 PDF(1809 KB)
PDF(1809 KB)


模拟大气CO2浓度升高与氮添加对宁夏枸杞生长及光合特性的影响
马冲, 陆晖, 李运毛, 曹兵, 朱金忠, 亢彦东
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 209-218.
 PDF(1809 KB)
PDF(1809 KB)
 PDF(1809 KB)
PDF(1809 KB)
模拟大气CO2浓度升高与氮添加对宁夏枸杞生长及光合特性的影响
Effects of elevated CO2 concentration and nitrogen addition in simulated atmosphere on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Lycium barbarum
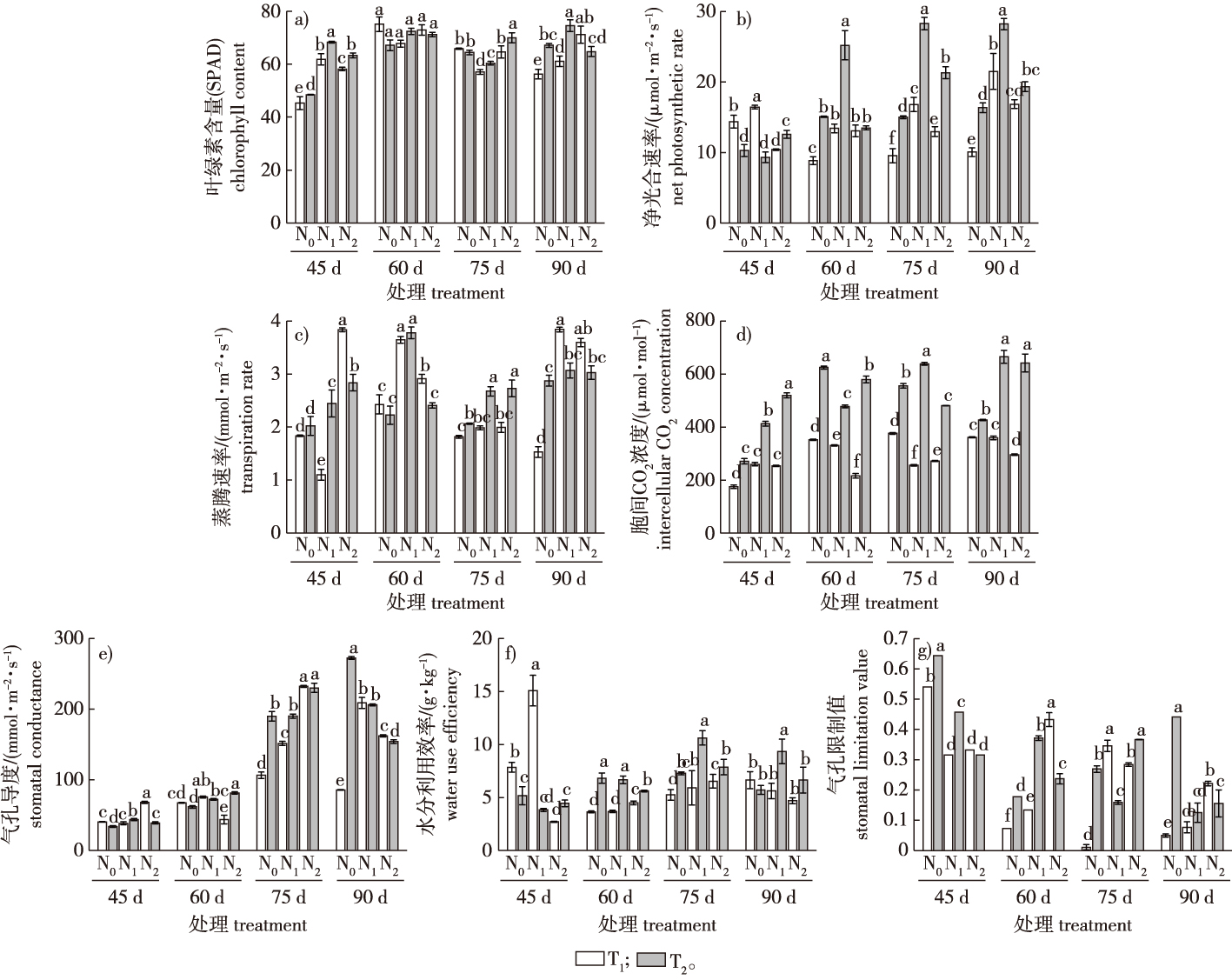
【目的】探究大气CO2浓度升高与氮添加对宁夏枸杞生长发育特性、光合特性及产量的影响,为更好发掘宁夏枸杞的生产潜力及适应性栽培提供理论参考。【方法】以1年生‘宁杞1号’扦插苗为试验材料,采用开顶气室控制系统设置自然环境CO2浓度[T1,(380±20)μmol/mol)]和升高CO2浓度[T2,(760±20)μmol/mol],设置3个氮添加水平(以每kg土壤施加高氮水溶肥量计)N0(0 g/kg)、N1(0.8 g/kg)和N2(1.6 g/kg),共计6个处理。分别于处理45、60、75、90 d测定‘宁杞1号’株型、光合指标、日均净光合速率及单株产量。【结果】随着CO2与氮素复合处理时间的延长,‘宁杞1号’苗地径、新梢长度和粗度、叶片气孔导度呈增加趋势,气孔限制值呈降低趋势,叶绿素含量呈先升后降再升模式。T2N1处理各时期新梢长度、粗度及叶片胞间CO2浓度较高。T2处理60、75、90 d‘宁杞1号’的净光合速率均显著高于T1处理,其中T2N1处理下‘宁杞1号’净光合速率同比增长87.72%、68.33%、67.56%(P<0.01);CO2浓度升高条件下,N1处理45、60、75、90 d时‘宁杞1号’的蒸腾速率均显著上升(P<0.05),但N2处理45、60 d时‘宁杞1号’的蒸腾速率均显著降低(P<0.05),分别为2.84、2.41 mmol/(m2·s)(P<0.05),N0处理75、90 d时‘宁杞1号’气孔导度显著升高(P<0.05),N1处理75、90 d时‘宁杞1号’的水分利用率显著增加(P<0.05),分别为10.68、9.34 g/kg,但气孔限制值处于较低水平。CO2浓度升高条件下氮素添加降低了气孔限制值与新梢长度、粗度、叶绿素含量及枸杞单株产量的相关性,提高了蒸腾速率、净光合速率、水分利用效率与新梢长度、粗度等株型指标及枸杞单株产量的相关性;根据日均净光合速率模型,CO2浓度升高条件下,‘宁杞1号’理论最佳施氮量为0.875 g/kg(土壤),此时‘宁杞1号’单株产量略高于T1N1处理。【结论】CO2浓度升高条件下,N1处理增加了‘宁杞1号’的地径、新梢粗度,提高了‘宁杞1号’叶绿素含量、净光合速率、气孔导度和水分利用率,降低了其气孔限制值,且N1处理可以保持‘宁杞1号’较高的产量,降低CO2浓度升高带来的负面影响,更适合CO2浓度升高条件下枸杞的种植。
【Objective】This study aims to investigate the effects of various nitrogen treatments on the growth, photosynthesis, and yield of Lycium barbarum under elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations. The objective is to optimize the production and adaptive cultivation of L. barbarum. 【Method】One-year-old cuttings of L. barbarum ‘Ningqi-1’ were used as experimental material. Two CO2 concentrations were tested: ambient (T1, (380±20) μmol/mol) and elevated (T2, (760±20) μmol/mol), using an open-top chamber control system. Additionally, three nitrogen levels were applied per kilogram of soil: 0 g/kg (N0), 0.8 g/kg (N1) and 1.6 g/kg (N2). Measurements of plant morphology, photosynthetic indices, daily net photosynthetic rates, and yield were taken at 45, 60, 75 and 90 days.【Result】Over time, the combination of elevated CO2 and nitrogen treatments enhanced the stem diameter, shoot length, thickness, and stomatal conductance of ‘Ningqi-1’, while inhibited the stomatal limit. The chlorophyll content initially increased, then decreased, and later increased again. The T2N1 treatment performs the best during each assessment period. The net photosynthetic rate of “Ningqi-1” treated with T2 for 60, 75 and 90 days was significantly higher than that of T1, with increases of 87.72%, 68.33% and 67.56%, respectively, reaching rates of 25.24, 28.33, and 28.25 μmol/(m2·s),respectively (P<0.01). With elevated CO2 levels, the transpiration rate of “Ningqi-1” significantly increased during the N1 treatment across 45, 60, 75, 90 days but significantly decreased during the N2 treatment at 45 and 60 days, recording 2.84 and 2.41 mmol/(m2·s), respectively. Additionally, stomatal conductance of “Ningqi-1” significantly increased from 75 to 90 days (P<0.05). Water use efficiency significantly increased from 75 to 90 days post-N1 treatment, reaching 10.68 and 9.34 g/kg, while the stomatal limit remained low. Increasing CO2 concentrations reduced the correlation among stomatal limitation and variables such as shoot length, thickness, chlorophyll content, and yield per plant. Conversely, it enhanced the correlation between transpiration rate, net photosynthetic rate, water use efficiency, and the aforementioned plant traits in “Ningqi-1.” Based on the CO2 concentration model for daily net photosynthetic rate, the optimal theoretical nitrogen application rate for “Ningqi-1” was estimated at 0.875 g/kg (soil). The yield per plant under this regime was slightly higher than that of the T1N1 treatment.【Conclusion】The N1 nitrogen treatment under elevated CO2 conditions effectively increased the stem diameter, shoot thickness, chlorophyll content, net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, and water use efficiency of “Ningqi-1,” while reduced the stomatal limit. This treatment also sustained higher yields and mitigated the adverse effects of increased CO2 levels, making it a more suitable option for cultivation in environments with higher CO2 concentrations.
宁夏枸杞‘宁杞1号’ / 夏果期 / 氮添加 / CO2浓度升高 / 光合特性
Lycium barbarum‘Ningqi-1’ / summer fruit period / nitrogen addition / increase of CO2 concentration / photosynthetic characteristic
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
周青, 黄晓华, 戴玉锦. CO2倍增对植物的生态生理效应[J]. 自然杂志, 2002, 24(1):20-26.
|
| [4] |
高慧璟, 肖能文, 李俊生, 等. 不同氮素水平下CO2倍增对转Bt棉花氮素代谢的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(11):2213-2219.
|
| [5] |
马雪峰, 高旻, 程治军. 植物氮素吸收与利用的分子机制研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 2013(4):32-38.
|
| [6] |
魏雪松, 王海洋, 孙智轩, 等. 宁夏枸杞化学成分及其药理活性研究进展[J]. 中成药, 2018, 40(11):2513-2520.
|
| [7] |
曹兵, 宋培建, 康建宏, 等. 大气CO2浓度倍增对宁夏枸杞生长的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2011, 47(7):193-198.
|
| [8] |
高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.
|
| [9] |
张志良, 瞿伟菁, 李小方. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高教育出版社, 2009.
|
| [10] |
马兴东, 郭晔红, 李梅英, 等. 施氮对干旱区黑果枸杞光合-CO2响应及药效成分的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(7):1209-1218.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
侯晶东, 曹兵, 宋丽华. CO2浓度倍增对宁夏枸杞光合特性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(5):71-76.
|
| [13] |
刘伟, 李志坤, 马宗斌, 等. 施氮方式对棉花赘芽生长、干物质积累和产量的影响[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2016, 50(5):587-592,608.
|
| [14] |
刘紫娟, 李萍, 宗毓铮, 等. 大气CO2浓度升高对谷子生长发育及玉米螟发生的影响[J]. 国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(1):55-60.
|
| [15] |
杨伟光, 苏颖, 张建华, 等. 玉米株高和穗位遗传模型测验[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2000(4):28-31+44.
|
| [16] |
胡笑涛, 王振昌, 马黎华. 番茄果实及茎秆微变化对分根区交替灌溉的响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(12):87-95.
|
| [17] |
贺春燕. 施肥对枸杞产量和品质的影响及效应研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2009.
|
| [18] |
王佩玲. CO2浓度倍增与介质施氮对冬小麦物质生产及氮素利用的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010.
|
| [19] |
宋淑英. 供氮水平小麦/玉米幼苗生理特性对CO2浓度倍增的响应[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010.
|
| [20] |
易亚凤, 彭诗涛, 张玲玲, 等. Cd污染及其与大气CO2浓度升高、N添加复合作用对大叶相思生长的影响[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2020, 28(1):17-24.
|
| [21] |
杨佳恒. 开放式大气CO2浓度和温度升高对冬小麦生长发育的影响及其模拟分析[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017.
|
| [22] |
李彦生, 金剑, 刘晓冰. 作物对大气CO2浓度升高生理响应研究进展[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(12):1819-1830.
|
| [23] |
宋培建, 侯晶东, 宋丽华, 等. CO2浓度倍增对宁夏枸杞光合特性的影响初报[C]// 第九届中国林业青年学术年会论文摘要集.成都, 2010:69.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
任彬彬. 氮素营养影响水稻水分吸收及光合特性的机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015.
|
| [27] |
孙鹏. 不同二氧化碳浓度、氮肥施用和温度处理对草莓(Fragaria×ananassa Duch.) 生长、果实产量和果实品质的影响[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2012.
|
| [28] |
张其德, 卢从明, 张群, 等. 不同氮素水平下CO2倍增对大豆叶片荧光诱导动力学参数的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1997, 3(1):24-30.
|
| [29] |
宋仰超, 陈小莉, 任小龙, 等. 调亏灌溉与减氮施肥对枸杞生长及产量的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2019, 28(10):1666-1673.
|
| [30] |
王璐. 不同水肥管理对枸杞地氨挥发及枸杞产量的影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2022.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |