 PDF(1308 KB)
PDF(1308 KB)


喀斯特原生林9个树种水力学性状与解剖结构对树干液流的影响
叶雨艳, 丁访军, 吴鹏, 周华, 李源永, 周汀, 崔迎春
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6) : 111-120.
 PDF(1308 KB)
PDF(1308 KB)
 PDF(1308 KB)
PDF(1308 KB)
喀斯特原生林9个树种水力学性状与解剖结构对树干液流的影响
Effects of hydraulics and anatomical structure on sap flow of nine tree species in Karst primary forest
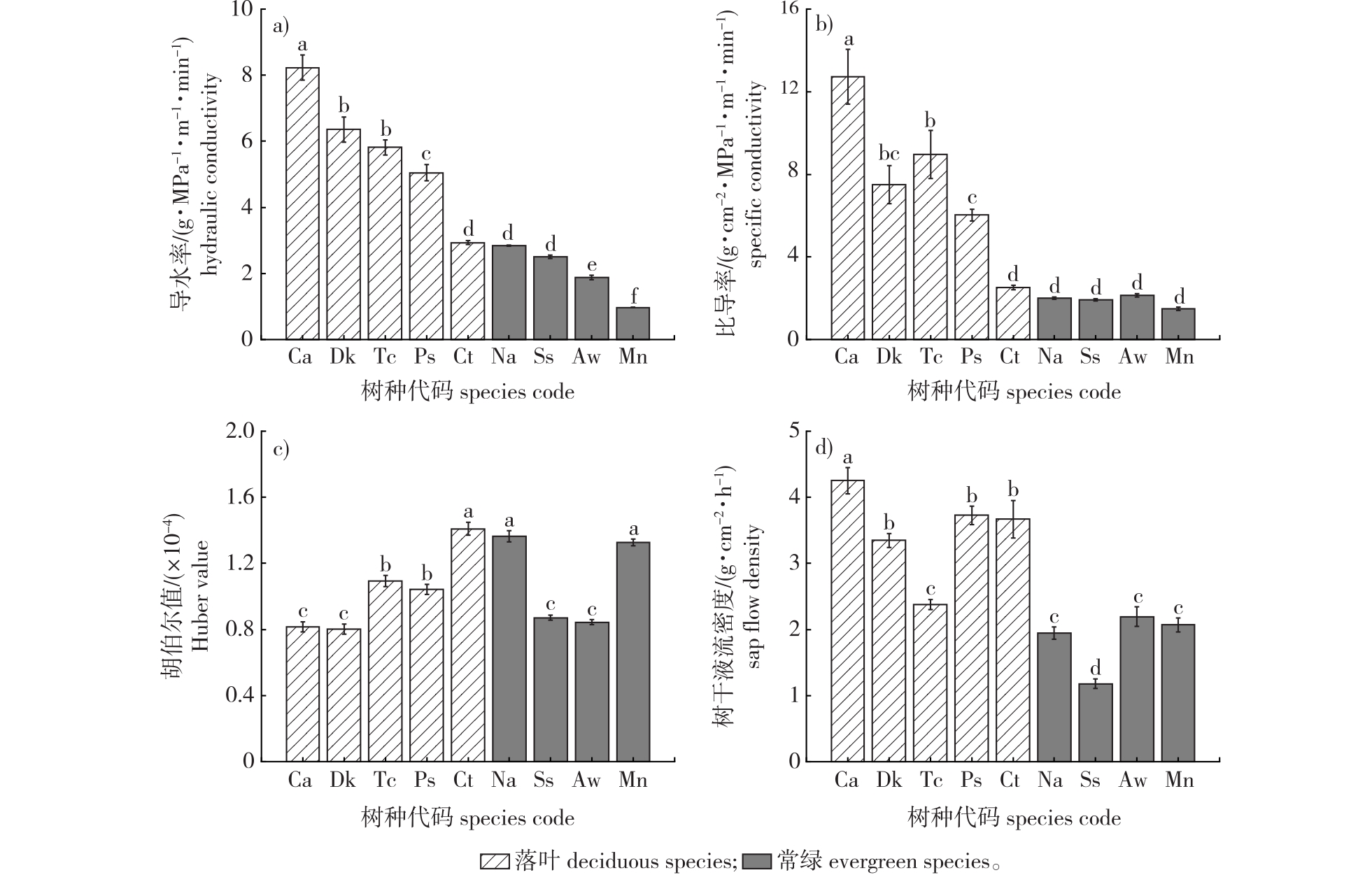
【目的】揭示茂兰喀斯特森林主要树种水力结构和解剖结构特征及其对树干液流密度的影响。【方法】以茂兰喀斯特森林9个树种为研究对象,用“冲洗法”测定其导水率(Kh)、比导率(Ks)、胡伯尔值(Hv);以解剖学方法测定其导管面积(A)、导管直径(D)、导管水力学直径(Dh)、导管密度(WD)、管胞壁厚度(WVD)等解剖结构参数;采用热扩散探针法监测树干液流密度(Js),并对已测的几个指标进行排序,比较各树种抗旱能力强弱。【结果】①Kh从大到小表现为南酸枣(Choerospondias axillaris)>柿(Diospyros kaki)>山乌桕(Triadica cochin chinensis)>化香(Platycarya strobilacea)>鹅耳枥(Carpinus turczaninovii)>新木姜子(Neolitsea aurata)>山矾(Symplocos sumuntia)>天峨槭(Acer wangchii)>润楠(Machilus nanmu);Ks从大到小表现为南酸枣>山乌桕>柿>化香>鹅耳枥>天峨槭>新木姜子>山矾>润楠;Hv表现为鹅耳枥>新木姜子>润楠>山矾>化香>山乌桕>天峨槭>南酸枣>柿,落叶树种的Kh和Ks大于常绿树种;②除鹅耳枥外,落叶树种的导管面积、直径、水力直径均大于常绿树种,而导管密度则相反;③各树种的Kh、Ks、Hv与Js的相关性均不显著(P>0.05),山乌桕树干液流密度与水力直径呈显著正相关(P<0.05),而天峨槭与水力直径呈显著负相关(P<0.05),山矾的液流密度与导管密度呈显著正相关(P<0.05),其余树种的解剖结构与树干液流密度相关性均不显著(P>0.05);④树种抗旱能力随导管直径的增大而增加,从大到小表现为南酸枣>山乌桕>柿>化香>鹅耳枥>新木姜子>山矾>润楠>天峨槭。【结论】茂兰喀斯特森林中落叶树种的导水、输水和抗旱能力均强于常绿树种。水分充足时,水力学性状对树干液流密度的影响较小,而解剖结构对其影响存在种间差异;优势树种通过增大单位横截面积上的蒸腾拉力抵消树高带来水分运输阻力,为叶片蒸腾和光合作用供给水分。在进行喀斯特植被恢复时应综合考虑落叶、常绿及林分垂直结构的群落配比。
【Objective】This study aims to explore the hydraulic and anatomical characteristics of predominant tree species in the Maolan Karst Forest and their impact on sap flow density.【Method】The hydraulic conductivity (Kh), specific conductivity (Ks), and Huber value (Hv) of nine tree species in the Maolan Karst Forest were determined through the ‘washing method’. Anatomical structure parameters such as vessel area (A), vessel diameter (D), hydraulic vessel diameter (Dh), vessel density (WD), and vessel wall thickness (WVD) were assessed using anatomical techniques. The thermal diffusion probe method was employed to monitor the sap flow density (Js) of the tree trunks. The measured indexes were subsequently ranked via the subordinate function method to discern drought resistance.【Result】(1)The Kh value behaved Choerospondias axillaris> Diospyros kaki> Triadica cochinchinensis> Platycarya strobilacea > Carpinus turczaninovii > Neolitsea aurata > Symplocos sumuntia > Acer wangchii> Machilus nanmu, the Ks value behaved C. axillaris > T. cochinchinensis > D. kaki > P. strobilacea > C. turczaninovii > A. wangchii > N. aurata > S. sumuntia> M. nanmu, and the Hv value behaved C. turczaninovii > N. aurata > M. nanmu > S. sumuntia > P. strobilacea > T. cochinchinensis > A. wangchii > C. axillaris > D. kaki, the Kh and Ks values of deciduous trees are higher than those of evergreen trees. (2) In addition to C. turczaninowii, the vessel area, vessel diameter and hydraulic diameter value of eight trees revealed that deciduous trees were lager than evergreen trees. In contrast, the vessel density of evergreen trees was larger than that of deciduous trees; overall, the relevance of nine anatomical parameters varied between trees. (3) No significant correlation was found between the Kh, Ks, Hv of the nine trees and sap flow density (P<0.05), Sap flow density of T. chinensis showed a significantly positive correlation with vessel hydraulic diameter(P<0.05), while that of A. wangchii indicated a significantly negative correlation(P<0.05). Conversely, the sap flow density of S. sumuntia positively correlated with vessel density (P<0.05), but the sap flow density of the remaining six species didn’t significantly correlate with anatomical structure parameters (P>0.05); (4) Drought resistance of the nine species increased with vessel diameter, ranking as follows: C. axillaris> T. cochin chinensis > D. kaki> P. strobilacea > C. turczaninovii > N. aurata> S. sumuntia> M. nanmu> A. wangchii.【Conclusion】The water conductivity, water transport, and drought resistance of the nine studied species were superior to evergreens. While water availability was ample, the hydraulic traits minimally impacted the sap flow density, whereas the anatomical structure variably influenced it. The dominant species managed to counterbalance the water transport resistance caused by tree height by boosting transpiration tension per unit cross-sectional area, thus facilitating leaf transpiration and photosynthesis. For the effective restoration of Karst vegetation, it is essential to consider the community ratio of deciduous to evergreen species and the stand vertical structure.
茂兰喀斯特森林 / 树干液流密度 / 水力学性状 / 解剖结构 / 抗旱能力
Maolan Karst forest / sap flow density / hydraulic trait / anatomy structure / drought resistance capacity
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
洪震, 刘术新, 洪琮浩, 等. 5种造林树种对干旱胁迫的抗性应答[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(2):111-119.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
刘娟娟, 张建国, 李吉跃, 等. CO2浓度升高对4种乔木幼树水力结构的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(7):1769-1776.
|
| [7] |
郑茹萍, 张马啸, 吴亚岚, 等. 杉木不同形态特征对水力结构的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2023, 43(1):17-25.
|
| [8] |
李吉跃, 翟洪波. 木本植物水力结构与抗旱性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2000, 11(2):301-305.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
龙翠玲. 不同地形部位喀斯特森林物种多样性的比较研究:以贵州茂兰自然保护区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2007, 26(1):55-60.
|
| [12] |
朱秀勤. 石林溶丘洼地区不同恢复阶段植物水分利用的稳定同位素研究[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2014.
|
| [13] |
梁千慧. 不同水分条件下黑麦草对喀斯特土壤深度的生长与生理响应[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016.
|
| [14] |
张启伟. 北热带喀斯特山地不同坡位木本植物的水力结构与功能[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2021.
|
| [15] |
程娟, 丁访军, 谭正洪, 等. 贵州茂兰喀斯特森林两树种叶片气孔形态特征及其对蒸腾的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(5):125-132.
|
| [16] |
袁丛军, 程娟, 丁访军, 等. 喀斯特森林优势树种蒸腾特征及其对气孔和气象因子的响应[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(7):96-105.
|
| [17] |
李成龙, 刘延惠, 丁访军, 等. 茂兰喀斯特森林小果润楠蒸腾特征及影响因素[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(3):51-58.
|
| [18] |
吴鹏, 杨文斌, 崔迎春, 等. 喀斯特区天峨槭(Acer wangchii)树干液流特征及其与环境因子的相关分析[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(22):7552-7567.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
樊大勇, 谢宗强, 赵常明, 等. 一种测定木本植物最大水力导度的装置及其使用方法[P]. 2015-11-11.
|
| [21] |
熊仕发, 吴立文, 陈益存, 等. 不同种源白栎幼苗叶片对干旱胁迫的响应及抗旱性评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(12):3924-3933.
|
| [22] |
车路平. 14个造林树种木质部、叶片解剖特征及抗旱性评价[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
赵延涛, 许洺山, 张志浩, 等. 浙江天童常绿阔叶林不同演替阶段木本植物的水力结构特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(2):116-126.
|
| [25] |
王佳敏, 成应杰, 陈金艺, 等. 模拟不同降雨时间格局下喀斯特垂直异质生境对桢楠幼苗光合和生长的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(18):7348-7356.
|
| [26] |
李吉跃, 翟洪波, 刘晓燕. 树木水力结构特征的昼夜变化规律[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2002, 24(4):39-44.
|
| [27] |
黄恺翔, 俞重阳, 钱海蓉, 等. 鸡公山国家级自然保护区散孔材、环孔材树种木质部结构和功能的关系[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(2):244-251.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
谭凤森. 桂西南北热带喀斯特季雨林木本植物的水力学特征研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019.
|
| [33] |
刘晓静, 赵平, 王权, 等. 树高对马占相思整树水分利用的效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(1):13-19.
|
| [34] |
赵平, 孙谷畴, 倪广艳, 等. 成熟马占相思水力导度对水分利用和光合响应的季节性差异[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(1):49-56.
|
| [35] |
倪鸣源. 中亚热带喀斯特天然林树种枝条木质部性状与生长速率的相关性研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2021.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
樊大勇, 谢宗强. 木质部导管空穴化研究中的几个热点问题[J]. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(1):126-132.
|
| [38] |
陈昭. 润楠属枝条和叶片的水力特征及协同关系[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2018.
|
| [39] |
陈模舜, 柯世省, 杨勇宇, 等. 珍稀濒危植物天台鹅耳枥营养器官的解剖学研究[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2010, 30(5):14-19.
|
| [40] |
韩丽娟, 周春丽, 吴树明. 国产胡桃科次生木质部导管分子的比较解剖及其系统位置的讨论[J]. 西北植物学报, 2002, 22(6):146-151,296.
|
| [41] |
张瑞婷, 杨金艳, 阮宏华. 树干液流对环境变化响应研究的整合分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5):113-120.
|
| [42] |
王连春. 酸枣荆条液流特征及其耗水尺度扩展研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2013.
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
宋波, 董豪, 全飞, 等. 橡胶树干CO2释放速率垂直变化及其与树干液流和木质部结构间的关系[J]. 热带生物学报, 2022, 13(1):1-6.
|
| [45] |
王秀伟, 毛子军. 输导组织结构对液流速度和树干CO2释放通量的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2013, 35(4):9-15.
|
| [46] |
刘春鹏, 马长明, 王连春, 等. 酸枣荆条耗水特征及其茎木质部解剖构造[J]. 水土保持通报, 2017, 37(5):92-97.
|
| [47] |
赵培强, 赵平, 牛俊峰, 等. 华南地区常见树种导管特征与树干液流的关系[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2014, 22(6):537-548.
|
| [48] |
方菁, 叶琳峰, 陈森, 等. 自然和人工生境被子植物枝木质部结构与功能差异[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(6):650-658.
|
| [49] |
董彦君, 李宗善, 陈颖, 等. 黄耆属草本植物根部导管结构对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(12):2936-2943.
|
| [50] |
张新英, 曹宛虹. 生长在不同生境下的沙棘次生木质部解剖学的研究[J]. 植物学报, 1990, 32(12):909-915,993-994.
|
| [51] |
张海昕. 几个杨属无性系木质部导管结构与栓塞脆弱性研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2013.
|
| [52] |
张硕新, 申卫军, 张远迎, 等. 几个抗旱树种木质部栓塞脆弱性的研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 1997, 12(2): 1-6.
|
| [53] |
艾绍水, 李秧秧, 陈佳村, 等. 陕北沙地3种典型灌木根木质部解剖结构及水力特性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(11):3277-3284.
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
周朝彬, 辛慧慧, 宋于洋. 梭梭次生木质部解剖特征及其可塑性研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2014, 29(2):207-212.
|
| [56] |
刘娟娟, 李吉跃, 王继强. 北京城市绿化树种的水力结构特征[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2006, 28(S1):38-46.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |