 PDF(1481 KB)
PDF(1481 KB)


4种玉兰的小白菊内酯含量变化动态研究
刘景胜, 唐鑫伟, 周虎, 陈雷, 戴晓港, 尹佟明
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (2) : 227-233.
 PDF(1481 KB)
PDF(1481 KB)
 PDF(1481 KB)
PDF(1481 KB)
4种玉兰的小白菊内酯含量变化动态研究
Dynamic content changes of parthenolide from four Magnolia species
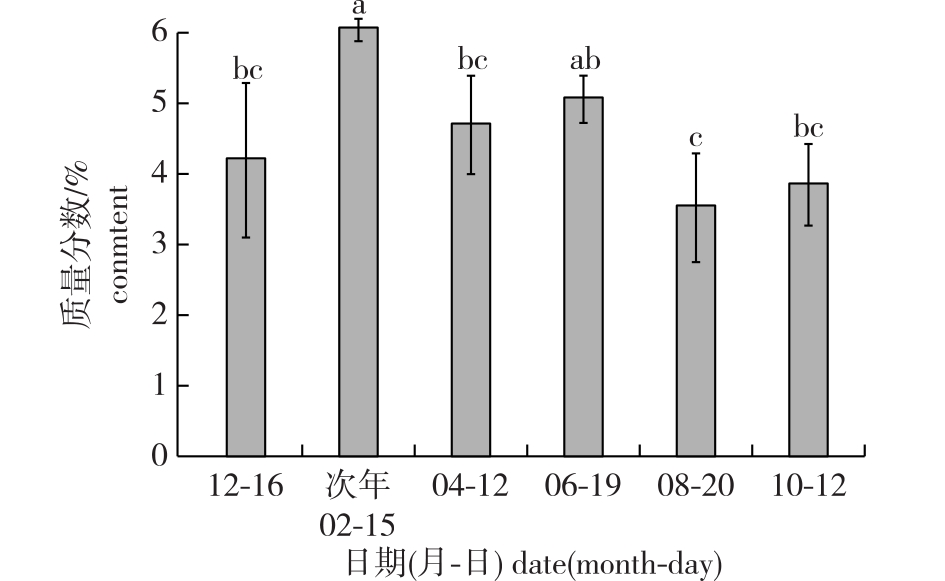
【目的】 测定4种玉兰不同组织中小白菊内酯含量,对其中小白菊内酯高含量树种开展不同生长期、树龄和产地的含量测定,为小白菊内酯高含量树种选育及栽培提供参考。【方法】 以玉兰(Magnolia denudate)、望春玉兰(M. delavayi)、山玉兰(M. biondii)和广玉兰(M. grandiflora)为试验材料,采用高效液相色谱法测定其叶片、花蕾和根皮中的小白菊内酯含量,同时测定小白菊内酯含量较高的望春玉兰在不同生长期、不同树龄和不同产地根皮中的含量。【结果】 望春玉兰根皮中小白菊内酯含量最高,平均质量分数达5.10%(干质量),在玉兰根皮中质量分数仅为0.72%,而在山玉兰和广玉兰根皮中未检测到小白菊内脂;4个树种叶片中均含有小白菊内酯,质量分数为0.06%~0.59%;但只有望春玉兰和广玉兰的花蕾中含有小白菊内酯,质量分数分别为0.88%和0.08%。2~4年生树龄望春玉兰根皮中小白菊内酯质量分数分别为2.43%、4.07%和4.31%,2年生和3年生、4年生根皮中的含量均呈显著差异,而3年生和4年生差异不显著。不同月份采集的望春玉兰根皮中小白菊内酯质量分数为3.51%~6.04%,含量最高的2月与前后两个月相比其差异均达到显著水平。不同产地望春玉兰根皮中的小白菊内酯质量分数为3.22%~5.51%,方差分析表明浙江临安种源和其余4个种源间差异显著。【结论】 4种玉兰中,望春玉兰根皮中小白菊内酯含量最高;其3年生树龄和2月采集根皮中小白菊内酯含量较高;建议望春玉兰根皮收获小白菊内酯的最佳树龄为3 a、最佳收获时间为2月中旬;在以收获小白菊内酯单一化合物为目标时,湖北襄阳、江苏南京和新沂为适合引种地。
【Objective】 The contents of parthenolide from different tissues were measured in four species of Magnolia, and contents of parthenolide were also measured at different growth periods, different tree ages and different production areas in tree species with high level of parthenolide, which will provide useful lessons for the breeding programs and for the planting of medicinal plant varieties from Magnoliaceae family.【Method】 Taking Magnolia denudata, M. biondii, M. grandiflora and M. delavayi as materials, the contents of parthenolide were measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in leaves, buds and root barks. Root barks from M. biondii at different growth stages, different tree ages and different production areas are measuring for its parthenolide contents. 【Result】 Among different tissues from the four species, root barks of M. biondii has the highest contents of parthenolide with an average level of 5.10%, and the contents falls to 0.72% in M. denudata, but parthenolide was not detected in M. grandiflora and M. delavayi root barks. All leaves from the four species contented parthenolide with the trace level between 0.06% and 0.59%. Only the buds of M. biondii and M. grandiflora contains parthenolide with the average level of 0.88% and 0.08% separately. The contents of parthenolide in root barks with two-year, three-year and four-year old stage of M. biondii were 2.43%, 4.07% and 4.31% separately, and the contents of two-year old was significantly different from three-year and four-year old, but no significant difference was detected from three-year and four-year old tree. During the growth period of one year, parthenolide reached the highest level of 6.04% in February, which was significantly different from that in April and December of the previous year. The contents of parthenolide in root barks of M. biondii varied from 3.22% to 5.51% in five different production areas, and the analysis of variance showed that only the tree growing in Lin'an, Zhejiang Province were significantly different from the other four sites. 【Conclusion】 The contents of parthenolide were compared in different tissues from four Magnolia species, and found that the root barks of M. biondii contained the highest level of parthenolide among the four species with different tissues. The optimal tree age determined for havesting parthenolide was three and the best harvest time was mid-February based on the comparison of root barks parthenolide contents from different tree ages and different grown stages. When aiming at harvesting a single compound of parthenolide, Nanjing and Xinyi City in Jiangsu Province and Xiangyang in Hubei Province can introduce the tree of M. biondii for parhtenolide extraction from its root bark.
Magnolia / Magnolia biondii / parthenolide / tree age / origin
| [1] |
国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典-一部:2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020:189-190.
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. People's Republic of China (PRC) pharmacopoeia-part I:2020 edition[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020:189-190.
|
| [2] |
于培明, 田智勇, 许启泰, 等. 辛夷研究的新进展[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2005, 16(7):652-653.
|
| [3] |
冯卫生, 何玉环, 郑晓珂, 等. 望春玉兰花蕾中木脂素类化学成分的研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43(5):970-976.
|
| [4] |
冯立国, 孟祥申, 周力, 等. 白玉兰与望春玉兰花香成分和含量的比较研究[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(3):377-380.
|
| [5] |
张泉, 陈悦, 范洪霞, 等. 源自山玉兰、紫玉兰、白玉兰的小白菊内酯的制备方法: 中国, 201110187388.7[P]. 2015.5.20.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
刘战培, 李艳艳, 高波, 等. 小白菊内酯诱导肝癌细胞SMMC 7721自噬性死亡的实验研究[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2014, 45(4):587-590.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
王玉青, 高玥, 韦荣, 等. 小白菊内酯通过靶向c-myc G-四链体抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖和迁移[J]. 药学学报, 2020, 55(7):1622-1626.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
周倩, 乔思薇, 印敏, 等. 木兰科8种植物和菊科23种植物叶片中小白菊内酯含量比较[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2022, 31(2):85-87.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
张康健, 董娟娥, 马柏林, 等. 杜仲次生代谢物部位差异性的研究[J]. 林业科学, 2002, 38(6):12-16.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
郭巧生. 药用植物栽培学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009.
|
| [24] |
谌金吾, 杨占南, 胡庭坤, 等. 不同树龄凹叶厚朴7种次生代谢产物积累研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(2):27-34.
|
| [25] |
李聪, 黄诗雨, 陈丽华, 等. 药材部位、产地及采收期对中药挥发油成分的差异性分析[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(20):5395-5404.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
徐玲玲, 黄礼杰, 顾国献. 不同产地和品种淫羊藿中淫羊藿苷的HPLC分析[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2000, 17(2):110-114.
|
| [28] |
中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.
Botanical Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |