 PDF(3100 KB)
PDF(3100 KB)


内蒙古半干旱地区空气与土壤加湿对植物生长微气候的影响
桑清田, 王宇, 李一丁, 张灏, 刘龙昌, 潘庆民, 刘伟, 袁文平
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 172-180.
 PDF(3100 KB)
PDF(3100 KB)
 PDF(3100 KB)
PDF(3100 KB)
内蒙古半干旱地区空气与土壤加湿对植物生长微气候的影响
Effects of air humidification and soil water addition on the microclimate of plant growth in semi-arid areas in Inner Mongolia
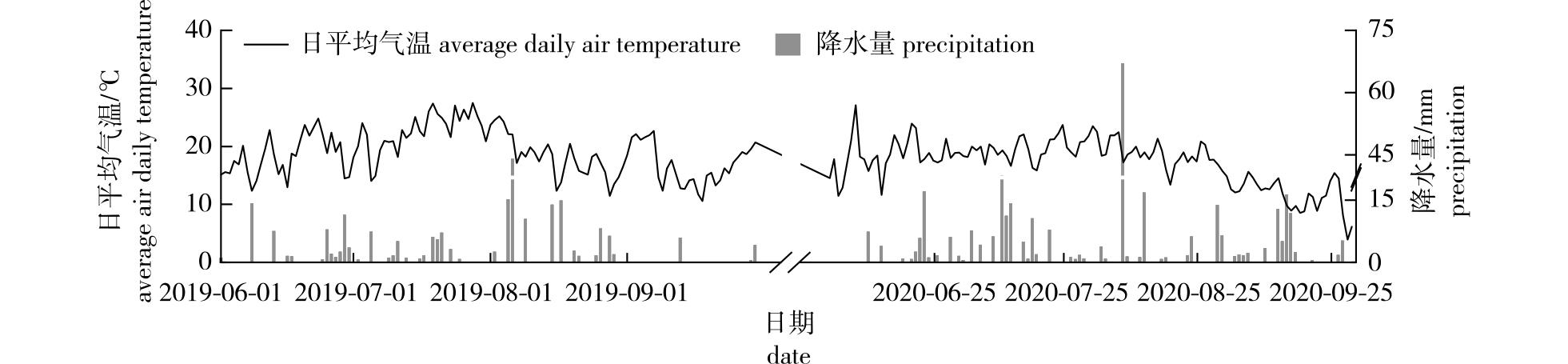
【目的】研究半干旱代表性地区高压喷雾空气加湿引起的微气候变化,为分析湿度改变对植物生长的影响提供研究基础。【方法】通过在内蒙古锡林郭勒地区建立加湿试验平台,以樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)为研究对象,在高透光塑料薄膜的开顶式围封内以高压喷雾及灌溉的方式进行空气与土壤加湿处理,对各处理的空气及土壤温湿度进行连续观测,分析空气与土壤加湿对植物生长微气候的影响。【结果】在2019和2020年樟子松生长季空气加湿均使日均空气湿度显著增加(14.18%、7.20%),日均饱和水汽压亏缺显著降低(3.74、1.98 hPa),20 cm土层含水率显著增加(2.31%、3.33%),但空气加湿总体上使空气温湿度的日变化幅度减小,对气温以及土壤温度无显著影响。土壤水分添加在2019和2020年生长季使20 cm土层含水率显著增加(2.31%、3.65%),仅在2020年生长季使日均空气湿度显著增加4.62%,对气温和土壤温度影响未达到显著水平。【结论】在不显著影响日均气温以及土壤温度的前提下,空气加湿显著提高了空气湿度与土壤含水率,显著降低了饱和水汽压亏缺,验证了在野外利用高压喷雾进行空气湿度控制实验的可行性。
【Objective】This study aims to examine the microclimate changes induced by high-pressure spray air humidification devices in typical semi-arid regions, providing a basis for understanding the effects of humidity variations on plant growth.【Method】Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica was selected as the study species. High-pressure spraying and irrigation manipulations were applied in an open-top enclosure using a high-transmittance plastic film to establish a field humidification platform in Xilin Gol, Inner Mongolia. Continuous monitoring of air and soil temperature and humidity was conducted for each treatment. The effects of air and soil humidification on the plant growth microclimate were then analyzed.【Result】During the growing seasons of 2019 and 2020, air humidification significantly increased the average daily air humidity by 14.18% and 7.20%, respectively, and reduced the average daily vapor pressure deficit by 3.74 and 1.98. Additionally, it significantly raised the soil moisture content at a depth of 20 cm by 2.31% and 3.33%, respectively. However, air humidification did not significantly affect air temperature and soil temperature. The application of air humidification generally reduced the diurnal fluctuations of both air temperature and humidity. Soil water addition significantly increased the soil moisture content at a 20 cm depth during both growing seasons (2.31% in 2019 and 3.65% in 2020) and increased the average daily air moisture by 4.62% in the 2020 growing season. However, it did not significantly affect air temperature and soil temperature.【Conclusion】Air humidification notably increased the average daily air humidity and soil water content while reducing the vapor pressure deficit. However, it did not significantly influence the daily average air temperature and soil temperature. These findings confirm the practicality of using high-pressure spray air humidification in field experiments.
三北防护林 / 野外控制实验 / 空气加湿 / 土壤水分添加 / 微气候 / 樟子松
the Three-north shelterbelt / field manipulative experiment / air humidification / soil water addition / microclimate / Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
姜大膀, 王晓欣. 对IPCC第六次评估报告中有关干旱变化的解读[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44(5):650-653.
|
| [4] |
王晨鹏, 黄萌田, 翟盘茂. IPCC AR6报告关于不同类型干旱变化研究的新进展与启示[J]. 气象学报, 2022, 80(1):168-175.
|
| [5] |
赵先丽, 李丽光, 贾庆宇, 等. 1988—2007年辽宁主要农业气象灾害分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2009, 25(2):33-37.
|
| [6] |
苏立娟, 李喜仓, 邓晓东. 1951—2005年内蒙古东部气候变化特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2008, 24(5):25-28.
|
| [7] |
牛书丽, 陈卫楠. 全球变化与生态系统研究现状与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(5):449-460.
|
| [8] |
于贵瑞, 牛书丽, 李发东, 等. 陆地生态系统环境控制实验的研究方法及技术体系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(7):2275-2289.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
李坤育. 降水增加和氮富集对温带典型草原土壤呼吸的影响[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2020.
|
| [12] |
霍治国, 白月明, 温民, 等. 水分胁迫效应对冬小麦生长发育影响的试验研究[J]. 生态学报, 2001, 21(9):1527-1535.
|
| [13] |
武静莲, 王淼, 蔺菲, 等. 降水变化和种间竞争对红松和蒙古栎幼苗生长的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(2):235-240.
|
| [14] |
赵文芹, 席本野, 刘金强, 等. 不同灌溉条件下杨树人工林蒸腾过程及环境响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(4):370-382.
|
| [15] |
白文明, 周青平, 张文浩. 青藏高原和内蒙古高原草地全球变化生态学控制实验研究比较[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 42(4):355-363.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
戚金存, 刘大泉, 刘泓, 等, 干旱胁迫及复水对槟榔幼苗形态和生理特性的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(4):615-624.
|
| [19] |
杭玉玲, 包刚, 包玉海, 等. 2000—2010年锡林郭勒草原植被覆盖时空变化格局及其气候响应[J]. 草地学报, 2014, 22(6):1194-1204.
|
| [20] |
翟培凤, 关家欣, 何鹏, 等. 沿干旱梯度樟子松人工林针叶和枝条非结构性碳水化合物及氮含量的变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(6):1518-1524.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
童思思, 孙旭, 郑飞翔, 等. 开顶式气室的内外环境差异及其对小麦生长的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2023, 42(1):17-26.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
赵晓涵, 张方敏, 韩典辰, 等. 内蒙古半干旱区蒸散特征及归因分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(6):1614-1623.
|
中国科学院内蒙古草原生态系统定位研究站窦山德等工作人员提供支持和帮助;中国科学院植物研究所吕亚香、李天琦和武运涛在野外实验中给予帮助!
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |