 PDF(2010 KB)
PDF(2010 KB)


 PDF(2010 KB)
PDF(2010 KB)
 PDF(2010 KB)
PDF(2010 KB)
施加生物炭对屋顶绿化土壤径流水质的影响
Effect of biochar application on soil runoff and water quality in green roof
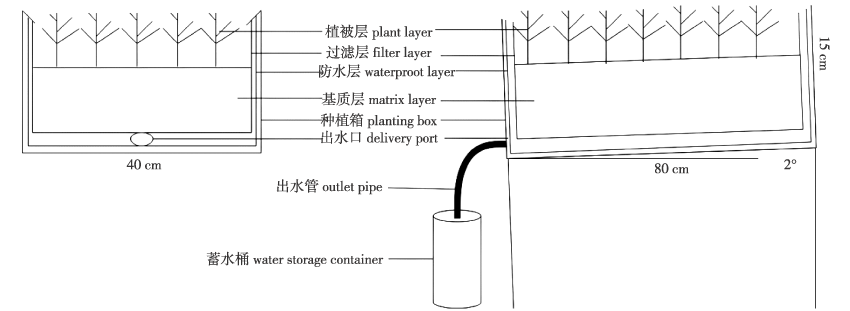
【目的】屋顶绿化可有效增加城市绿化率并缓解城市“热岛效应”,已逐渐成为城市绿化的重要途径之一。近年来,生物炭作为土壤改良剂被广泛应用于农林业生产中,其质量轻、孔隙度大等特点也适于改良屋顶绿化土壤的生态特性。通过研究不同生物炭施用量以及不同热解温度制备的生物炭对屋顶绿化土壤径流量及径流中养分析出特征的影响,为城市屋顶绿化中生物炭的适宜施用量提供参考依据。【方法】设置3个水平生物炭施用量(0%、10%、20%,体积分数),3个水平热解温度(300、400、500 ℃),每一水平各设4个重复。在种植箱中装填10 cm厚经处理的土壤基质,种植植物为佛甲草(Sedum lineare)。每次降水后收集土壤径流进行测定。【结果】①施用生物炭可提高屋顶绿化土壤pH,显著降低土壤径流中的全氮(TN)和溶解有机碳(DOC)质量浓度;施用10%生物炭可降低径流中的全磷(TP)质量浓度,而施用20%生物炭则会增加径流中全磷(TP)质量浓度。②与未施用生物炭的对照相比,施用适量生物炭可降低屋顶绿化土壤径流量及径流中养分浓度,从而减少屋顶绿化土壤的养分流失量。③在不同生物炭施用量下,施用不同热解温度(300、400、500 ℃)制备的生物炭对屋顶绿化土壤径流水质的影响差异不显著。【结论】施用适量生物炭可降低屋顶绿化土壤径流量及径流中N、P养分流失量,间接减轻城市径流污染负荷,在城市暴雨径流管理中具有一定的应用前景。
【Objective】Roof greening has become a popular method for increasing urban green spaces and mitigating the urban “heat island effect”. Recently, biochar, known for its lightweight and highly porous nature, has been utilized as a soil amendment in the agricultural and forestry sectors. This study explores the impacts of varying biochar application rates and pyrolysis temperatures on soil runoff and nutrient content in roof greening, to assess biochar’s potential for enhancing urban roof greening practices.【Method】The experiment involved three levels of biochar application (0%, 10% and 20%, volume fraction) and three pyrolysis temperatures (300, 400 and 500 ℃), with four replicates per treatment. Each planting box was filled with a 10 cm thick layer of treated soil matrix and planted with Sedum lineare. Soil runoff was collected and analyzed after each rainfall event.【Result】The findings indicated that biochar application could increase soil pH and significantly reduce the levels of total nitrogen (TN) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the runoff. While a 10% biochar addition decreased the total phosphorus (TP) concentration in the runoff, a 20% addition had the opposite effect. Moreover, biochar was effective in reducing soil runoff and nutrient concentration, thus minimizing nutrient loss from the soil. There was no significant difference in the effects of biochar processed at different pyrolysis temperatures on runoff quality. 【Conclusion】Optimal biochar application can significantly decrease N and P loss in roof soil runoff, indirectly reducing urban runoff pollution. This suggests a promising application for biochar in managing urban stormwater runoff.
屋顶绿化 / 生物炭 / 施加量 / 热解温度 / 土壤 / 径流水质 / 城市污染
roof greening / biochar / addition amount / pyrolysis temperature / soil / runoff water quality / urban pollution
| [1] |
董菁, 左进, 吝涛, 等. 高度城市化地区屋顶绿化径流调控效益评价:以厦门岛为例[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(6):2237-2250.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
陈智龙, 董雨琴, 陈凌静, 等. 城市热岛效应变化及其影响因素分析研究[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2021, 48(6):34-40,52.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
张鹏. 屋顶绿化专用草坪草筛选研究:以济南地区为例[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2021.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
陈颢明. 屋顶绿化基质中添加生物炭的生态效应研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
周之栋, 卜晓莉, 吴永波, 等. 生物炭对土壤微生物特性影响的研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(6):1-8.
|
| [18] |
王娟, 黄成真. 生物炭对土壤改良效果的研究进展[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2020, 31(3):246-253.
|
| [19] |
黄康. 不同热解温度秸秆生物炭还田培肥土壤及其固碳潜力的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022.
|
| [20] |
丁应祥. 下蜀森林生态定位站径流场土壤性状及分类[J]. 南京林业大学学报, 1999, 23(6):37-42.
|
| [21] |
国家环保局《水和废水监测分析法》编委会. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 236-284.
Editorial Committee of The Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Law of the National Environmental Protection Administration. Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods[M]. Fourth Edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002: 236-284.
|
| [22] |
生态环境部.环境影响评价技术导则地表水环境:HJ 2.3—2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2018.
|
| [23] |
国家环境保护总局,国家质量监督检验检疫总局.地表水环境质量标准:GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002.
|
| [24] |
刘楠. 缙云山典型林分对径流水质的作用及评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2011.
|
| [25] |
罗婷, 许文年, 程虎, 等. 粗放型绿色屋顶基质层对降雨出流水质影响[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(4):39-45.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
戴子云, 谢军飞, 许蕊. 北京地区绿色屋顶的径流特征研究[J]. 建筑节能(中英文), 2022, 50(5):99-104.
|
| [28] |
张千千, 王慧玮, 翟天伦. 绿色屋面基质添加生物炭对降雨径流水质和水量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(6):1026-1033.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
闫代红, 马亚培, 宋凯悦, 等. 原料和热解温度对生物炭中可溶性有机质的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(10):5030-5036.
|
| [35] |
丁思惠, 方升佐, 田野, 等. 不同热解温度下杨树各组分生物质炭的理化特性分析与评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6):193-200.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
孙涛, 朱新萍, 李典鹏, 等. 不同原料生物炭理化性质的对比分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2017, 34(6):543-549.
|
| [39] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |