 PDF(2212 KB)
PDF(2212 KB)


3种有机酸对铝毒下马尾松幼苗抗氧化系统调控效应评价
缪聪林, 刘亚敏, 姚虹宇, 刘玉民, 纪雨薇, 李峻安
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1) : 112-118.
 PDF(2212 KB)
PDF(2212 KB)
 PDF(2212 KB)
PDF(2212 KB)
3种有机酸对铝毒下马尾松幼苗抗氧化系统调控效应评价
An evaluation of the regulatory effects of three organic acids on the antioxidant system of Pinus massoniana under aluminum toxicity
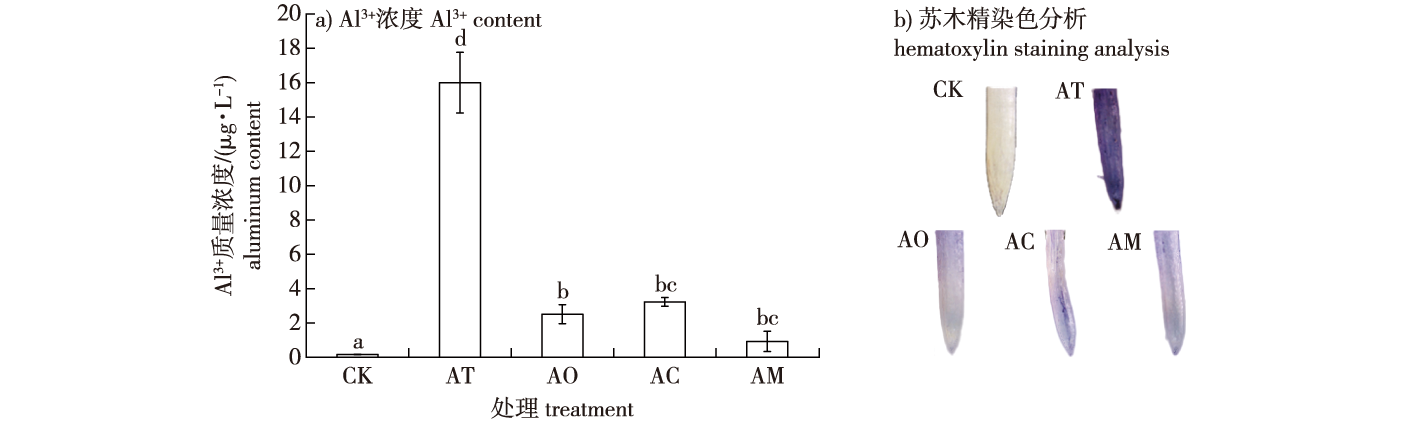
【目的】比较草酸、柠檬酸、苹果酸对铝敏感型GD20(广东20号)马尾松家系幼苗铝(Al)毒害的缓解能力,为有机酸缓解Al耐受的潜在机制提供理论依据。【方法】采用水培法,测定草酸、柠檬酸、苹果酸对Al毒环境下铝敏感型 GD20马尾松家系生长、抗氧化系统和非酶物质相关生理指标的影响,按照生长、根叶抗氧化系统[超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、丙二醛(MDA)]、针叶活性氧(H2O2、$\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}$)、根叶非酶物质(可溶性糖、脯氨酸、蛋白质)对测定指标进行分类。依据模糊数学多因素综合决策原理,运用加权平均法和最大原则,对GD20在铝毒状态下外施有机酸测定的生理指标进行综合评判。【结果】3种有机酸能有效降低根系Al3+含量,缓解Al毒害对马尾松生长的抑制。外施有机酸可以激发马尾松幼苗抗氧化防御系统缓解Al毒所致的膜脂过氧化和细胞损伤,还可通过调节马尾松体内非酶物质的含量来维持稳定的代谢环境。在对抗氧化系统的调节中,草酸(0.20 mmol/L)对根系SOD、POD和CAT酶活性的促进作用强于苹果酸(0.01 mmol/L)和柠檬酸(0.02 mmol/L);另外草酸也能有效降低因Al毒导致的根系MDA积累。熵权法的综合评价结果也表明草酸能有效调节Al胁迫下马尾松幼苗的抗氧化酶活性,得分系数为0.20,总得分0.26,高于柠檬酸和苹果酸。【结论】柠檬酸、草酸、苹果酸可能共同参与了缓解马尾松幼苗Al毒害,但3种有机酸在解毒效果上存在差异,草酸解Al毒能力优于柠檬酸和苹果酸。
【Objective】 This study compares the mitigating ability of oxalic acid, citric acid, and malic acid on Al toxicity in GD20 (Al-sensitive) genotypes of Pinus massoniana seedlings. It provides theoretical bases for the potential mechanisms through which organic acids mitigate Al tolerance. 【Method】 The effects of oxalic acid, citric acid and malic acid on the physiological indices related to growth, antioxidant system, and non-enzymatic substances of Al toxicity environment in Al3+ sensitive GD20 Pinus massoniana family lines were determined by hydroponics. Based on the growth, antioxidant system of root and leaf (SOD, POD, CAT, MDA), ROS of needles and leaves (H2O2, $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}$), non-enzymatic substances of root and leaf (soluble sugars, proline, protein) were classified for the determination indices. Using the principle of multi-factor integrated decision-making in fuzzy mathematics, the weighted average method and the maximum principle were applied to comprehensively evaluate the physiological indices affected by the external application of organic acids in the aluminum toxicity state of GD20. 【Result】The three organic acids effectively reduce the aluminum content in the root system and alleviate the inhibition of Al toxicity on the growth of horsetail pine. The application of these acids stimulates the antioxidant defense system, mitigating membrane lipid peroxidation and cellular damage caused by Al toxicity. They also maintain a stable metabolic environment by regulating the content of non-enzymatic substances in Pinus massoniana. In regulating the antioxidant system, oxalic acid (0.20 mmol/L) enhances the activities of SOD, POD, and CAT enzymes in the root system more effectively than malic acid (0.01 mmol/L) and citric acids(0.02 mmol/L); it also significantly reduces the accumulation of MDA in the root system due to aluminum toxicity. The comprehensive evaluation results, using the entropy weighting method, indicated that oxalic acid effectively regulates the antioxidant enzyme activities of P. massoniana seedlings under aluminum stress, achieving a scoring coefficient of 0.20 and a total score of 0.26, higher than those of citric acid and malic acid. 【Conclusion】 Citric acid, oxalic acid, and malic acid can jointly alleviate aluminum toxicity in horsetail pine seedlings. However, the detoxification effects of these acids vary, with oxalic acid demonstrating a superior ability to detoxify aluminum compared to citric acid and malic acid.
Pinus massoniana / organic acids / Al toxicity / antioxidant enzymes / non-enzymatic substances
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
姚虹宇, 刘亚敏, 张盛楠, 等. 外源柠檬酸对铝胁迫下马尾松生理特性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(7):155-164.
|
| [8] |
李峻安. 酸铝环境下外源有机酸对马尾松铝毒害的缓解作用及调控机制[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2021.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
姚虹宇. 根系分泌有机酸参与缓解马尾松铝毒害机制研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020.
|
| [11] |
纪雨薇. 马尾松铝胁迫生理响应机制[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016.
|
| [12] |
郭妮, 刘亚敏, 周文颖, 等. 外源草酸缓解马尾松根系铝毒[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(7):1086-1095.
|
| [13] |
刘玉民. 酸铝环境马尾松根系分泌物特性及其缓解铝毒的根际效应[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018.
|
| [14] |
张盛楠, 刘亚敏, 刘玉民, 等. 马尾松幼苗生长及生理特性对铝胁迫的响应[J]. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(10):2022-2029.
|
| [15] |
熊庆娥. 植物生理学实验教程[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 2003.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
韩艳红, 于沐, 石彦召, 等. 基于隶属函数法对13个花生品种品质的综合评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(2):7-11.
|
| [19] |
孙鲁云, 王力. 基于层次分析法-熵权法的中国棉花质量综合评价与分析[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(3):642-649.
|
| [20] |
张圳. 镁营养在杨树响应铝毒害胁迫中的作用机制研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020.
|
| [21] |
邱晓. 铝胁迫对紫花苜蓿的影响及外源有机酸的缓解机制[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2010.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
朱海凤. 水稻和荞麦抗铝毒转录因子ART1调控机制的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2016.
|
| [24] |
艾佐佐. 磷铝耦合对油茶幼苗生长及生理指标的影响[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2017.
|
| [25] |
谭贵良, 顾明华, 杨博, 等. 铝胁迫对甘蔗初生根生长及酶活性的效应[J]. 广西农业生物科学, 2003, 22(4):271-274.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
孙琴, 倪吾钟, 杨肖娥. 有机酸在植物解铝毒中的作用及生理机制[J]. 植物学通报, 2002, 19(4):496-503.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |