 PDF(3409 KB)
PDF(3409 KB)


基于MaxEnt模型的白鹤越冬栖息地潜在适生区分布研究
刘小燕, 张增信, 李军, 陈娟, 华军, 彭冶, 晏欣, 邱健
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 181-188.
 PDF(3409 KB)
PDF(3409 KB)
 PDF(3409 KB)
PDF(3409 KB)
基于MaxEnt模型的白鹤越冬栖息地潜在适生区分布研究
An prediction of the potential distribution of suitable habitat for Grus leucogeranus using the MaxEnt model
【目的】近年来白鹤(Grus leucogeranus)的适生区分布因气候变化和人类活动等因素受到了极大影响,故运用最大熵模型(MaxEnt)模拟白鹤在中国不同时期的适生区分布,以预测不同气候变化情景下白鹤越冬栖息地的潜在适生区变化,为濒临灭绝的水鸟保护提供数据支撑和理论依据。【方法】根据白鹤在中国越冬栖息地适生区的分布变化,基于白鹤在中国区域的分布点位、植被、地形、实测气温、降水以及全球气候模式(GCMs)等数据,分析其适宜生境与各环境因子的关系,利用MaxEnt开展白鹤越冬栖息地潜在适生区预测研究。【结果】①MaxEnt模型在研究白鹤越冬栖息地适生区分布和气候适宜性方面具有较高的适用性,其中海拔、最湿月降水量、坡度和归一化植被指数(NDVI)是影响白鹤适生区分布的主要环境因素。②白鹤的适生区主要分布在长江中下游地区,其中鄱阳湖流域是最主要的高适生区,而中、低适生区也主要围绕鄱阳湖周边分布。此外,长江中下游干流区、渤海湾沿岸、海河、辽河以及嫩江和松花江流域等地也有低适生区分布。③全球气候模式预测结果显示,在未来20年,白鹤越冬区低适生区面积呈上升趋势,但中、高适生区面积普遍下降。其中,中适生区面积将收缩2 500~25 700 km2,高适生区面积将收缩3 800~12 200 km2。【结论】不同温室气体排放情景对珍稀物种白鹤分布产生的影响有所差异。在全球气候变暖背景下,白鹤越冬栖息地中、高适生区面积可能会出现明显萎缩,对白鹤的保护带来严峻挑战,应加强气候变化背景下白鹤栖息地的研究,为白鹤保护和栖息地管理提供数据支撑。
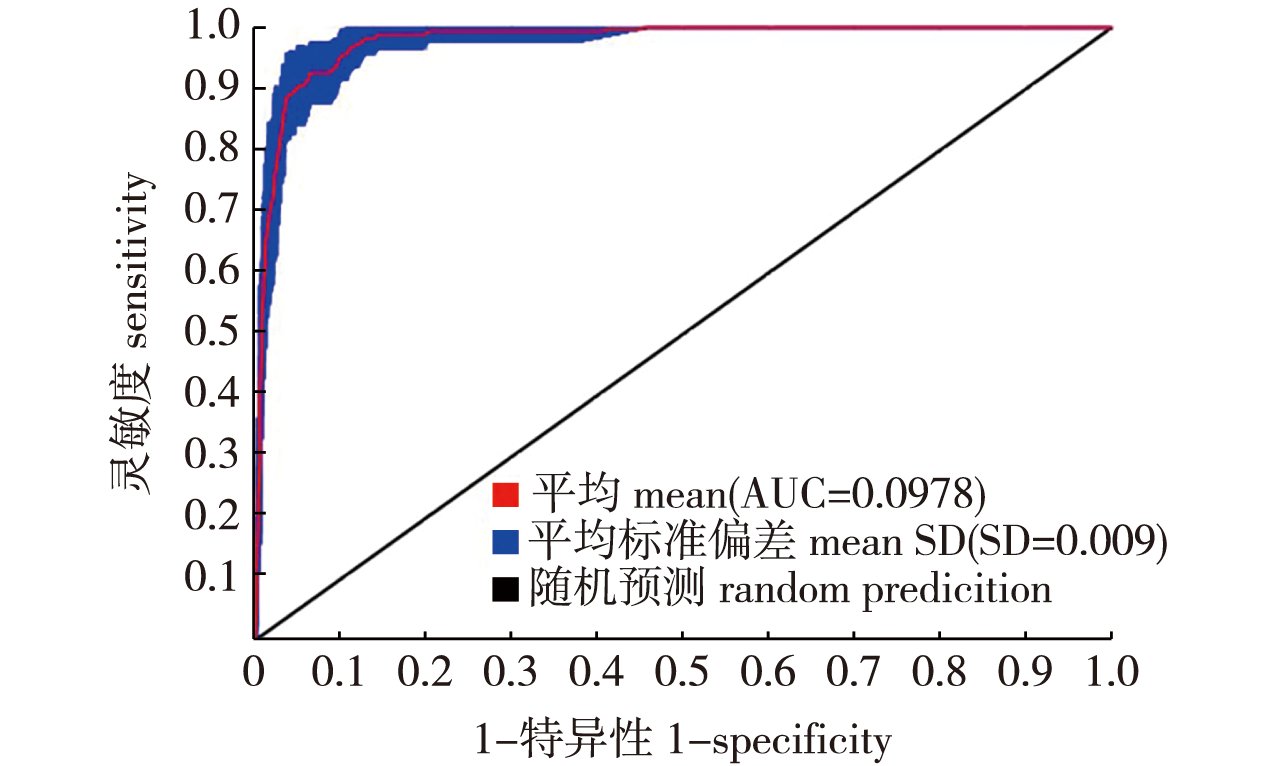
【Objective】The middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin are the most important wintering habitats for the Grus leucogeranus. However, in recent years, the distribution of suitable habitats for the G. leucogeranus in this area has been greatly altered by the combined effects of climate change and various other factors. Therefore, conducting research on the habitat suitability of G. leucogeranus in this area is of great significance for the protection and scientific management of this endangered species.【Method】In this study, based on the changes in the distribution of suitable areas of the G. leucogeranus wintering habitat in China, we used the Maximum Entropy Model (MaxEnt) to predict the potential suitable areas of the G. leucogeranus wintering habitat. The prediction was based on the G. leucogeranus distribution points, vegetation, topography, observed air temperature, precipitation, Global Climate Models (GCMs) data, and other various environmental factors.【Result】(1) The MaxEnt model proved highly effective in predicting the distribution of suitable habitats and assessing climate suitability for G. leucogeranus in their wintering grounds, with an AUC value of 0.978. The most influential environmental factors affecting the distribution of suitable habitat for G. leucogeranus were elevation, precipitation during the wettest month, slope, and NDVI. (2) The contemporary suitable habitat of the G. leucogeranus mainly distributed in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, with the the Poyang Lake being the most important high suitable area for the species. The medium and low suitable areas also mainly distributed around the the Poyang Lake. In addition, low suitable areas were found in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, along the coast of the Bohai Bay, and in the Haihe River, the Liaohe River, the Nenjiang, and the Songhua River basins. (3) Global climate model prediction results showed predictions indicate that the next 20 years, although the low suitable areas for G. leucogeranus during wintering is on the rise, the medium and high suitable areas generally decreasing. Among them, compared to the contemporary period, the medium suitable living area are projected to shrink by 2 500 to 25 700 km2, and the high suitable living area will shrink by 3 800 to 12 200 km2.【Conclusion】Different greenhouse gas emission scenarios will have different varying impacts on the distribution of G. leucogeranus. In the context of global warming, the wintering habitat of G. leucogeranus may shrink significantly, which will pose a serious challenge to the conservation of this rare species, and we should strengthen the research on G. leucogeranus habitat in the context of climate change, to provide data support for the conservation of G. leucogeranus and the management of their habitats.
白鹤 / 适生区分布 / 气候情景 / MaxEnt模型 / 栖息地 / 中国
Grus leucogeranus / suitable habitat distribution / climate scenario / MaxEnt model / habitat / China
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
曹垒, 孟凡娟, 赵青山. 基于前沿监测技术探讨“大开发”对鸟类迁徙及其栖息地的影响[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(4):436-447.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
耿国彪. 我国湿地保护形势不容乐观:第二次全国湿地资源调查结果公布[J]. 绿色中国, 2014(3):8-11.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
白雪红, 王文杰, 蒋卫国, 等. 气候变化背景下京津冀地区濒危水鸟潜在适宜区模拟及保护空缺分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(6):1001-1011.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
翁宇威, 蔡闻佳, 王灿. 共享社会经济路径(SSPs)的应用与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(2):215-222.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
翟新宇, 申宇芳, 朱圣华, 等. 未来气候变化对孑遗植物鹅掌楸地理分布的影响[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2021, 29(2):151-161.
|
| [17] |
李丽鹤, 刘会玉, 林振山, 等. 基于MAXENT和ZONATION的加拿大一枝黄花入侵重点监控区确定[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(9):3124-3132.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
孙颖, 秦大河, 刘洪滨. IPCC第五次评估报告不确定性处理方法的介绍[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8(2):150-153.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
王新建, 周立志, 陈锦云, 等. 长江下游沿江湿地升金湖越冬水鸟觅食集团结构及生态位特征[J]. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(2):518-528,651.
|
| [24] |
吴庆明, 王磊, 朱瑞萍, 等. 基于MAXENT模型的丹顶鹤营巢生境适宜性分析:以扎龙保护区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(12):3758-3764.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
马柱国, 符淙斌, 周天军, 等. 黄河流域气候与水文变化的现状及思考[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(1):52-60.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
高浩翔, 申立泉, 刘瑞, 等. 基于最大熵模型的野生马麝夏季生境适宜性研究[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(1):441-448.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
王会军, 唐国利, 陈海山, 等. “一带一路”区域气候变化事实、影响及可能风险[J]. 大气科学学报, 2020, 43(1):1-9.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |