 PDF(1913 KB)
PDF(1913 KB)


氮磷配施对青钱柳生长及叶生物活性物质含量的影响
刘小芳, 岳喜良, 方升佐, 李晴, 孙昕
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 57-66.
 PDF(1913 KB)
PDF(1913 KB)
 PDF(1913 KB)
PDF(1913 KB)
氮磷配施对青钱柳生长及叶生物活性物质含量的影响
Effects of various ratios of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on the growth and contents of leaf bioactive substances in Cyclocarya paliurus
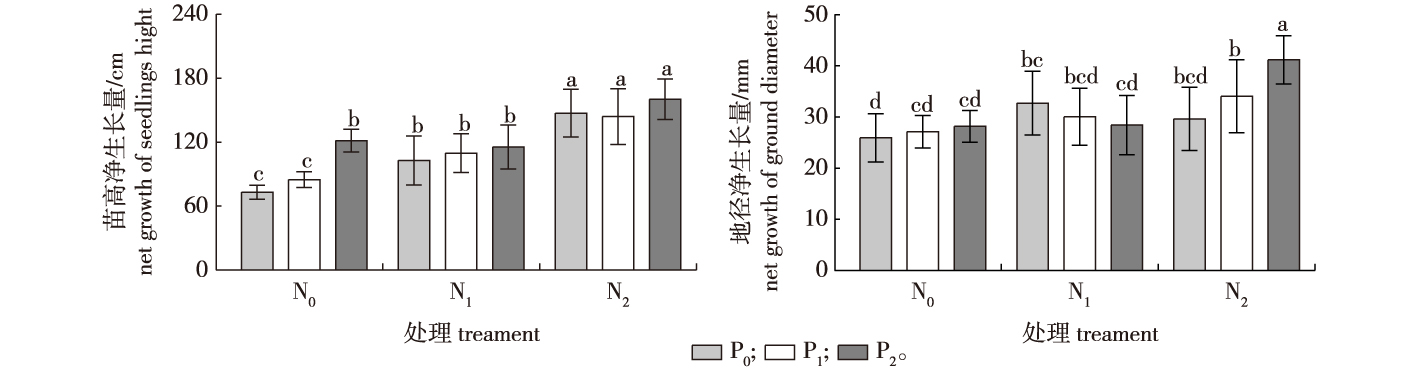
【目的】研究不同水平氮、磷肥配施对青钱柳(Cyclocarya paliurus)生长及叶生物活性物质含量的影响,为青钱柳叶用人工林的定向培育以及提高青钱柳叶生物活性物质含量提供理论依据。【方法】以江西铜鼓种源的青钱柳2年生实生苗为试验材料进行田间试验,采用双因素完全区组试验设计,设置3个施氮水平(N0、N1和N2),3个施磷水平(P0、P1和P2),共9个处理,每个处理3个重复,进行苗木生长指标和叶总黄酮、总三萜、总多酚及总多糖含量测定,采用双因素方差分析比较氮、磷及二者交互作用对相关指标的影响。【结果】氮磷配施对青钱柳幼苗高和地径生长以及叶总黄酮、总三萜、总多酚和总多糖含量均有显著(P<0.05)影响。青钱柳叶总黄酮、总三萜、总多酚含量表现出抛物线形的季节变化,均在7月达最大值,而叶总多糖含量在9月最高。与N0P0处理相比,不同氮磷配施处理均促进了林木生长,且在N2P2处理下树高和地径净生长量最大;但不同氮磷配施处理对叶生物活性物质含量影响不同,且在不同月份以及不同生物活性物质间存在差异。总体看,试验期内各处理间6月叶的总黄酮、总三萜、总多酚和总多糖含量的变化范围分别为17.01~34.25、39.11~55.77、22.74~53.98和22.36~33.24 mg/g,而10月的为16.95~35.26、38.03~54.17、19.78~33.98和23.33~32.46 mg/g。相关分析结果表明,青钱柳苗高月净生长量与对应月的叶生物活性物质含量(总黄酮、总三萜、总多酚和总多糖)相关性不显著(P>0.05),地径月净生长量与对应月的叶次生代谢物含量弱负相关但不显著(P>0.05);青钱柳苗高生长和地径生长之间,以及叶生物活性物质(总黄酮、总三萜、总多酚和总多糖)含量间均存在极显著正相关关系(P<0.01)。【结论】高水平的氮磷肥配施有利于青钱柳生长和叶总三萜含量的提高,中等水平的磷肥有利于青钱柳叶次生代谢物含量的提高,氮磷配施反而抑制青钱柳叶多糖含量;青钱柳幼树生长与其叶次生代谢物质含量之间存在权衡关系。
【Objective】This study aimed to provide a theoretical basis for the strategic cultivation of plantations, and to increase the content of bioactive substances in leaves by investigating the effects of various nitrogen and phosphorus levels on the growth and bioactive substance content in Cyclocarya paliurus leaves.【Method】The research is conducted in the field and utilized a two-factor complete block design, incorporating three levels of nitrogen application (N0, N1, N2) and three levels of phosphorus application (P0, P1, P2), creating nine treatments with three replicates each. The growth indexes of seedlings and the contents of total flavonoids, total triterpenoids, total polyphenols and total polysaccharides in leaves were determined. A two-way ANOVA was used to compare the effects of nitrogen and phosphorus and their interaction on related indexes.【Result】The study found that different ratios of nitrogen and phosphorus significantly influenced both the growth and the bioactive substance content in C. paliurus leaves (P<0.05). The contents of total flavonoids, triterpenoids, and polyphenols in the leaves exhibited a parabolic seasonal variation, peaking in July, while the highest polysaccharides content was observed in September. Compared to the control treatment (N0P0), all nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizations enhanced tree growth, with the most substantial growth in tree height and ground diameter occurring in the N2P2 treatment. The effects of nitrogen and phosphorus ratios on the bioactive substances varied, displaying differences among the substances and the sampling months sampled. The variation in the contents of total flavonoid, total triterpenoids, total polyphenols and total polysaccharides in June ranged from 17.01 to 34.25 mg/g, from 39.11 to 55.77 mg/g, from 22.74 to 53.98 mg/g, and from 22.36 to 33.24 mg/g, respectively, while in October, the ranges were 16.95-35.26, 38.03-54.17, 19.78-33.98 and 23.33-32.46 mg/g, respectively. Correlation analysis revealed no significant relationship between the monthly growth in tree height and the content of bioactive substances (total flavonoid, total triterpenoids, total polyphenols and total polysaccharides) in the leaves (P>0.05). However, weakly negative correlations were observed between the ground diameter growth and the contents of total triterpenoids and total polyphenols in the leaves (P<0.05). Notably, there were significant positive correlations between the growth of tree height and ground diameter, as well as among the different bioactive substances (P<0.01).【 Conclusion】A high ratio of nitrogen and phosphorus addition benefit the growth of C. paliurus and enhances the content of total triterpenoids in the leaves. Sole nitrogen or phosphorus supplements boost the content of secondary metabolites, whereas a combined application tends to decrease the content of total polysaccharides. There is a noticeable trade-off between the growth of C. paliurus and the content of secondary metabolites in its leaves.
Cyclocarya paliurus / fertilization / tree net growth / bioactive substances
| [1] |
吴巍, 赵军. 植物对氮素吸收利用的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(13):75-78.
|
| [2] |
张志录, 刘中华, 彭舜磊, 等. 氮磷添加对考来木光合特性和叶绿素荧光的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(3):459-467.
|
| [3] |
刘欢, 王超琦, 吴家森, 等. 氮素指数施肥对杉木无性系苗生长及养分含量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(10):3123-3128.
|
| [4] |
李树萍, 董琼, 李世民, 等. 树番茄幼苗生长及氮积累与分配对光照和氮素添加的响应[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2023, 45(1):156-168.
|
| [5] |
张小燕, 李雨菲, 刘桂华, 等. 施氮对1年生青钱柳生长和三萜类化合物积累的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(4):60-68.
|
| [6] |
刘盈盈, 张珍明, 任春光, 等. 施肥对青钱柳幼苗生长及叶片快速光响应与糖含量的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2016, 29(10):2361-2365.
|
| [7] |
刘鑫, 王天, 宋佳承, 等. 不同磷肥施用量对油橄榄根际土壤微环境及生长发育的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(6):78-87.
|
| [8] |
李军宏, 王远远, 李楠楠, 等. 水磷供应对棉花根系生长、分布及生物量的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(3):95-101.
|
| [9] |
董璐, 张永清, 杨春婷, 等. 氮磷肥配施对苦荞根系生理生态及产量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(5):947-956.
|
| [10] |
方升佐. 青钱柳产业发展历程及资源培育研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):115-126.
|
| [11] |
谢明勇, 谢建华. 青钱柳研究进展[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2008, 27(1):113-121.
|
| [12] |
方升佐, 洑香香. 青钱柳资源培育与开发利用的研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(1):95-100.
|
| [13] |
李海玲, 方升佐. 青钱柳繁殖技术研究进展[J]. 林业科技开发, 2005, 19(6):3-5.
|
| [14] |
楚秀丽. 不同种源青钱柳苗年生长及叶内含物含量研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2009.
|
| [15] |
刘洋, 秦健, 周明明, 等. 光质和基因型对青钱柳叶黄酮类化合物积累的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(3):99-104.
|
| [16] |
秦健, 刘洋, 方升佐, 等. 光质和光强对青钱柳生长和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(4):13-18.
|
| [17] |
岳喜良, 秦健, 洑香香, 等. 氮素水平对青钱柳叶片主要次生代谢物含量和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(2):35-42.
|
| [18] |
谢建华, 谢明勇, 聂少平, 等. 苯酚-硫酸法测定青钱柳中多糖含量[J]. 食品工业, 2010, 31(4):93-95.
|
| [19] |
张鑫, 邢玥, 刘照霞, 等. 氮磷配施对苹果幼苗生长、土壤无机磷形态和磷素利用的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(4):237-242.
|
| [20] |
李亚麒, 许玉兰, 唐军荣, 等. 氮磷配施对云南松苗木生长及养分积累的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2023, 40(1):115-125.
|
| [21] |
凌岩, 秦健, 尚旭岚, 等. 施氮量对青钱柳幼苗生长和总酚积累的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2020, 29(4):45-51.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
潘晓华, 石庆华, 郭进耀, 等. 无机磷对植物叶片光合作用的影响及其机理的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1997, 3(3):201-208.
|
| [25] |
李海霞, 李正华, 戴伟男, 等. 氮磷水平对中美山杨幼苗碳氮积累与分配的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2013, 33(3):8-14,19.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |