓敏. 基于R的结构方程模型在生态学中的应用[J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(5):1015-1023.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
郑芬, 李兆佳, 邱治军, 等. 广东南岭天然常绿阔叶林林下光环境对林下幼树功能性状的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(13):4516-4527.
|
| [46] |
谭一波, 申文辉, 付孜, 等. 环境因子对桂西南蚬木林下植被物种多样性变异的解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(9):970-983.
|
| [47] |
徐耀粘, 刘检明, 万丹, 等. 林冠结构和地形对亚热带常绿落叶阔叶林林下幼苗物种多样性和功能多样性的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 2020, 38(6):733-742.
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
徐武美, 宋彩云, 李巧明. 西双版纳热带季节雨林土壤养分空间异质性对乔木树种多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(23):7756-7762.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |