 PDF(1661 KB)
PDF(1661 KB)


林业废弃物与猪粪堆肥过程中理化性质变化及腐熟度评价
郑捷翔, 王艮梅, 刘亚柏, 李嘉欣, 贺紫莹, 程锦萍, 程新宇
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 195-205.
 PDF(1661 KB)
PDF(1661 KB)
 PDF(1661 KB)
PDF(1661 KB)
林业废弃物与猪粪堆肥过程中理化性质变化及腐熟度评价
Changes of physicochemical properties and maturity evaluation during forestry waste and pig manure co-composting
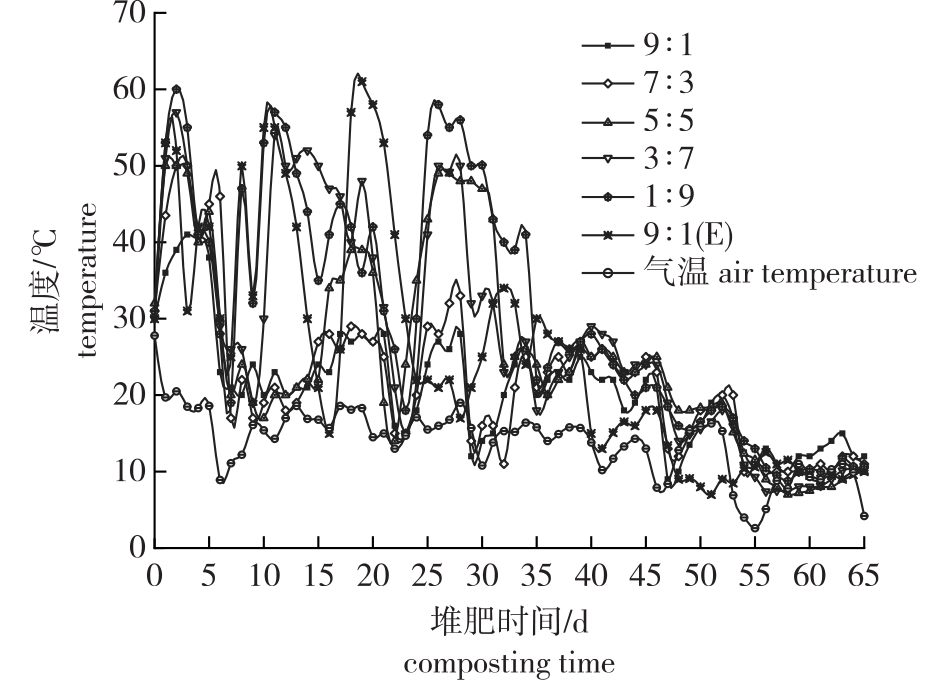
【目的】研究林业废弃物在猪粪地肥过程中的性状变化,为林业废弃物合理处置及资源化利用提供依据。【方法】以修剪的猕猴桃(Actinidia arguta)枝条(取自江苏句容市某果园)和猪粪(取自当地养猪场)为研究对象,采用好氧堆肥的方法,按照猕猴桃枝条与猪粪的不同质量比例共设置6组处理[分别为9∶1、7∶3、5∶5、3∶7、1∶9,以及9∶1处理的基础上添加了微生物菌剂的9∶1(E)处理],研究猕猴桃枝条与猪粪混合堆肥过程中养分含量的变化,并进行腐熟程度评价。【结果】除9∶1、7∶3处理的堆体未达到高温阶段,其余处理在堆肥2~4 d后均达到高温阶段(>50 ℃),且高温持续时间达7 d以上,其中9∶1(E)处理持续高温阶段的时间最长,达10 d以上。除9∶1和7∶3处理外,其余处理的堆体种子发芽指数(GI)均达到50%(第10天)和80%(第20天)以上。堆肥过程中堆体pH和电导率(EC)无明显变化规律,所有处理堆体的pH在堆肥第20天时全部达到腐熟标准,EC在堆肥全过程中均符合腐熟标准。堆肥过程中堆体有机碳含量呈持续下降趋势,堆肥结束时堆体有机碳含量较开始时下降34.19%~55.54%;全氮含量呈先下降后上升趋势,较开始时增加28.07%~48.51%;堆肥后堆体有效磷和速效钾含量较开始分别增加8.77%~200.00%和66.14%~385.55%,其中9∶1(E)处理有效磷、速效钾含量增加幅度均最大。【结论】根据主成分分析综合排名结果及林业废弃物的资源化应用,建议优先选择猕猴桃枝条与猪粪质量比5∶5或9∶1的基础上添加微生物菌剂[(9∶1)E]这2种处堆肥配比处理进行推广。
【Objective】This study aims to provide a basis for the rational disposal and resource utilization of forestry waste.【Method】The pruned Acinidia arguta (kiwifruit) branches (taken from an orchard in Jurong City, Jiangsu Province) and pig manure (taken from the local pig farm) were utilized as aerobic composting materials. Six groups of treatments were established based on the varying mass ratios of kiwifruit branches and pig manure, specifically 9∶1, 7∶3, 5∶5, 3∶7, 1∶9, and 9∶1 (E) (microbial inoculants were added to the 9∶1 ratio). The dynamic changes in nutrient content and evaluation of maturity were monitored through temperature, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), C/N, and seed germination index (GI) during composting.【Result】With the exception of the 9∶1 and 7∶3 treatments, which did not reach the high-temperature stage, all other treatments attained high temperatures (> 50 ℃) after two to four days of composting. The duration of the high-temperature stage exceeded seven days, particularly for the 9∶1 (E) treatment, which sustained high temperatures for more than ten days. The results also indicated that the GI values of all treatments, excluding the 9∶1 and 7∶3 treatments, exceed 50% and 80% for composting durations of 10 and 20 days, respectively. No significant changes were observed in pH and EC during composting for all treated piles. The pH values achieved the maturity standard on the 20th day of composting, while the electrical conductance (EC) values consistently met the maturity standard throughout the process. During composting, organic carbon contents exhibited a continuous downward trend across all treatments, while the total nitrogen contents initially decreased and then increased. After composting, the organic carbon content declined by 34.19% to 55.54%, whereas the total nitrogen content increased by 28.07% to 48.51% compared to the values at the beginning of composting. Following composting, the mass fraction of available phosphorus and available potassium content raised by 8.77% to 200.00% and 66.14% to 385.55%, respectively, with the 9∶1 (E) treatment demonstrating the highest percentage increases for both available phosphorus and available potassium.【Conclusion】Based on the comprehensive ranking results from principal component analysis and the resource utilization of forestry waste, the composting ratios of 5∶5 or 9∶1 (E) are recommended as priorities.
林业废弃物 / 猪粪 / 好氧堆肥 / 资源化利用 / 腐熟度
forestry waste / pig manure / aerobic composting / resource utilization / maturity
| [1] |
艾娟娟, 厚凌宇, 邵国栋, 等. 林业废弃物基质配方特性及其对柚木生长的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(6):1027-1037.
|
| [2] |
戴小红, 孙伟生, 樊权, 等. 农林废弃物混配基质的理化性质及其对油茶幼苗生长效应的综合评价[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2016, 25(1):54-61.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
田赟, 王海燕, 孙向阳, 等. 农林废弃物环保型基质再利用研究进展与展望[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(2):497-502.
|
| [5] |
徐鹏翔, 沈玉君, 丁京涛, 等. 规模化养猪场粪污全量收集及贮存工艺设计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(9):255-262.
|
| [6] |
陈广银, 董金竹, 吴佩, 等. 不同贮存方式对猪粪水理化特性的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2022, 43(4):38-46.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
刘超, 徐谞, 顾文文, 等. 典型畜禽粪便配伍食用菌菌渣堆肥研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(21):84-90.
|
| [9] |
周文兵, 刘大会, 朱端卫. 不同调理剂对猪粪堆肥过程及其养分状况的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2004, 23(4):421-425.
|
| [10] |
张继宁, 吕凡, 邵立明, 等. 木炭对污泥堆肥有机质减量和腐熟度的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(4):577-581.
|
| [11] |
王义祥, 李波, 叶菁, 等. 生物炭添加对猪粪菌渣堆肥过程中Cu、Zn的钝化作用[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(5):1176-1184.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
李磊, 王淑琦, 郭小平, 等. 初始粒径和外源添加剂对绿化废弃物堆肥腐熟效果的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(10):2804-2812.
|
| [14] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
张雯琪, 李建安, 吴玲利, 等. 油茶低产林改造剩余物的发酵堆肥技术[J]. 经济林研究, 2022, 40(3):46-54.
|
| [17] |
商佳胤, 李凯, 王丹, 等. 不同湿度葡萄冬剪废弃物堆肥效果研究[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2021(5):55-59.
|
| [18] |
谢胜禹, 余广炜, 潘兰佳, 等. 添加生物炭对猪粪好氧堆肥的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(6):1365-1372.
|
| [19] |
黄光群, 黄晶, 张阳, 等. 沼渣好氧堆肥种子发芽指数快速预测可行性分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(5):177-182.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
柴晓利, 张华, 赵由才, 等. 固体废物堆肥原理与技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
周江明, 王利通, 徐庆华, 等. 适宜猪粪与菌渣配比提高堆肥效率[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(7):201-207.
|
| [25] |
黄向东, 韩志英, 石德智, 等. 畜禽粪便堆肥过程中氮素的损失与控制[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(1):247-254.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
王洁洁, 杨金艳, 陈步涨, 等. 优化好氧发酵木屑添加量提升污泥再利用潜力[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(3):662-670.
|
| [28] |
马利民, 陈玲, 吕彦, 等. 污泥土地利用对土壤中重金属形态的影响[J]. 生态环境, 2004, 13(2):151-153.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
杨婷, 钟全林, 李宝银, 等. 短期铵态氮与硝态氮配施对刨花楠幼苗生长及叶片性状的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(1):25-32.
|
| [31] |
单德鑫, 李淑芹, 许景钢. 好氧堆肥对难溶性磷转化的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(1):146-150.
|
| [32] |
席北斗, 李英军, 刘鸿亮, 等. 温度对生活垃圾堆肥效率的影响[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2005, (7): 33-36.
|
| [33] |
冯海萍, 曲继松, 杨冬艳, 等. C/N比对枸杞枝条基质化发酵堆体腐熟效果的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2014, 51(6):1112-1118.
|
| [34] |
赵啸林, 刘朝斌, 耿增超, 等. 菌剂和辅料对核桃青皮堆肥进程及腐熟度的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2023, 38(2):153-159,216.
|
| [35] |
秦莉, 沈玉君, 李国学, 等. 不同C/N比对堆肥腐熟度和含氮气体排放变化的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(12):2668-2673.
|
| [36] |
丁晓艳, 王越, 王宁, 等. 外接堆肥微生物在餐厨废弃物好氧堆肥中的应用[J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(5):47-55.
|
| [37] |
徐宏强, 沈加禾, 张焕朝, 等. 银杏残叶添加比例对猪粪好氧堆肥的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(1):39-43.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |