 PDF(36328 KB)
PDF(36328 KB)


基于多源数据的城市型风景名胜区边界划定研究——以南京钟山风景名胜区为例
申世广, 张珮瑶, 邱冰
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 225-232.
 PDF(36328 KB)
PDF(36328 KB)
 PDF(36328 KB)
PDF(36328 KB)
基于多源数据的城市型风景名胜区边界划定研究——以南京钟山风景名胜区为例
Research on boundary delimitation of urban scenic area based on multi-source data——A case study of Zhongshan Scenic Spot in Nanjing
【目的】探讨城市型风景名胜区边界判别的有效方法,为城市型风景名胜区边界划定提供科学依据。【方法】以钟山风景名胜区为例,在多源数据支持下,构建风景区资源等级综合评价模型,应用空间核密度、植被覆盖度(FVC)、GIS重分类与叠加等分析,利用自然间断点分级法按评价结果将研究区分为风景资源丰富、较丰富、一般、较匮乏和匮乏5个等级。在此基础上,在ArcGIS中利用Cartography Tool的Aggregate Polygons工具将聚合面积小于1 000 m2的小斑块合并到邻近的大斑块,并对边界范围进行平滑处理。再依据景源保护、游客密度和相关规划标准,在边界范围带内划定钟山风景名胜区的边界线。【结果】基于以上方法划定的边界对钟山风景区范围进行测算,风景区总面积为37.48 km2,其中新增区域面积约2.06 km2,减少区域面积约0.49 km2,与原有边界相比总体面积增加了1.57 km2左右。【结论】在多源数据支持下,构建资源综合评价模型划定城市型风景区边界的方法,综合考虑了景源、生态、社会环境、城市开发现状等多种因素,准确性高,客观性强,更有利于风景区资源的保护与可持续利用。
【Objective】This study aims to explore effective methods for identifying boundaries of urban scenic spots and to provide a scientific basis for their delimitation.【Method】This study used Zhongshan Scenic Spot as a case study. utilizing multi-source data, a comprehensive evaluation model for scenic resource grades was constructed. Spatial kernel density analysis, fractional vegetation cover (FVC), GIS reclassification, and overlay analysis were employed to create a scenic resources evaluation distribution map categorized into five grades by the natural discontinuity classification method: rich, relatively rich, general, relatively scarce, and scarce in scenic resources. The aggregate polygons function in ArcGIS was then used to merge small patches (less than 1 000 m2) into adjacent larger patches and smooth the boundary. Finally, the boundary of Zhongshan Scenic Spot was delineated based on source protection, tourist density, and related planning standards.【Result】The resulting boundary delineation showed that the total area of Zhongshan Scenic Spot was 37.48 km2, with a new area of approximately 2.06 km2 and a reduced area of about 0.49 km2, resulting in an overall increase of about 1.57 km2 compared with the original boundary.【Conclusion】Supported by multi-source data, this method provides a comprehensive evaluation model that considers landscape, ecology, social environment, and urban development, offering high accuracy and objectivity for the protection and sustainable use of scenic resources.
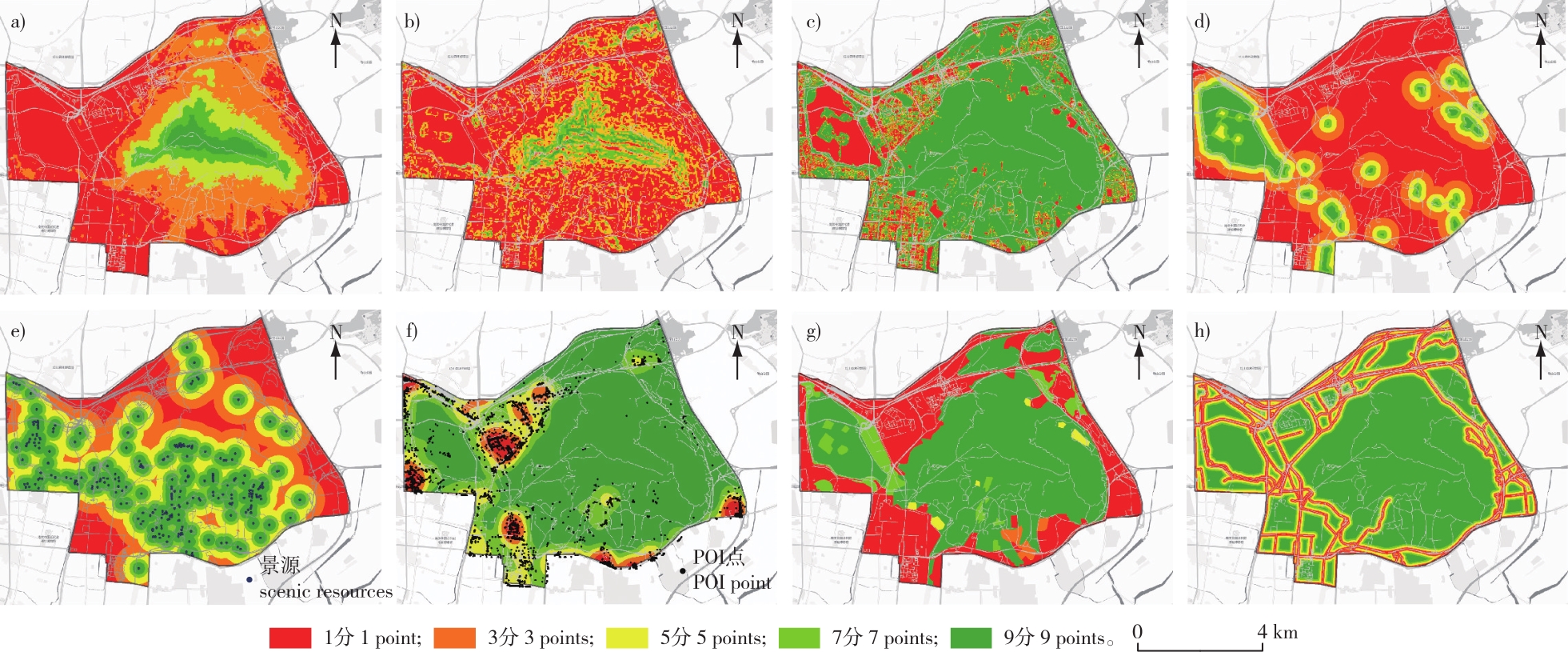
多源数据 / 边界划定 / 城市型风景名胜区 / 核密度分析 / 资源评价 / 钟山风景名胜区
multi-source data / boundary delimitation / urban scenic spot / kernel density analysis / resource evaluation / Zhongshan Scenic Spot
| [1] |
王琦, 王辉, 虞虎. 基于生态安全格局的国家公园边界划定:以雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家公园为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2023, 38(4):951-965.
|
| [2] |
疏良仁, 黄利, 昝丽娟. 论我国风景名胜区在自然保护地体系中的重要地位与基础作用[J]. 城乡规划, 2020(1):119-124.
|
| [3] |
董东箭, 白伟岚, 牛萌, 等. 城市型风景名胜区规划策略浅析:以漳州市云洞岩风景名胜区为例[J]. 城乡建设, 2021(12):4-8.
|
| [4] |
邓武功, 宋梁, 王笑时, 等. 城市型风景名胜区景城协调发展的规划方法:青城山—都江堰风景名胜区总体规划例证研究[J]. 小城镇建设, 2019, 37(6):35-40,48.
|
| [5] |
住房和城乡建设部. 风景名胜区总体规划标准:GB/T 50298—2018[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for scenic and historic area general planning:GB/T 50298—2018[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018.
|
| [6] |
胡一可, 杨锐. 风景名胜区边界划定方法研究—以老君山风景名胜区为例[C]// 中国风景园林学会2009年会论文集.2009:272-280.
|
| [7] |
廖波. 基于区域统筹视角下的城镇型风景名胜区边界划定方法初探:以长寿湖风景名胜区保护规划为例[J]. 室内设计, 2011, 26(6):10-13,27.
|
| [8] |
南京市规划和自然资源局. 钟山风景名胜区总体规划(2017—2035)[Z].2018.
Nanjing Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. Overall planning of Zhongshan Scenic area (2017-2035)[Z].2018.
|
| [9] |
袁士聪, 谷甫刚. 基于归一化指数(NDVI)的植被覆盖度分级研究:以贵州省为例[J]. 环保科技, 2018, 24(3):38-42.
|
| [10] |
谷佳贺, 薛华柱, 董国涛, 等. 归一化水体指数用于河南省干旱监测适用性分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(6):209-217.
|
| [11] |
陈伟强, 潘元庆, 马月红, 等. 基于约束性CA模型的城市开发边界划定方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(4):278-284.
|
| [12] |
周亮, 赵琪, 杨帆. 基于POI与NPP/VIIRS灯光数据的城市群边界定量识别[J]. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(6):840-850.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
薛冰洁, 张玉钧, 安童童, 等. 生态格局理念下的国家公园边界划定方法探讨:以秦岭国家公园为例[J]. 规划师, 2020, 36(1):26-31.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
赵烨, 高翅. 名山风景区风景特质理论体系及其实践:以武当山为例[J]. 中国园林, 2019, 35(10):107-112.
|
| [17] |
杨阳, 唐晓岚, 谢楠. 基于公众感知的牛首山风景区人工林植物景观视觉评价[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(2):199-207.
|
| [18] |
王金辉, 赵怀石. 基于GIS技术的生态敏感性研究:以松花湖风景名胜区为例[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2015, 5(33):63.
|
| [19] |
张蜜, 陈存友, 胡希军. 苍南县玉苍山风景区生态敏感性评价[J]. 林业资源管理, 2019(4):92-100,150.
|
| [20] |
李苗苗, 吴炳方, 颜长珍, 等. 密云水库上游植被覆盖度的遥感估算[J]. 资源科学, 2004, 26(4):153-159.
|
| [21] |
刘金花, 张家玮, 贾琨. 基于POI数据的中心城区边界识别与空间格局优化:以高唐县为例[J]. 城市发展研究, 2021, 28(6):74-83.
|
| [22] |
刘佳, 梁一行, 李鹏, 等. 2001—2018年印度尼西亚MODIS活跃火的发生特征与响应[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75 (9): 1907-1920.
|
| [23] |
李佳. 生态敏感性评价技术在山岳型风景名胜区规划中的应用研究:以河南林州市林虑山为例[J]. 中国名城, 2020, 34(3):69-73.
|
| [24] |
俞孔坚. 景观敏感度与阀值评价研究[J]. 地理研究, 1991, 10(2):38-51.
|
| [25] |
索可欣, 韩肖, 苏宇, 等. 基于RS与GIS的野三坡风景区景观敏感度评价研究[J]. 绿色科技, 2021, 23(10):12-16.
|
| [26] |
全国人民代表大会常务委员会. 《中华人民共和国文物保护法》[Z]. 2017.
The Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress. Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Protection of Cultural Relics[Z]. 2017.
|
| [27] |
南京市人民政府办公厅. 南京市第四批市级文物保护单位保护范围和建设控制地带四至范围列表[EB/OL].(2018-12-24)[2022-12-28]. https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/zdgk/201812/t20181228_1356236.html.
General Office of Nanjing Municipal People’s Government. List of the protection scope and construction control zone of the fourth batch of municipal cultural relics protection units in Nanjing[EB/OL]. (2018-12-24)[2022-12-28]. https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/zdgk/201812/t20181228_1356236.html.
|
| [28] |
吴榛, 王玮, 王浩. 基于GIS的苏南水网地区乡镇景观资源综合评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(4):202-208.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |