 PDF(3567 KB)
PDF(3567 KB)


 PDF(3567 KB)
PDF(3567 KB)
 PDF(3567 KB)
PDF(3567 KB)
松花江百里生态长廊生境网络构建研究
Research on the construction of ecological corridor habitat network in Songhua River
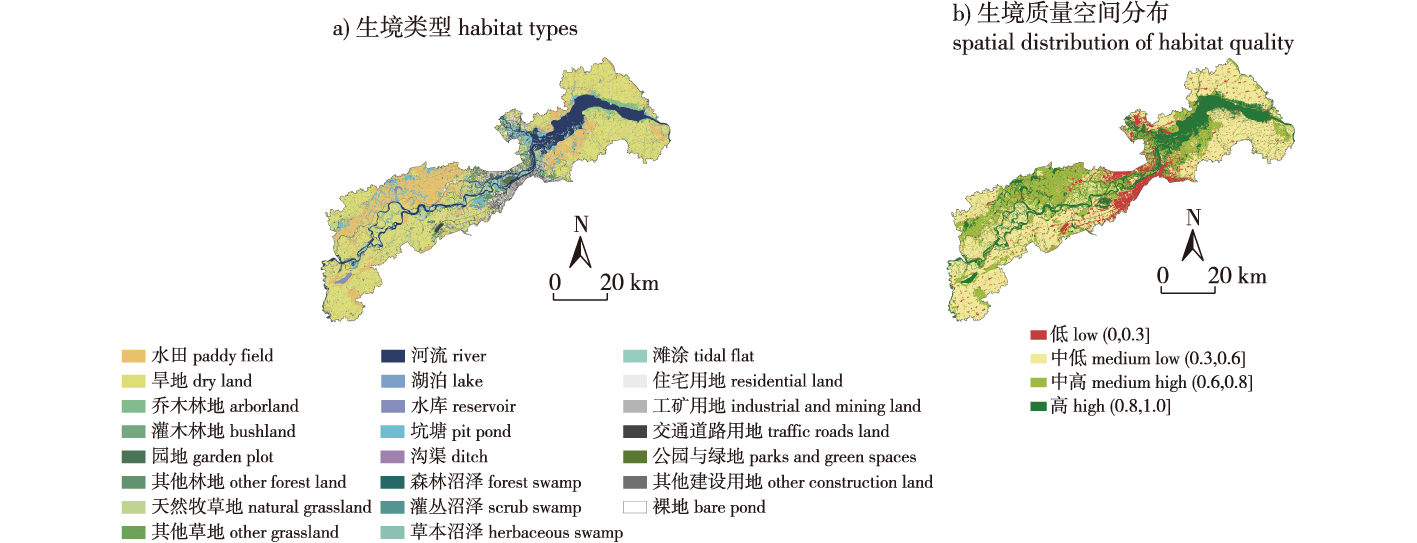
【目的】松花江百里生态长廊生态环境多样、生物资源丰富,研究其生境网络构建与分级,有助于提升区域内的生物多样性和生态健康稳定性。【方法】以松花江百里生态长廊为研究对象,首先识别区域生境类型,并基于InVEST分析评估区域内生境质量状况;其次,基于焦点物种的生境适宜性分析和电路理论识别生境源地、生境廊道和生境节点,并共同构成研究区域内的生境网络;最后基于电流密度划分源地和廊道的重要等级。【结果】①松花江百里生态长廊有23类生境,生境类型丰富,同时有44.31%的区域生境质量较高;②区域内共识别82个生境源地、147条生境廊道和57个生境节点,共同构成研究区域的生境网络。③根据电流密度划分等级,其中一级生境源地有7个,面积共484.82 km2,基本位于大型自然保护区内;一级生境廊道有14条,长度共7 560 m,主要分布在松花江干流上,且廊道长度相对较短。【结论】松花江百里生态长廊总体生境状况较好,但仍需注意城市快速发展带来的生态威胁,做好发展与保护的协调工作,如:通过生境源地分级与扩充,保护并新增生境源地;通过生境廊道分级管控与疏通,保护提升廊道连通性;通过生境节点修复与新增,为生物迁徙提供“踏脚石”等,进一步优化生境网络。
【Objective】The hundred-mile ecological corridor of the Songhua River is a diverse environment with abundant biological resources. Studying the construction and classification of its habitat network is crucial for enhancing regional biodiversity and ecological stability.【Method】Using the Songhua River Ecological Corridor as a case study, we first identified regional habitat types and assessed habitat quality using the InVEST analysis. We then pinpointed habitat sources, habitat corridors, and habitat nodes based on habitat suitability analysis for focal species and circuit theory, forming a comprehensive habitat network. Lastly, we classified the importance levels of sources and corridors based on current density.【Result】(1) The corridor features 23 habitat types; 44.31% of the areas are classified as having high habitat quality. (2) The habitat network consists of 82 sources, 147 corridors and 57 nodes. (3) Analysis of current density revealed seven primary habitat sources covering 484.82 km2, primarily in large nature reserves, and 14 first-class habitat corridors totaling 7 560 meters, mainly along the main stream of the Songhua River, though the corridors are relatively short.【Conclusion】The habitat conditions in the Songhua River ecological corridor are generally favorable. However, attention must be given to ecological threats posed by rapid urban development. Effective strategies include classifying and expanding habitat sources, managing and enhancing corridor connectivity, and restoring and adding habitat nodes. These measures will optimize the habitat network and facilitate biological migration, providing essential “Stepping stones.”
生境网络 / 生境质量 / 焦点物种 / 电路理论 / 松花江流域
habitat network / habitat quality / focal species / circuit theory / Songhua River basin
| [1] |
陈婷, 雍娟, 何奥. 新加坡城市生物多样性保护经验对我国的启示[J]. 城市建筑, 2021, 18(24):163-167.
|
| [2] |
曹加杰, 傅剑玮. 基于InVEST模型和最小成本路径的城市绿色空间生境网络构建方法研究:以南京为例[J]. 中国园林, 2023, 39(1):53-58.
|
| [3] |
何文捷, 金晓玲, 胡希军. 德国生境网络规划的发展与启示[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2011, 31(7):190-194,208.
|
| [4] |
史娜娜, 韩煜, 王琦, 等. 青海省保护地生态网络构建与优化[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(6):1910-1916.
|
| [5] |
荣月静, 严岩, 王辰星, 等. 基于生态系统服务供需的雄安新区生态网络构建与优化[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(20):7197-7206.
|
| [6] |
王倩娜, 谢梦晴, 张文萍, 等. 成渝城市群区域生态与城镇发展双网络格局分析及时空演变[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(4):1380-1398.
|
| [7] |
贾一非, 王云才. 由单一走向多样:平原农业区生物多样性保护的规划途径:以辽宁省黑山县为例[J]. 中国园林, 2022, 38(7):26-31.
|
| [8] |
汪洁琼, 李心蕊, 王敏, 等. 基于水鸟栖息地保育的城市滨水生境网络构建与优化策略:以昆山市为例[J]. 风景园林, 2021, 28(6):76-81.
|
| [9] |
陆禹, 佘济云, 罗改改, 等. 基于粒度反推法和GIS空间分析的景观格局优化[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(2):534-545.
|
| [10] |
陈瑾, 赵超超, 赵青, 等. 基于MSPA分析的福建省生态网络构建[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(2):603-614.
|
| [11] |
张晓琳, 金晓斌, 韩博, 等. 长江下游平原区生态网络识别与优化:以常州市金坛区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(9):3449-3461.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
于颖, 孟京辉, 宋增明, 等. 基于MCR模型和景观连通性的县域生态网络构建[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):226-234.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
王建起. 哈尔滨松花江百里生态长廊修复实践与思考[J]. 黑龙江科技信息, 2014(22):208.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
高周冰, 王晓瑞, 隋雪艳, 等. 基于FLUS和InVEST模型的南京市生境质量多情景预测[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2022, 39(5):1001-1013.
|
| [19] |
李骞国, 王录仓, 严翠霞, 等. 基于生境质量的绿洲城镇空间扩展模拟研究:以黑河中游地区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9):2920-2931.
|
| [20] |
张梦迪, 张芬, 李雄. 基于InVEST模型的生境质量评价:以北京市通州区为例[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(6):95-99.
|
| [21] |
汤鹏, 王浩. 基于MCR模型的现代城市绿地海绵体适宜性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(3):116-122.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
赵闪闪, 褚一凡, 姜小玉, 等. 河南新乡黄河湿地鸟类国家级自然保护区苍鹭巢特征与巢址选择[J]. 四川动物, 2018, 37(3):317-323.
|
| [25] |
朱曦, 邹小平. 中国鹭类[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2001.
|
| [26] |
范培莉, 宋成祺, 李成绪, 等. 大庆龙凤湿地绿头鸭巢址选择[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(8):2232-2236.
|
| [27] |
程晓福, 殷小慧. 宁夏六盘山自然保护区环颈雉秋季栖息地的选择[J]. 野生动物, 2009, 30(4):193-196,200.
|
| [28] |
邵继峰, 鲁庆彬, 金晶, 等. 清凉峰环颈雉冬季觅食地选择[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 2008, 25(4):507-512.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
刘阳, 欧小杨, 郑曦. 整合绿地结构与功能性连接分析的城市生物多样性保护规划[J]. 风景园林, 2022, 29(1):26-33.
|
| [31] |
陈泓宇, 李雄. 基于MSPA-InVEST模型的北京中心城区绿色空间生境网络优化[J]. 风景园林, 2021, 28(2):16-21.
|
| [32] |
付凤杰, 刘珍环, 刘海. 基于生态安全格局的国土空间生态修复关键区域识别:以贺州市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(9):3406-3414.
|
| [33] |
闫玉玉, 孙彦伟, 刘敏. 基于生态安全格局的上海国土空间生态修复关键区域识别与修复策略[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(12):3369-3378.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
林美玲, 莫惠萍, 黄宇斌, 等. 基于Linkage Mapper的漳州市生态网络构建研究[J]. 林业调查规划, 2022, 47(3):85-94.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
宋利利, 秦明周. 整合电路理论的生态廊道及其重要性识别[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(10):3344-3352.
|
| [38] |
刘佳, 尹海伟, 孔繁花, 等. 基于电路理论的南京城市绿色基础设施格局优化[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(12):4363-4372.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |