 PDF(1727 KB)
PDF(1727 KB)


 PDF(1727 KB)
PDF(1727 KB)
 PDF(1727 KB)
PDF(1727 KB)
东北地区3个树种不同器官氮磷含量及计量特征
Nitrogen, phosphorus contents and stoichiometric characteristics in different organs of three tree species in northeast China
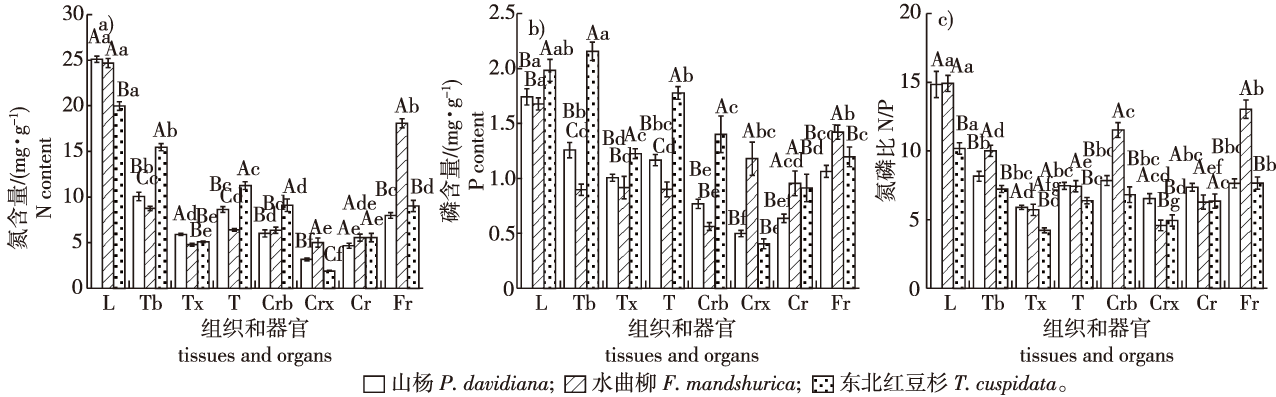
【目的】探究东北地区生态习性各异的山杨(Populus davidiana)、水曲柳(Fraxinus mandshurica)和东北红豆杉(Taxus cuspidata)地上地下器官氮(N)、磷(P)养分分配模式,为深入揭示树种间养分分配策略与权衡关系提供理论参考。【方法】以野外山杨、水曲柳和东北红豆杉成年植株为研究对象,对比分析3个树种地上器官叶片枝条和地下器官粗根细根N、P含量以及叶与枝、根N、P分配比例,采用标准主轴回归斜率检验3个树种地上、地下器官N与P元素之间及地上与地下器官养分双向运输N、P同一元素的增长关系。【结果】①山杨与水曲柳叶片N、P含量接近,山杨与水曲柳叶片N、P含量分别显著高于、低于东北红豆杉针叶相应数值(P<0.05);东北红豆杉枝条N、P含量最高;3个树种粗根N含量接近,水曲柳粗根P含量及细根N、P含量均最高。②水曲柳叶片与枝条、山杨叶片与粗根N、P含量比均最高,水曲柳叶片与细根N、P含量比最低。③山杨和东北红豆杉地上器官、地下器官N与P含量分别为异速、等速关系,且地下器官N与P元素间的变化斜率仅为地上部分的1/2;而水曲柳地上器官、地下器官两元素之间的变化斜率相似,均为显著大于1的异速增长关系。山杨地上与地下双向P、东北红豆杉上行方向P含量斜率均为相应N含量的一半,东北红豆杉下行方向N、P关系均不显著,水曲柳上行方向N、P含量斜率相似,下行方向P含量斜率是N的2/3左右。【结论】与山杨和东北红豆杉相比,水曲柳倾向于将N和P养分分配到代谢活跃的叶片和细根,且其地上(地下)器官N与P含量、地上与地下N、P含量变化速率具有协调一致性。
【Objective】The objective of this study is to investigate the nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) allocation patterns in the above- and below-ground organs of three different tree species in northeast China, namely Populus davidiana, Fraxinus mandshurica and Taxus cuspidata, and to provide theoretical insights into the trade-offs and allocation strategies of nutrient distribution among tree species.【Method】Mature individuals of P. davidiana, F. mandshurica and T. cuspidata were selected as research subjects. The N and P contents in aboveground organs, i.e., leaves, twigs and belowground organs, i.e., coarse roots, fine roots, were analyzed and the allocation ratios of N and P contents in the leaves, twigs and roots were calculated. Standardized major axis regressions were employed to examine the relationships of N and P elements between aboveground (belowground) organs of three tree species and the bidirectional nutrient transport of the same elements between aboveground and belowground organs.【Result】(1)The N and P contents in the leaves of P. davidiana and F. mandshurica were similar. However, the N and P contents in the leaves of these two species were significantly higher and lower, respectively, compared to T. cuspidata (P<0.05). The twigs of T. cuspidata exhibited the highest N and P contents, while F. mandshurica had the highest P content in coarse roots and N and P contents in fine roots. The N content in coarse roots was similar among the three species. (2)The ratios of N and P contents in leaves to twigs and leaves to coarse roots were the highest in F. mandshurica and P. davidiana, respectively, while the ratios of leaves to fine roots were the lowest in F. mandshurica. (3)For P. davidiana and T. cuspidata, the aboveground and belowground organs showed an allometric and isometric relationship respectively between N and P contents, with the scaling exponent in belowground being approximately half of that in aboveground. In contrast, F. mandshurica exhibited similar scaling exponents aboveground and belowground, both exhibiting significantly greater than 1 allometric relationship. For P. davidiana, the slopes of both aboveground and belowground P in both directions are half of the corresponding N values. For T. cuspidata, the slopes of P content in the upward direction were also half of the corresponding N values, and the downward N and P relationships were not significant. For F. mandshurica, the slopes of N and P content in the upward direction were similar, whereas in the downward direction, the P content slope was approximately 2/3 of N.【Conclusion】In contrast to P. davidiana and T. cuspidata, F. mandshurica tended to allocate N and P to metabolically active organs such as leaves and fine roots. The relationships between N and P in aboveground (or belowground) organs and N and P between above- and below-ground showed distinct coordinations for F. mandshurica compared to P. davidiana and T. cuspidata.
氮磷计量 / 养分分配 / 种间差异 / 山杨 / 水曲柳 / 东北红豆杉
nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry / nutrient allocation / inter-specific variation / Populus davidiana / Fraxinus mandshurica / Taxus cuspidate
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
蒋高明. 植物生理生态学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 128-132.
|
| [3] |
田地, 严正兵, 方精云. 植物生态化学计量特征及其主要假说[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(7): 682-713.
|
| [4] |
贺金生, 韩兴国. 生态化学计量学:探索从个体到生态系统的统一化理论[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(1): 2-6.
|
| [5] |
卢建男, 刘凯军, 王瑞雄, 等. 中国荒漠植物-土壤系统生态化学计量学研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 173-182.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
陈美玲, 崔君滕, 邓蕾, 等. 黄土高原两种针叶树种不同器官水碳氮磷分配格局及其生态化学计量特征[J]. 地球环境学报, 2018, 9(1): 54-63.
|
| [8] |
杨婷, 钟全林, 李宝银, 等. 3种功能型林木幼苗叶片与细根碳氮磷化学计量特征及其异速关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(12): 4051-4057.
|
| [9] |
张耀艺, 倪祥银, 杨静, 等. 中亚热带同质园不同树种氮磷重吸收及化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(4): 1154-1162.
|
| [10] |
赵瑞, 王传宽, 全先奎, 等. 黑龙江省帽儿山温带阔叶树种不同器官的生态化学计量特征[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(2): 1-11.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
沙刚, 黄庆阳, 徐明怡, 等. 五大连池新期火山熔岩台地4种乔木植物化学计量及其内稳性特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 127-138.
|
| [16] |
王亚东, 魏江生, 周梅, 等. 大兴安岭南段不同生长衰退程度山杨林生态化学计量特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2021, 52(4): 854-864.
|
| [17] |
郝玉琢, 周磊, 吴慧, 等. 4种类型水曲柳人工林叶片-凋落物-土壤生态化学计量特征比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(4): 101-108.
|
| [18] |
罗芊芊, 周志春, 邓宗付, 等. 南方红豆杉天然居群叶片的表型性状和氮磷化学计量特征的变异规律[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2021, 30(1): 27-35.
|
| [19] |
张志录, 刘中华, 陈明辉. 伏牛山区红豆杉不同叶龄叶片性状对海拔梯度的响应[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(2): 265-271, 278.
|
| [20] |
陈黎, 刘成功, 钱莹莹, 等. 南方红豆杉人工林针叶C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(5): 53-61.
|
| [21] |
杨克彤, 陈国鹏. 红豆杉幼树异龄叶的功能性状[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(2): 329-336.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
温璐宁. 东北地区21种乔木根系形态及组织化学特征[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019.
|
| [24] |
师伟, 王政权, 刘金梁, 等. 帽儿山天然次生林20个阔叶树种细根形态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2008, 32(6): 1217-1226.
|
| [25] |
张林, 罗天祥. 植物叶寿命及其相关叶性状的生态学研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(6): 844-852.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
成俊卿. 中国木材志[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1992.
|
| [38] |
|
黑龙江帽儿山森林生态系统国家野外科学观测研究站对本研究提供支持和帮助。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |