 PDF(3267 KB)
PDF(3267 KB)


基于LoRa组网的超低功耗径流含沙量检测系统
杨鹏城, 刘砚一, 陈书畅, 沈奕聪, 宋晨悦
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 161-168.
 PDF(3267 KB)
PDF(3267 KB)
 PDF(3267 KB)
PDF(3267 KB)
基于LoRa组网的超低功耗径流含沙量检测系统
An ultra-low-power sediment concentration detecting system in runoff based on LoRa networking
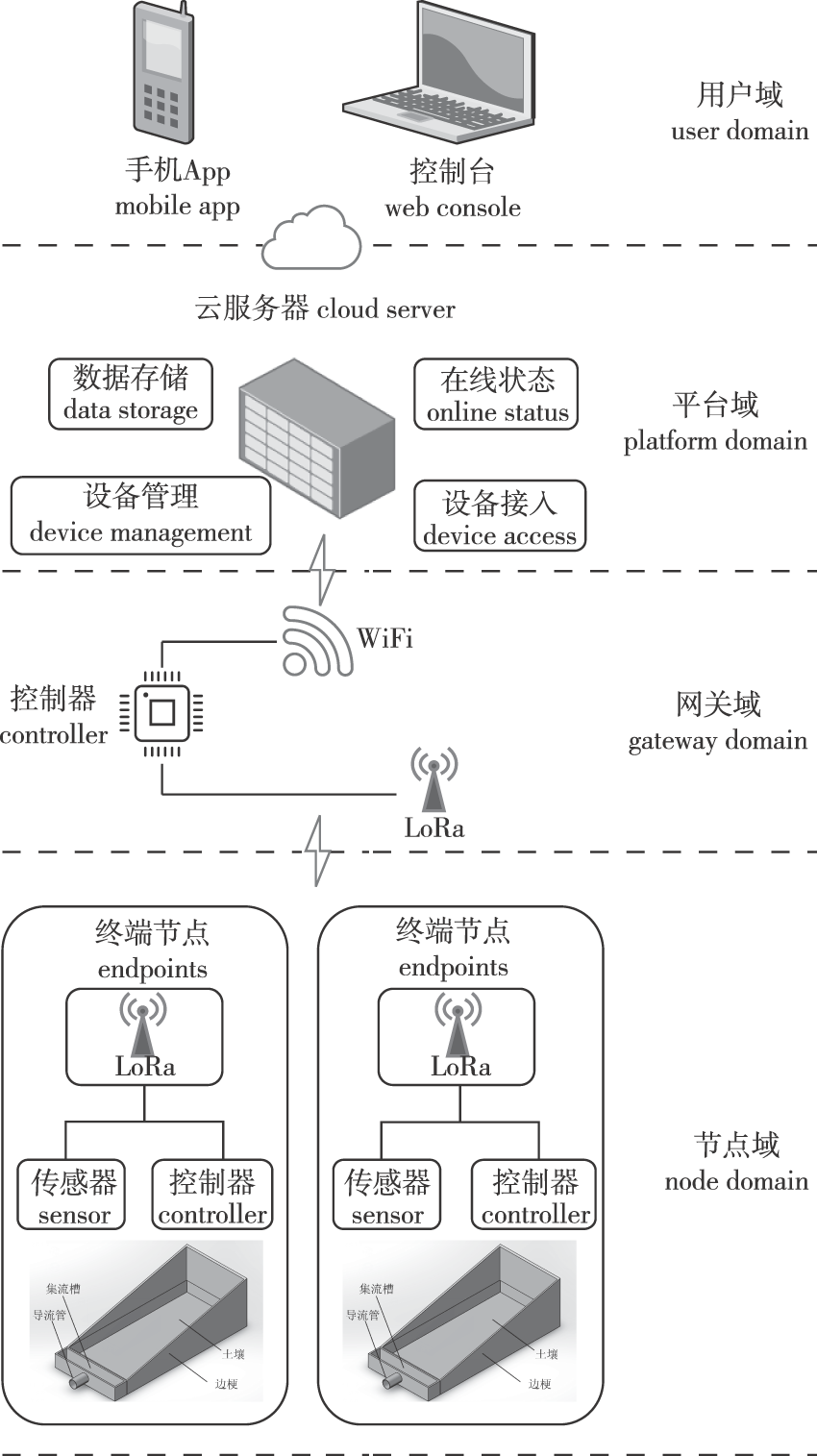
【目的】我国水土流失现象严重,通过对水土流失状况进行有效、可靠的检测,为研究人员提供可靠的数据依据,助力水土流失和水土保持效益定量评价,更好地掌握水土流失情况和治理效果。【方法】基于物联网架构,设计了一套基于远距离无线电(long range radio, LoRa)组网的坡面土壤侵蚀动态检测系统,该系统采用LoRa Standby-CAD工作策略实现超低功耗。【结果】与传统技术相比,本研究设计的径流含沙量检测系统可降低40%电耗,待机时长可提高8.5倍;基于ECharts框架和华为云平台设计可视化大屏,实现检测数据可视化。实地测试结果表明,与传统比重法相比,本系统检测数据相对误差均值为3.08%。【结论】本研究设计的径流含沙量检测系统能持续地实时检测野外坡面径流小区径流含沙量及降水量,相比传统物联网技术方案,该系统功耗低、测试精度高、数据可视化、投产建设及维护成本低,可为相关生产、研究工作提供真实有效的实测数据及解决方案。
【Objective】Soil erosion represents a critical issue in China. It is necessary to quantitatively evaluate soil erosion and the benefits of soil conservation, and to understand the situation of soil erosion and the effectiveness of treatment measures. This study involves effectively and reliably detecting the soil erosion status and providing a dependable data foundation for researchers. 【Method】The study used an internet of things (IoT) architecture to design an ultra-low-power sediment concentration detection system in runoff based on long range radio (LoRa) networking. The Standby-CAD with LoRa was employed to achieve ultra-low power consumption. 【Result】This system reduced energy consumption by 40% and increased standby time by 8.5 times compared to traditional techniques. The ECharts framework and Huawei cloud platform were utilized to design a visualization screen for data visualization. Through multiple tests, the average value of the relative error of data measured by this system was 3.08% compared to the traditional gravity method. 【Conclusion】This system can continuously detect the runoff sediment concentration and also rainfall in runoff plots on hillsides in real-time. Compared to traditional IoT technical solutions, this system demonstrates low power consumption, high testing accuracy, data visualization, and also reduced production and maintenance costs, providing accurate and effective measurement data and solutions for related production and research activities.
sediment concentration detection / ultra-low power consumption / long rang radio (LoRa) / runofff
| [1] |
王一峰, 屈丽琴, 李建明, 等. 基于近20年《中国水土保持公报》的水土流失治理分析[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2023, 40(7):59-65.
|
| [2] |
陈群香. 中国水土保持生态环境建设现状与社会经济可持续发展对策[J]. 水土保持通报, 2000, 20(3):1-4,34.
|
| [3] |
张相, 丁鸣鸣, 李卓远, 等. 水蚀作用下红壤丘陵区土壤特性的空间分异特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(6):77-84.
|
| [4] |
林杰, 张相, 姜姜, 等. 水力侵蚀过程中土壤有机碳循环研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):187-194.
|
| [5] |
李月, 周运超, 白晓永, 等. 径流小区法监测水土流失的百年历程(1915—2014年)[J]. 中国水土保持, 2014(12):63-66.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
罗勇钢, 程鸿雨, 邹君, 等. 一种散射式浊度传感器设计[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2015, 34(6):67-69.
|
| [8] |
王辉, 雷廷武, 赵军, 等. LTW-1型径流泥沙含量与流量动态测量系统研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2003, 23(2):43-45.
|
| [9] |
赵昕, 田岳明, 徐汉光, 等. 激光类测沙仪在长江泥沙测验中的应用[J]. 水文, 2011, 31(S1):117-120.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
张勇, 李仁华, 姚赫, 等. 水土保持自动监测设备现状及新设备研发[J]. 人民长江, 2022, 53(9):43-48.
|
| [12] |
赵岩, 张永成, 康军, 等. 一种低功耗的NB-IoT温湿度采集器设计[J]. 中国测试, 2022, 48(9):140-144,157.
|
| [13] |
唐菲. 基于物联网的分布式水质在线监控系统设计[J]. 传感技术学报, 2022, 35(4):565-572.
|
| [14] |
何诚刚. 基于LoRa的无线监测系统设计[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(3):528-530.
|
| [15] |
陈思. 基于OneNET的农业大棚物联网环境监控系统的研究与实现[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2019.
|
| [16] |
张铮, 曹守启, 朱建平, 等. 面向大面积渔业环境监测的长距离低功耗LoRa传感器网络[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(1):164-171.
|
| [17] |
展小云, 郭明航, 赵军, 等. 径流泥沙实时自动监测仪的研制[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(15):112-118.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |