 PDF(2524 KB)
PDF(2524 KB)


1990—2020年长江源地区生态环境质量动态变化及驱动力分析
王天宏, 蒋馥根, 龙依, 邓目丽, 孙华
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 110-118.
 PDF(2524 KB)
PDF(2524 KB)
 PDF(2524 KB)
PDF(2524 KB)
1990—2020年长江源地区生态环境质量动态变化及驱动力分析
Dynamic changes and driving forces of ecological environment quality in the source region of the Yangtze River from 1990 to 2020
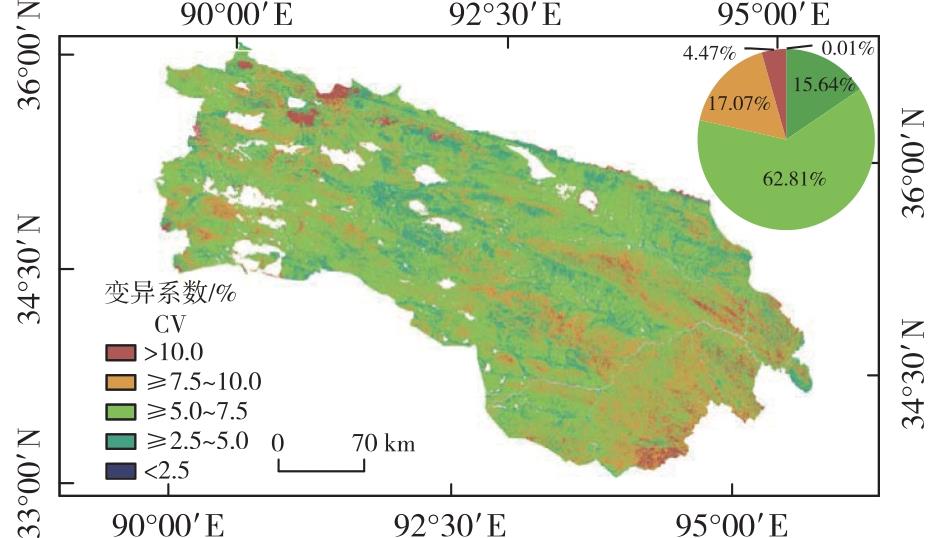
【目的】高效监测长江源地区生态环境质量的时空分布特征及其变化趋势,对维护三江源地区生态环境质量、制定长期且有效的生态保护恢复措施具有重要意义。由于遥感影像空间分辨率和数据获取及处理的限制,大区域遥感生态指数(remote sensing ecological index,RSEI)评价仍然存在局限性,需要完善方法,发挥其快速、客观、高效、可视化和可预测的优势。【方法】以Landsat系列影像为数据源,基于云端运算平台Google Earth Engine(GEE)快速云计算获取1990—2020年植被生长季(6—9月)长江源地区的遥感影像,并计算区域长时间序列RSEI。使用变异系数、Sen+MK趋势分析、Hurst指数及趋势分析法,对长江源地区RSEI稳定性、时空变化特征、未来演化趋势及驱动力进行分析。【结果】①1990—2020年长江源地区RSEI主要分布于0.4~0.6,空间尺度上呈东高西低、南高北低的分布特征;②长江源地区RSEI变异系数均值为6.52%,表明东部和西部地区变化相对剧烈,中部地区变化相对稳定。RSEI整体呈现缓慢波动增加的趋势,年平均增速为0.004 7。在空间上,RSEI呈现整体改善,其中改善的区域占研究区面积的83.63%。③长江源地区RSEI的Hurst指数平均值为0.53,未来变化持续性强于反持续性。长江源地区生态环境质量未来变化以持续改善为主,但整体趋势性偏弱,仍然存在退化的风险。④长江源地区RSEI与气温、夜间灯光指数、潜在蒸散发量均表现为正相关,表明自然因子和人类活动在一定程度上均能够影响生态环境质量改善。【结论】使用GEE获取遥感数据并结合时间序列数据分析,有快速监测大尺度生态环境质量的潜力,可以为三江源地区生态环境监测和保护提供参考。
【Objective】Accurately and efficiently monitoring the spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of the ecological environment quality and its evolving trends in the source area of the Yangtze River is of great significance for maintaining the high-standard protection of the ecological environment. It also serves as a fundamental basis for formulating long-term and effective ecological protection and restoration strategies in the Sanjiangyuan region. The remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) has distinct advantages over traditional evaluation methods relying on single monitoring indices. It boasts rapid assessment capabilities, objectivity, high efficiency, strong visual interpretability, and reliable predictability. Nevertheless, the spatial resolution constraints and the complexity of data acquisition and processing in remote sensing images still present challenges to the large-scale and accurate evaluation of the RSEI.【Method】In this study, the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform was utilized, with Landsat series images as the data source. Remote sensing images of the Yangtze River source area during the vegetation-growing season (from June to September) from 1990 to 2020 were obtained. Subsequently, long-time-series RSEI data were calculated. To comprehensively analyze the RSEI in the Yangtze River source area from 1990 to 2020, the coefficient of variation was applied to measure its stability, the Sen + Mann-Kendall (Sen + MK) trend analysis was used to explore the spatio-temporal change trends, the Hurst index was employed to predict future evolution, and the trend analysis method was adopted to identify the driving forces behind these changes.【Result】(1) From 1990 to 2020, the RSEI values in the Yangtze River source region were predominantly distributed within the range of 0.4-0.6. Geographically, the region exhibited a clear pattern where the RSEI values were higher in the eastern and southern parts and lower in the western and northern parts.(2) The average coefficient of variation of the RSEI in the source region was 6.52%. This indicates that the ecological environment in the eastern and western regions underwent relatively more pronounced fluctuations, while the central region remained relatively stable. Overall, the RSEI showed a slow oscillating trend, with an average annual growth rate of 0.004 7. Spatially, the RSEI presented an overall upward trend, and the area with improved ecological conditions accounted for 83.63% of the total study area.(3) The average Hurst index value of the RSEI in the source region was 0.53, implying that the future changes of the RSEI were more likely to be continuous rather than show anti-sustainability. The future ecological environment quality in the Yangtze River source region was expected to experience continuous improvement, yet the overall trend was relatively mild, and there still existed an underlying risk of degradation.(4) In the Yangtze River source region, the RSEI was positively correlated with air temperature, night-light index, and potential evapotranspiration. This reveals that both natural factors and human activities had a certain degree of influence on the enhancement of the ecological environment quality.【Conclusion】The integration of using GEE for remote sensing data acquisition and time-series data analysis has significant potential for rapidly and comprehensively monitoring the ecological environment quality on a large scale. This approach can offer valuable references and technical support for ecological monitoring and protection efforts in the Sanjiangyuan area, thereby contributing to the sustainable development of the regional ecological environment.
长江源地区 / 遥感生态指数(RSEI) / 生态环境质量 / Google Earth Engine(GEE) / Hurst指数
Yangtze River source region / remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) / ecological environment quality / Google Earth Engine (GEE) / Hurst index
| [1] |
樊江文, 邵全琴, 刘纪远, 等. 1988—2005年三江源草地产草量变化动态分析[J]. 草地学报, 2010, 18(1):5-10.
|
| [2] |
张彩红, 薛伟, 辛颖, 等. 基于层次分析法的贵州玉舍国家森林公园休养地适宜度评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(2):215-219.
|
| [3] |
任继周, 林慧龙. 江河源区草地生态建设构想[J]. 草业学报, 2005, 14(2):1-8.
|
| [4] |
陈兴, 余正勇. 三江源国家公园生态保护研究进展与展望[J]. 国土资源科技管理, 2022, 39(2):13-24.
|
| [5] |
刘栩位, 周启刚, 周浪, 等. 基于RSEI的三峡库区重庆段水土保持生态功能区生态环境质量动态监测[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(5):278-286.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
徐涵秋. 区域生态环境变化的遥感评价指数[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(5):889-897.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
李婷婷, 马超, 郭增长. 基于RSEI模型的贺兰山长时序生态质量评价及影响因素分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(4):1154-1165.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
叶有华, 梁永贤, 沈一青, 等. 《生态环境状况评价技术规范(试行)》中若干值得商榷的问题[J]. 热带地理, 2009, 29(4):404-406.
|
| [14] |
陈炜, 黄慧萍, 田亦陈, 等. 基于Google Earth Engine平台的三江源地区生态环境质量动态监测与分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2019, 21(9):1382-1391.
|
| [15] |
赵慧芳, 曹晓云. 三江源国家公园植被覆盖时空变化及其气候驱动因素[J]. 高原气象, 2022, 41(2):328-337.
|
| [16] |
许茜, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 等. 近40 a三江源地区土地利用变化动态分析及预测[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(3):695-704.
|
| [17] |
李璠, 颜亮东, 赵梦凡, 等. 三江源地区生长季降水特征对土壤水分的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(6):121-128.
|
| [18] |
张妹婷, 翟永洪, 张志军, 等. 三江源区草地生态系统质量及其动态变化[J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(1):75-81.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
李洪果, 陈达镇, 许靖诗, 等. 濒危植物格木天然种群的表型多样性及变异[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(4):69-83.
|
| [21] |
黄晓军, 祁明月, 李艳雨, 等. 关中地区PM2.5时空演化及人口暴露风险[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12):5245-5255.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
徐嘉昕, 房世波, 张廷斌, 等. 2000—2016年三江源区植被生长季NDVI变化及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2020, 32(1):237-246.
|
| [24] |
周侃, 张健, 虞虎, 等. 国家公园及周边地区人为扰动强度的时空变化与驱动因素:以三江源国家公园为例[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(14):5574-5585.
|
| [25] |
桑国庆, 唐志光, 邓刚, 等. 基于MODIS NDVI时序数据的湖南省植被变化研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2021, 30(5):1100-1109.
|
| [26] |
徐丽娇, 胡泽勇, 赵亚楠, 等. 1961—2010年青藏高原气候变化特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2019, 38(5):911-919.
|
| [27] |
卢明星, 徐传红, 朱咏莉, 等. Cd诱导土壤ALP的Hormesis效应:土地利用变化的驱动机制[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(2):173-180.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
赵风华, 于贵瑞. 陆地生态系统碳-水耦合机制初探[J]. 地理科学进展, 2008, 27(1):32-38.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |