 PDF(1509 KB)
PDF(1509 KB)


斑皮柠檬桉种源树高生长稳定性评价
陈升侃, 郭东强, 邓紫宇, 唐庆兰, 廖长琨, 杨植旺, 朱原立, 李昌荣
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 67-74.
 PDF(1509 KB)
PDF(1509 KB)
 PDF(1509 KB)
PDF(1509 KB)
斑皮柠檬桉种源树高生长稳定性评价
Stability evaluation on tree height for introduced provenances of Corymbia citriodora subsp. variegata
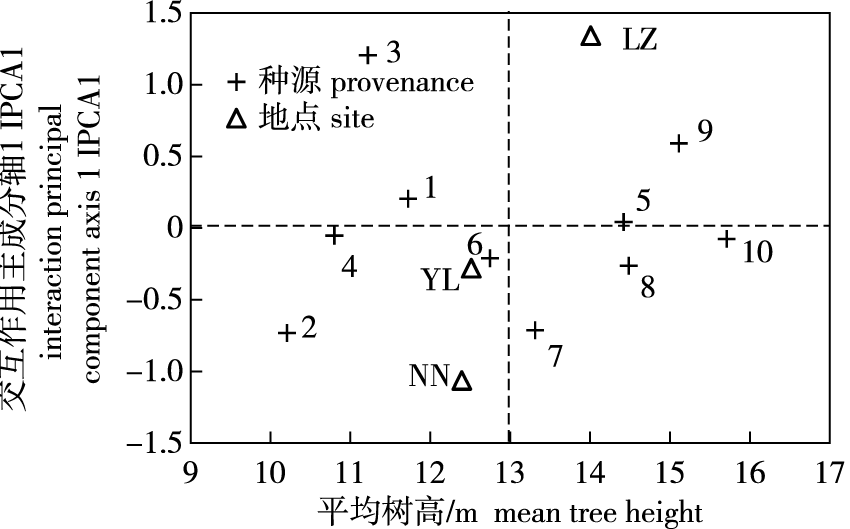
【目的】对引种至广西的斑皮柠檬桉(Corymbia citriodora subsp. variegata)种源进行适应性和稳定性评价,为斑皮柠檬桉的选择和推广提供理论依据。【方法】对建立在南宁、玉林和柳州的6年生斑皮柠檬桉种源试验林进行树高测定,分析其树高生长和保存率,以评价种源的生长适应性;通过主效可加互作可乘(AMMI)模型和基因型主效应加基因型与环境互作(GGE)双标图分析种源的稳定性,划分适宜推广区域,筛选优良引种种源。【结果】斑皮柠檬桉6年生时所有种源的树高均值达13.0 m,各种源存活率为21.23%~54.81%。树高在种源间存在极显著差异,种源与地点的交互作用显著,有必要进一步进行分解,AMMI模型分析结果显示有1个互作效应主成分轴达到极显著水平,解释了79.9%的互作效应。根据稳定性的定量指标(Di),10个种源的稳定性由大到小排序依次为19694、19691、20883、19664、20396、20756、20787、20753、19665和19666号,其中20883、20756和19694号种源为速生稳定型种源。GGE双标图分析结果显示,3个试验点可划分为2个立地环境区,南宁和玉林试验点划分为同一立地环境区,柳州试验点单独划分为一个立地环境区,20883号种源为所有引种至广西种源的最优种源。【结论】斑皮柠檬桉引种至广西后在各试验点表现出良好的生长适应性,对种源进行选择可获得较好的改良效果;20883、20756和19694号种源适宜在南宁和玉林试验点立地环境相似的地区推广,20787号种源适宜在柳州试验点立地环境相似的地区推广。
【Objective】This study evaluates the adaptability and stability of Corymbia citriodora subsp. variegata (CCV) provenances introduced to Guangxi, China, providing a theoretical basis for their selection and extension. 【Method】The tree height of six-year-old CCV specimens established in Nanning, Yulin and Liuzhou was measured. An analysis of tree height and survival for each provenance was conducted to assess growth adaptability. The additive main effects and multiplicative interaction (AMMI) model and genotype main effect plus genotype-environment interaction (GGE) biplot were employed to analyze the stability of provenances, classify suitable extension areas, and identify superior provenances. 【Result】The average tree height of all CCV provenances in sixth years was 13.0 m, with individual provenance survival rates ranging from 21.23% to 54.81%. Significant differences were observed in tree height among provenances, and the interaction with the site was also significant, suggesting a need for further decomposition of the interaction effect. The AMMI model results indicated that one interaction principal component axis achieved a significant level, accounting for 79.9% of the interaction effect. The stability Di index for each provenance was calculated, revealing the following order of stability ranking: 19694, 19691, 20883, 19664, 20396, 20756, 20787, 20753, 19665 and 19666. Provenances 20883, 20756 and 19694 were identified as fast-growing and stable. The GGE biplot demonstrated that the three trial sites could be divided into two ecological regions, with Nanning and Yulin falling within one region and Liuzhou representing the other. Provenance 20883 emerged as the most suitable provenance for introduction to Guangxi. 【Conclusion】The CCV provenances introduced to Guangxi exhibited strong growth adaptability. The selection of provenances can significantly enhance planting outcomes. Provenances 20883, 20756 and 19694 are recommended for Nanning and Yulin, while provenance 20787 is suitable for Liuzhou.
Corymbia citriodora subsp. variegata / provenance / adaptability / stability
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
刘天颐, 刘纯鑫, 林元震, 等. 桉树伞房属4个种在广东清新的早期生长表现[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2009, 30(4):61-64.
|
| [6] |
刘宇, 徐焕文, 尚福强, 等. 3个地点白桦种源试验生长稳定性分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(5):50-57.
|
| [7] |
赵兴堂, 夏德安, 曾凡锁, 等. 水曲柳生长性状种源与地点互作及优良种源选择[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(3):140-147.
|
| [8] |
程玲, 张心菲, 张鑫鑫, 等. 基于BLUP和GGE双标图的林木多地点试验分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(3):87-93.
|
| [9] |
李金花. 基于BLUP和GGE双标图的黑杨派无性系生长性状基因型与环境互作效应[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(6):64-73.
|
| [10] |
徐焕文, 刘宇, 李志新, 等. 5年生白桦杂种子代多点稳定性分析及优良家系选择[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(12):24-31.
|
| [11] |
乔转运, 王军辉, 顾万春, 等. 桤木种源区域试验的AMMI模型分析[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2005, 39(2):171-177.
|
| [12] |
郑聪慧, 张鸿景, 王玉忠, 等. 基于BLUP和GGE双标图的华北落叶松家系区域试验分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(8):73-83.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
刘天颐, 刘纯鑫, 孔凡启, 等. 伞房属四个树种在广东的早期生长表现[J]. 广东林业科技, 2009, 25(1):32-36.
|
| [16] |
孔凡启, 祝文娟, 刘天颐, 等. 伞房属4个树种/亚种在广东德庆的早期生长表现[J]. 桉树科技, 2016, 33(3):12-18.
|
| [17] |
周维, 卢翠香, 杨中宁, 等. 6年生大花序桉不同种源木材纤维特性的差异分析[J]. 西部林业科学, 2016, 45(2):29-34.
|
| [18] |
杨汉波, 郭洪英, 陈炙, 等. 引种桉树种源生长性状的遗传变异及早期评价[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(6):109-114,177.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
郭东强, 邓紫宇, 郑永邓, 等. 桉树伞房属4个树种在广西的早期病害调查[J]. 桉树科技, 2017, 34(4):47-52.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
王军辉, 顾万春, 李斌, 等. 桤木优良种源/家系的选择研究:生长的适应性和遗传稳定性分析[J]. 林业科学, 2000, 36(3):59-66.
|
| [23] |
沈熙环. 油松、华北落叶松良种选育实践与理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.
|
| [24] |
徐化成. 油松地理变异与种源选择[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1992.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
李昌荣, 郭东强, 李建凡, 等. 大花序桉种源/家系生长性状和树干通直度及基本密度的评价与选择[J]. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(12):2734-2740.
|
| [29] |
廖柏勇, 刘丽婷, 莫晓勇, 等. 10年生粗皮桉种源家系选择分析[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2011, 32(4):72-77,81.
|
| [30] |
吴世军, 徐建民, 李光友, 等. 滇中南巨桉种源/家系年度变异分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(23):60-64.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |