 PDF(1822 KB)
PDF(1822 KB)


薄壳山核桃-油用牡丹多种种植模式下土壤质量评价
陈慧, 王改萍, 彭方仁, 朱允芬, 张钰, 王晗
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 177-183.
 PDF(1822 KB)
PDF(1822 KB)
 PDF(1822 KB)
PDF(1822 KB)
薄壳山核桃-油用牡丹多种种植模式下土壤质量评价
Soil quality assessment for Carya illinoensis-Paeonia ostii under various patterns
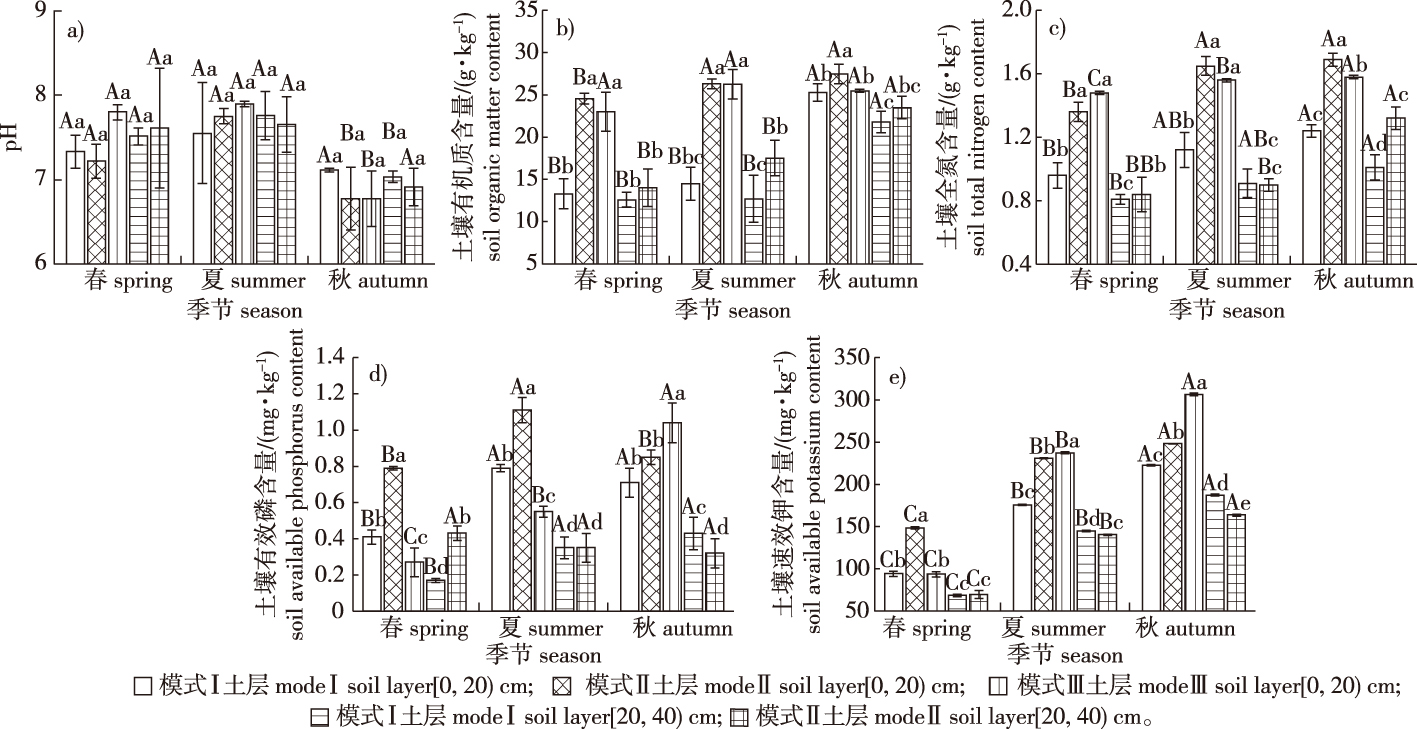
【目的】探究不同经营模式下薄壳山核桃‘波尼’(Carya illinoensis ‘Pawnee’)与油用牡丹‘凤丹’(Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’)林地土壤的理化性质及酶活性变化特征,分析季节变化对各模式经营种植下土壤性状的影响。【方法】分别以薄壳山核桃纯林模式(模式Ⅰ)、薄壳山核桃-油用牡丹复合模式(模式Ⅱ)、油用牡丹单植模式(模式Ⅲ)为研究对象,分析不同经营模式下土壤的理化性状及酶活性的季节变化特征,通过最小数据集法(MDS)计算土壤肥力综合质量指数(IFI),并对土壤肥力变化进行评价。【结果】在各模式下,林地表层土壤养分及酶活性高于深层;土壤含水量和容重随春、夏、秋季节变化而变化;土壤pH在秋季最低,春、夏两季差异不显著;夏季土壤过氧化氢酶活性高于春、秋季;土壤有机质、全氮、速效钾含量及土壤蔗糖酶、脲酶活性基本表现为随春、夏、秋季节变化逐渐升高。模式Ⅲ下土壤有效磷含量秋季高于春、夏两季;夏季土壤肥力综合质量指数最低,但以模式Ⅱ最高。【结论】林地土壤酶活性与理化性质间具有相关性;各季节下薄壳山核桃-油用牡丹复合模式(模式Ⅱ)土壤肥力均显著优于其余模式,且夏季土壤肥力显著低于其他季节;土壤肥力受容重、全氮、有效磷、速效钾含量及脲酶、蔗糖酶活性直接影响,其中蔗糖酶活性在季节土壤肥力综合质量评价中均较为敏感。
【Objective】The aim of the present study was to investigate the soil physical properties, chemical properties, and enzyme activities under different Carya illinoensis ‘Pawnee’ and Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ planting modes, as well as analyze the effects of different modes and seasons on soil characteristics.【Method】The treatments included single cultivation of C. illinoensis (mode Ⅰ), compound cultivation of C. illinoensis ‘Pawnee’-P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ (mode Ⅱ), and single cultivation of P. ostii (mode Ⅲ). Seasonal variation of soil physical properties, chemical properties, and enzyme activities were measured under different modes, and the minimum date set method and soil integrated fertility index (IFI) were utilized to evaluate the changes of soil fertility.【Result】The nutrient and enzyme activity in the surface soil were higher than those in the deep soil. The soil moisture content and bulk density gradually varied with the seasons of spring, summer and autumn. There was no significant difference on soil pH between the spring and summer seasons, and the lowest soil pH was observed in autumn. The soil catalase activity in summer was higher than that in spring and autumn. The soil organic matter content, total nitrogen content, available potassium content, sucrase activity, and urease activity increased during the seasonal variation of spring, summer, and autumn. In mode Ⅲ, the soil available phosphorus content in autumn was higher than that in spring and summer. The seasonal variation of the soil IFI was the lowest in summer and highest in mode Ⅱ.【Conclusion】There is a correlation among soil physical properties, chemical properties and enzyme activities. The soil fertility of the compound cultivation of C. illinoensis ‘Pawnee’-P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ (mode Ⅱ) is significantly higher than single cultivation of either species, and the soil fertility quality is lower in summer than in spring and autumn. The soil fertility quality is directly affected by bulk density, total nitrogen content, available potassium content, available phosphorus content, sucrase activity, and urease activity. Further, sucrase activity is more sensitive in evaluating the soil IFI in all seasons.
薄壳山核桃 / 油用牡丹 / 复合经营 / 土壤理化性状 / 土壤酶活性
Carya illinoensis / Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ / compound management / soil physical and chemical property / soil enzyme activity
| [1] |
张日清, 吕芳德. 优良经济树种:美国山核桃[J]. 广西林业科学, 1998, 27(4):202-206.
|
| [2] |
陈文霞, 吴文浩, 彭方仁. 江苏丘陵地区薄壳山核桃适宜栽培模式及其产业发展对策[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2016, 43(3):53-57.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
彭方仁, 李永荣, 郝明灼, 等. 我国薄壳山核桃生产现状与产业化发展策略[J]. 林业科技开发, 2012, 26(4):1-4.
|
| [5] |
陈幸良. 林下经济学的缘起、发展与展望[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):105-114.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
王怡晨, 孙海燕, 李永荣, 等. 油用牡丹‘凤丹’单株结实量及产油品质分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(4):155-160.
|
| [8] |
邓瑞雪, 刘振, 秦琳琳, 等. 超临界CO2流体提取洛阳牡丹籽油工艺研究[J]. 食品科学, 2010, 31(10):142-145.
|
| [9] |
韩继刚, 李晓青, 刘炤, 等. 牡丹油用价值及其应用前景[J]. 粮食与油脂, 2014, 27(5):21-25.
|
| [10] |
沈永涛, 张胜昔, 岳长江, 等. 核桃—小麦间作土壤养分与酶活性的变化[J]. 甘肃林业科技, 2021, 46(2):40-42,50.
|
| [11] |
李孟, 刘琅, 刀梅, 等. 栗-茶间作茶园土壤化学性质和细菌丰富度分析[J]. 经济林研究, 2022, 40(1):58-65,81.
|
| [12] |
孟凡旭, 王树森, 秦富仓, 等. 残塬沟壑区不同果农复合模式对土壤理化性质及水源涵养功能的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(5):192-199.
|
| [13] |
唐瑾暄, 秦晓威, 鱼欢, 等. 槟榔间作香露兜对土壤养分和养分吸收的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(9):2571-2578.
|
| [14] |
赵春建, 李玉正, 关佳晶, 等. 东北红豆杉-无花果复合种植对两种植物生长和土壤酶活性影响[J]. 植物研究, 2020, 40(5):679-685.
|
| [15] |
马占霞, 孙武, 李鑫鑫, 等. 不同间作模式茶园对土壤理化性质和茶叶化学成分的影响[J]. 热带农业科学, 2022, 42(5):1-8.
|
| [16] |
田洪敏, 罗美玲, 杨雪梅, 等. 茶树-核桃树间作模式对茶园土壤养分的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2019, 40(4):657-663.
|
| [17] |
鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000:1-19,146-195.
|
| [18] |
关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1986:260-339.
|
| [19] |
徐建明, 张甘霖, 谢正苗. 土壤质量指标与评价[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010:40-119.
|
| [20] |
张文学, 王少先, 刘增兵, 等. 基于土壤肥力质量综合指数评价化肥与有机肥配施对红壤稻田肥力的提升作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(5):777-790.
|
| [21] |
邓绍欢, 曾令涛, 关强, 等. 基于最小数据集的南方地区冷浸田土壤质量评价[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5):1326-1333.
|
| [22] |
常旭, 邱新彩, 刘欣, 等. 塞罕坝华北落叶松纯林和混交林土壤肥力质量评价[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(8):50-59.
|
| [23] |
周楷玲, 陈绪文, 龚伟, 等. 核桃林下复合种植对土壤培肥效果的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2019, 37(6):807-813.
|
| [24] |
李晨晨, 周再知, 梁坤南, 等. 南药立体经营模式土壤质量综合评价[J]. 植物研究, 2017, 37(5):778-788.
|
| [25] |
郭颖, 聂朝俊, 向仰州, 等. 不同核桃农林复合经营模式对土壤肥力的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(2):391-397.
|
| [26] |
吕丽茹, 扎西尼玛, 陈识澳, 等. 季节性因素对土壤微生物的影响研究进展[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2022, 61(11):62-66,71.
|
| [27] |
刘建玲, 张凤华. 土壤磷素化学行为及影响因素研究进展[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2000, 23(3):36-45.
|
| [28] |
任子文, 吴佳美, 石佩佩, 等. 红壤磷素化学行为及影响因素研究进展[J]. 内蒙古林业调查设计, 2017, 40(2):100-104.
|
| [29] |
汪贵斌, 曹福亮, 程鹏, 等. 不同银杏复合经营模式土壤酶活性及综合评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 34(4):1-6.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
李林海, 邱莉萍, 梦梦. 黄土高原沟壑区土壤酶活性对植被恢复的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(12):3355-3360.
|
| [32] |
徐宏强, 汪贵斌, 曹福亮, 等. 生物覆盖对银杏用材林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(2):21-26.
|
| [33] |
汪贵斌, 曹福亮, 程鹏, 等. 不同银杏复合经营模式土壤肥力综合评价[J]. 林业科学, 2010, 46(8):1-7.
|
| [34] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |