 PDF(1947 KB)
PDF(1947 KB)


 PDF(1947 KB)
PDF(1947 KB)
 PDF(1947 KB)
PDF(1947 KB)
不同抗螨性板栗差异次生代谢物筛选与分析
Screening and analysis of differential secondary metabolites in Castanea mollissima with different levels of resistance to Oligonychus ununguis
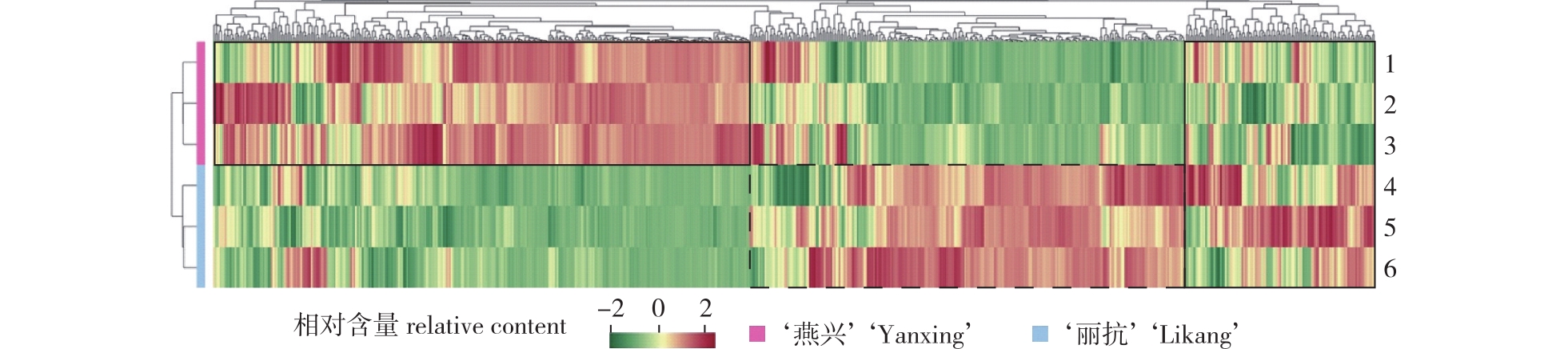
【目的】 筛选分析抗螨性不同的板栗(Castanea mollissima)叶片中的差异次生代谢物,为抗螨机理解析与高抗螨板栗品种选育提供参考。【方法】 以板栗品种‘燕兴’(‘Yanxing’)和‘丽抗’(‘Likang’)为材料,采用田间调查法进行抗螨性鉴定,确定‘燕兴’和‘丽抗’对针叶小爪螨的抗性等级;利用超高效液相色谱和串联质谱(UPLC-MS/MS)进行代谢组学检测,通过差异倍数(fold change)和VIP(variable importance in projection)值相结合的方法筛选差异代谢物,使用R软件ComplexHeatmap包和MetaboAnalystR包分别绘制聚类热图和OPLS-DA得分图;利用KEGG(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)数据库对差异代谢物进行注释,并按通路类型分类。【结果】 ‘丽抗’和‘燕兴’对针叶小爪螨的抗性等级分别为1级(高抗)和7级(感);两品种共检测到704个次生代谢物,筛选出差异代谢物165个,有73个代谢物在 ‘丽抗’中的含量显著高于‘燕兴’,有92个差异代谢物在‘丽抗’中的含量比‘燕兴’低;差异代谢物种类包括酚酸(56个)、黄酮(60个)、木质素和香豆素(19个)、鞣质(4个)、生物碱(5个)、萜类(16个)和其他类(5个),差异代谢物中黄酮和酚酸类占比较高,分别为36%和34%;仅在‘丽抗’中检测到的代谢物有7个,分别是咖啡酰胆、6'-O-反式肉桂酰-8-表金吉苷酸、落叶松脂素-4'-O-葡萄糖苷、阿尔本酚B、地榆素H11、3-羟基-5甲基苯酚-O-葡萄糖苷和苜蓿素-7-O-葡萄糖醛酸苷等;仅存在于‘燕兴’中的代谢物有15个,包括4-甲基-5-噻唑乙醇、2,4-二羟基苯甲酸、异嗪皮啶、水杨苷、刺梨酸等。‘燕兴’和‘丽抗’中有33个差异代谢物被注释到12条通路上。【结论】 感螨品种‘燕兴’和高抗品种‘丽抗’次生代谢谱存在差异,可能与板栗抗螨性相关的次生代谢物有樱黄素、表没食子儿茶素、咖啡酸、阿魏酸、几种木质素以及4-甲基-5-噻唑乙醇;‘燕兴’和‘丽抗’的差异次生代谢物主要注释和富集在黄酮、黄酮醇生物合成及类黄酮生物合成通路。
【Objective】 The differential secondary metabolites in chestnut (Castanea mollissima) leaves with different mite resistance levels were screened to provide a reference for the analysis of the mite(Oligonychus ununguis) resistance mechanism and the breeding of highly mite-resistant chestnut varieties.【Method】 The chestnut varieties ‘Yanxing’ and ‘Likang’ were used to identify and determine the mite resistance levels to O. ununguis with the field investigation method. Metabolomics detection was performed using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry, and the differential metabolites were screened using a combination of fold change and the variable importance in projection value. The R software (ComplexHeatmap and MetaboAnalystR package) was used to draw the clustering heat map and orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis score map. Identified metabolites were annotated using the Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) database, and the annotation results were classified by pathway types.【Result】 The resistance levels of ‘Likang’ and ‘Yanxing’ to O. ununguis were high resistance and susceptible, respectively. A total of 704 secondary metabolites were detected, including 165 differential metabolites. The content of 73 metabolites in ‘Likang’ was significantly higher than in ‘Yanxing’, and the content of 92 metabolites was lower in ‘Likang’ than in ‘Yanxing’. The types of differential metabolites included 56 phenolic acids, 60 flavonoids, 19 lignins and coumarins, four tannins, five alkaloids, 16 terpenoids and five other types. Flavonoids and phenolic acids accounted for 36% and 34%, respectively. Metabolites present only in ‘Likang’ included caffeoylcholine-4-O-glucoside, 3-hydroxy-5-methylphenol-1-O-(6'-galloyl)glucoside, tricin-7-O-glucuronide, 6'-trans-cinnamoyl-8-epikingisidic acid, lariciresinol-4'-O-glucoside, albanol B and sanguiin H11. There were 15 metabolites present only in ‘Yanxing’, including 4-methyl-5-thiazoleethanol, 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, isofraxidin, salicin and roxburic acid. Thirty-three differential metabolites in ‘Yanxing’ and ‘Likang’ were annotated to 12 metabolic pathways.【Conclusion】 The secondary metabolic profiles between the mite-susceptible variety ‘Yanxing’ and the highly resistant variety ‘Likang’ differed. Secondary metabolites that may be related to chestnut mite resistance were prunetin, epigallocatechin, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, several lignans and 4-methyl-5-thiazoleethanol. The differential secondary metabolites were mainly annotated and enriched in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway and the flavone and flavonol biosynthesis pathway.
Castanea mollissima / Oligonychus ununguis / mite resistance / secondary metabolites
| [1] |
温素卿. 燕山地区板栗针叶小爪螨的重发原因分析及综合防治[J]. 河北果树, 2021(2):50-52.
|
| [2] |
张文辉, 刘光杰. 植物抗虫性次生物质的研究概况[J]. 植物学通报, 2003, 20(5):522-530.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
袁平丽, 何楠, 赵胜杰, 等. 籽瓜、黏籽和普通西瓜的果实代谢组比较[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(19):4179-4195.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
王景顺, 吴秋芳, 路志芳. 植物次生代谢物与林木抗虫性研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(8):4-7.
|
| [8] |
轩静渊, 王辅. 植物抗虫性概论[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社,1991.
|
| [9] |
李菁, 骆有庆, 石娟, 等. 利用植物源引诱剂监测与控制舞毒蛾[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2011, 33(4):85-90.
|
| [10] |
左彤彤, 迟德富, 王牧原, 等. 不同品系杨树酚酸类物质对青杨脊虎天牛的驱避作用[J]. 植物保护学报, 2008, 35(2):160-164.
|
| [11] |
杨振德, 赵博光. 苦豆子生物碱对柳蓝叶甲产卵行为的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(1):152-160.
|
| [12] |
栾风福, 刘玉刚, 鲁刚, 等. 板栗新品种丽抗的选育[J]. 中国果树, 2003(4):1-2.
|
| [13] |
张继亮, 马玉敏, 孙海伟, 等. 栗红蜘蛛对板栗不同品种的危害调查[J]. 落叶果树, 2004, 36(5):50-51.
|
| [14] |
雷恒久, 苏淑钗, 张海成. 板栗对板栗红蜘蛛和桃蛀螟的抗性机制初探[J]. 河北林果研究, 2009, 24(1):73-76.
|
| [15] |
刘庆忠, 孙山, 张力思, 等. 板栗种质资源描述规范和数据标准[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006:67-68.
|
| [16] |
焦蕊, 许长新, 于丽辰, 等. 针叶小爪螨的研究进展[J]. 河北农业科学, 2013, 17(1):61-64.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
李树安. 肉香型香料4-甲基-5-噻唑乙醇的合成[J]. 精细化工, 2005, 22(7):521-523.
|
| [23] |
刘玲玲, 武彦文, 袁亚荣, 等. 鸡味脂肪香精的制备、香气成分分析和抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2010, 36(10):107-111.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |