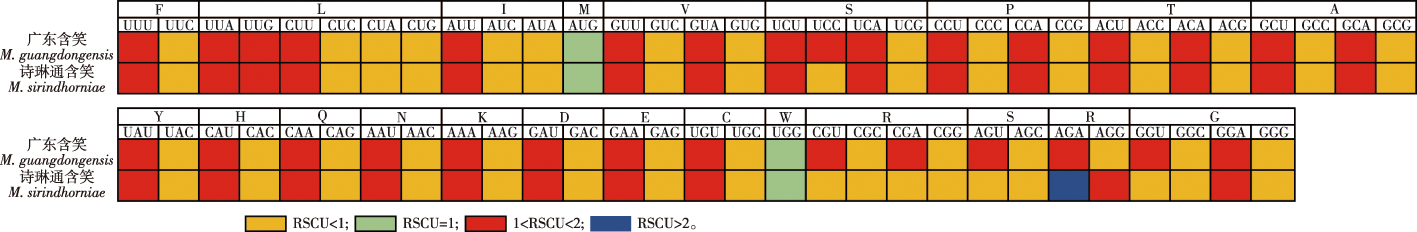
【目的】研究广东含笑(Michelia guangdongensis)和诗琳通含笑(M. sirindhorniae)的叶绿体全基因组序列,并对55种木兰科植物进行系统发育分析,为木兰科植物分类及广东含笑、诗琳通含笑遗传资源保护研究提供参考。【方法】使用高通量测序技术对广东含笑和诗琳通含笑进行叶绿体全基因组测序,获得测序结果后使用SOAPnuke 1.3.0和SPAdes 3.10.1进行组装,使用GeSeq进行基因注释, 最终获得广东含笑、诗琳通含笑叶绿体基因组序列完整的注释。注释的序列提交至GenBank,广东含笑和诗琳通含笑获得的登录号分别是MT800938、MT7876670根据注释结果,使用Chloroplot绘制叶绿体基因组结构图,用Geneious 7.1.4软件计算GC含量,使用MEGA 7.0.26检测出相对同义密码子使用频率,运用mVISTA在线软件比较叶绿体基因组序列变异,借助DnaSP 6.12.03研究基因选择压力,并基于55个木兰科叶绿体基因组中的蛋白质编码基因(protein coding gene, PCG),使用RAxML 构建了系统发育树。【结果】广东含笑、诗琳通含笑的叶绿体基因组全长分别是160 142和160 109 bp,大单拷贝区(large single-copy region, LSC)长度分别为88 170和88 137 bp,小单拷贝区(small single-copy region, SSC) 长度分别为18 822和18 810 bp,反向重复区(inverted repeat, IR)长度分别为26 575和26 581 bp。广东含笑、诗琳通含笑叶绿体基因组的总GC含量均为39.24%,成功注释基因均有112个,均包括78个蛋白质编码基因,30个tRNA基因,4个rRNA基因。【结论】对比发现广东含笑和诗琳通含笑的叶绿体基因组大小、PCT类型、结构与近源种高度相似。广东含笑、诗琳通含笑和另外53种木兰科植物种叶绿体PCG共同构建系统发育树显示,广东含笑和诗琳通含笑同在含笑属分支,首次从叶绿体基因组层面上证明诗琳通含笑属于含笑属。
【Objective】This study investigated the complete chloroplast genome sequences of Michelia guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae to explore their genomic characteristics and facilitate the comprehensive phylogenetic analysis alongside 55 other species within the family Magnoliaceae. The study aimed to provide robust genetic resource references to support the taxonomic classification of Magnoliaceae and to determine strategies for the conservation of the genetic resources of these two Michelia species, both of which hold ecological and botanical significance. 【Method】 A high-throughput sequencing technology was employed to sequence the chloroplast genomes of M. guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae. The sequencing data was processed and assembled using SOAPnuke 1.3.0 and SPAdes 3.10.1 to reconstruct the complete chloroplast genome sequences. The gene annotation was conducted using the GeSeq annotation tool, ensuring that both structural and functional gene information was comprehensively identified and recorded. This annotation process resulted in the full, detailed chloroplast genome sequences for both species. These annotated genome sequences were subsequently submitted to GenBank, with accession numbers MT800938 for M. guangdongensis and MT787667 for M. sirindhorniae. The structural analysis of the chloroplast genome was conducted using the Chloroplot visualization tool, which enabled the generation of detailed graphical representations of the genome structures. Geneious 7.1.4 was employed to calculate the GC(Guanine & Cytosine) content of the genomes, which serves as an important indicator of genomic stability and evolution. Relative synonymous codon usage, a metric often associated with translational efficiency and gene evolution, was analyzed using MEGA 7.0.26. mVISTA was employed for comparative genomic analysis, allowing for the exploration of sequence variations between the chloroplast genomes of these two species and other related species. Gene selection pressure, indicative of evolutionary pressures on individual genes, was analyzed using DnaSP 6.12.03. Finally, to elucidate the phylogenetic relationships within the Magnoliaceae family, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the protein-coding sequences from the chloroplast genomes of 55 species, including M. guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae. This analysis was performed using RAxML, which provided a maximum likelihood framework for the construction of highly accurate phylogenetic trees. 【Result】The complete chloroplast genome of M. guangdongensis was found to be 160 142 base pairs (bp) in length, while that of M. sirindhorniae was slightly shorter, at 160 109 bp. Both genomes exhibited a typical quadripartite structure consisting of a large single-copy (LSC) region, a small single-copy (SSC) region, and two inverted repeat (IR) regions. Specifically, the LSC regions were 88 170 and 88 137 bp in length for M. guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae, respectively. The SSC regions measured 18 822 and 18 810 bp, while the IR regions were nearly identical, at 26 575 and 26 581 bp. The GC content, a key indicator of genome composition and function, was found to be 39.24% for both species. Chloroplast genome annotation identified a total of 112 genes in each species. These included 78 protein-coding genes, 30 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, and 4 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes. The high degree of similarity in genome size, structure, and composition between these two species underscores their close evolutionary relationship and aligns with observations made in other species within the genus Michelia. The comparative analysis using mVISTA revealed that the chloroplast genomes of M. guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae share high levels of conservation with other members of Magnoliaceae, particularly in coding regions. However, some sequence variations were observed, predominantly in intergenic spacer regions, which can provide valuable insights into species-specific adaptations and evolutionary divergence. Selection pressure analysis using DnaSP revealed that most protein-coding genes in the chloroplast genomes were under purifying selection, consistent with the evolutionary conservation observed in chloroplast genomes across plant species. The phylogenetic tree constructed from the protein-coding genes of the chloroplast genomes provides new insights into the taxonomic positioning of M. guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae. Both species were clustered within the same branch of the genus Michelia, confirming their close genetic relationship. Remarkably, this study marks the first instance of placing M. sirindhorniae definitively within the genus Michelia at the chloroplast genome level. This finding not only enhances our understanding of the evolutionary history of these species but also provides a more accurate framework for their taxonomic classification within Magnoliaceae. 【Conclusion】The analysis of the chloroplast genome sequences of M. guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae significantly enhances our understanding of their genomic structure and evolutionary relationships. The observed high similarity in genome size, structure, and GC content between these two species aligns with the general characteristics of the genus Michelia. Furthermore, the phylogenetic analysis based on protein-coding genes provides compelling evidence for the placement of M. sirindhorniae within Michelia. This study enriches the genetic resource base for the family Magnoliaceae and offers valuable insights into the conservation and classification of these ecologically important species. Future studies can expand on these findings by incorporating additional molecular markers and sequencing data from nuclear genomes to further refine the taxonomic and phylogenetic frameworks for Magnoliaceae. Conservation strategies for M. guangdongensis and M. sirindhorniae should leverage the genetic insights gained from this study to ensure the sustainable preservation of their unique genetic resources in the face of habitat loss and environmental change.
 PDF(14780 KB)
PDF(14780 KB)


 PDF(14780 KB)
PDF(14780 KB)
 PDF(14780 KB)
PDF(14780 KB)