 PDF(1714 KB)
PDF(1714 KB)


基于荧光SSR标记的接骨木种质资源遗传多样性分析
姚俊修, 任飞, 王因花, 李庆华, 燕丽萍, 郑岩, 吴德军
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 75-82.
 PDF(1714 KB)
PDF(1714 KB)
 PDF(1714 KB)
PDF(1714 KB)
基于荧光SSR标记的接骨木种质资源遗传多样性分析
Genetic diversity of germplasm resources of Sambucus based on SSR fluorescent marker
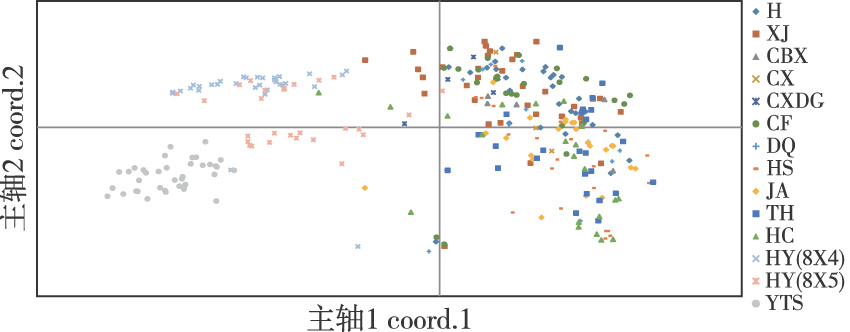
【目的】以收集的245份接骨木属(Sambucus)种质资源和60份接骨木杂交种质为材料,基于SSR分子标记对不同种源接骨木的遗传多样性及亲缘关系进行分析,为接骨木种质资源的合理保护、评价与利用提供科学依据。【方法】以11个种源的305个体为研究对象,根据转录组测序结果,开发100对SSR引物,对8个不同种接骨木个体进行扩增筛选,获得13对多态性较好的SSR引物,使用Popgene、Genemarker、GeneALeX和NTSYSpc等软件,对接骨木种质资源及杂交子代的遗传多样性、遗传距离、不同种源主坐标、UPGMA关系及进化树等进行分析。【结果】利用13对荧光引物对305个体进行扩增,检测到等位基因总数为162,不同位点等位基因变异幅度为4~34个,平均为12.5个;有效等位基因总数(Ne)为50.408个,变异幅度为1.066 1~11.070 2个,平均为3.878;平均观察杂合度(Ho)为0.331 5,平均期望杂合度(He)为0.521 5,平均Nei’s遗传距离为0.520 4,平均多态性信息含量为0.496 4,表明遗传多样性较高;42号位点Ho/He大于1,表明该位点杂合度高,种群内遗传变异程度较大。不同种源参试样本中Ho为0.208(杂交组合1)~0.486(长白县),平均Ho为0.372。He为0.242(杂交组合1)~0.552(大庆),平均He为0.434,其中,长白县、朝鲜种源及杂交组合2的Ho/He均大于1,表明这3个种源/杂交组合内群体杂合度较高,种群内遗传变异程度也较大。主坐标分析表明:遗传变异主要存在于个体间,占80%,而种源间遗传变异仅占20%,可能由于不同地区的栽培种源来源于相同省域,造成不同种源间变异较小;Nei’s遗传距离和聚类结果表明,种源/杂交组合间的遗传距离变化范围为0.023~0.637,山东青州仰天山天然群体和吉林长白县的遗传分化差异最大;内蒙赤峰和新疆阿勒泰的遗传分化差异最小;聚类可分为3大类群,同一种源个体并未完全聚到相同分支,可能原因是遗传变异或相互引种造成的。【结论】 接骨木种质资源具有较高的遗传多样性,在进行接骨木遗传改良时,应首先进行种源内选择育种及单株改良的育种方法,其次可考虑种源间研究。研究结论为接骨木种质资源精准鉴定、核心种质构建及新品种创制等奠定基础。
【Objective】This study analyzed the genetic diversity and genetic relationship of Sambucus williamsii from different provenances based on SSR molecular markers, to provide a scientific basis for the rational protection, evaluation, and utilization of S. williamsii germplasm resources.【Method】Using 245 samples of Sambucus germplasm resources and 60 samples of Sambucus hybrid germplasm as the test materials, 100 pairs of SSR primers were developed based on the transcriptome sequencing results. Through the amplification and screening of eight different individuals of Sambucus species, 13 pairs of SSR primers with good polymorphism were obtained. The genetic diversity, genetic distance, principal coordinates of different species origins, UPGMA relationships, and evolutionary trees of the Sambucus germplasm resources and their hybrid offspring were examined using the Popgene, Genemarker, GeneALeX and NTSYSpc software packages.【Result】We employed 13 pairs of fluorescent primers to amplify 305 individuals, and 162 alleles were detected. The variation range of alleles at different loci was determined as 4-34, with an average of 12.5 alleles. The total number of effective number of allele ( Ne) was 50.408, with a variation range of 1.066 1-11.070 2. The average Ne, abserved heterozygosity (Ho), and expected heterozygosity (He) values were 3.878, 0.331 5 and 0.521 5, respectively. Moreover, we determined the average Nei’s genetic distance (Nei) and polymorphism information content (PIC) values of 0.520 4 and 0.496 4, respectively. These results suggest a high genetic diversity. The Ho/He ratio at site 42 was greater than 1, indicating high degrees of heterozygosity and genetic variation within the species. Among the tested samples from different species origins, Ho ranged from 0.208 (hybrid combination 1) to 0.486 (Changbai County), with an average Ho value of 0.372. He ranged from 0.242 (hybrid combination 1) to 0.552 (Daqing), with an average He value of 0.434. Notably, the Ho/He ratios for the species origins (or hybrid combinations) of Changbai County, North Korea provenances, and hybrid combination 2 were all greater than 1, indicating that these three species origins (or hybrid combinations) had higher population heterozygosity and greater degrees of genetic variation within the populations. Principal coordinate analysis revealed that the majority of genetic variation, accounting for 80%, was found among individuals, while genetic variation among species origins accounted for only 20%. This may be because the cultivated varieties from different regions originated from the same provincial area, leading to smaller genetic variation among species of different origins. The genetic distance of Nei among species origins (or hybrid combinations) ranged from 0.023 to 0.637. The greatest genetic differentiation was observed between the natural populations of Yangtianshan in Qingzhou, Shandong, and Changbai County, Jilin, and the lowest between the populations of Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, and Altay, Xinjiang. The clustering could be divided into three groups, and the same source individuals were not completely clustered into the same branch, which may be caused by genetic variation or mutual introduction.【Conclusion】We demonstrated the high genetic diversity of the germplasm resources of S. williamsii. To achieve genetic improvement, intra-provenance selection and single plant improvement should initially be performed, followed by inter-provenance selection. This study provides a theoretical basis for the precise identification of S. germplasm resources, the construction of core germplasms, and the creation of new varieties.
fluorescent SSR marker / Sambucus williamsii / germplasm resources / genetic diversity
| [1] |
韩华, 闫雪莹, 匡海学, 等. 接骨木的研究进展[J]. 中医药信息, 2008, 25(6):14-16.
|
| [2] |
沈植国. 木本接骨木属植物种质资源研究综述[J]. 山西农业科学, 2011, 39(11):1223-1226,1231.
|
| [3] |
徐亮, 陈功锡, 张代贵, 等. 接骨木属植物研究进展[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2010, 29(5):1-5,10.
|
| [4] |
郝广明, 胡荣, 高泰, 等. 接骨木研究综述[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 1(2):167-170.
|
| [5] |
胡荣, 戚继忠, 薛振平, 等. 药食两用木本新油源:接骨木油[J]. 林业科学, 2005, 41(1):65-70.
|
| [6] |
曹梦晔, 高昂, 巩江, 等. 接骨木属植物药用研究概况[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2011, 52(4):59-60,62.
|
| [7] |
孙华, 王桂清. 珍贵观赏树种接骨木的研究现状与展望[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2010, 49(3):727-730,735.
|
| [8] |
姚俊修, 刘学良, 李善文, 等. 接骨木无性系苗期干旱胁迫响应及抗旱性综合评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(9):75-81.
|
| [9] |
刘学良, 姚俊修, 刘翠兰, 等. 7个接骨木无性系苗木对盐胁迫的生理响应与评价[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(1):37-44,79.
|
| [10] |
孙丹丹, 姚俊修, 王刚, 等. 接骨木3个品种药材成分含量比较分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019, 25(24):124-130.
|
| [11] |
孙丹丹, 姚俊修, 刘富裕, 等. 基于GC-MS分析接骨木3个品种果实中挥发油成分[J]. 中国现代中药, 2020, 22(4):546-551.
|
| [12] |
许丽, 李玥莹, 林凤. DNA分子标记及其在作物遗传育种中的应用[J]. 沈阳师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 24(4):466-469.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
毛秀红, 郑勇奇, 孙百友, 等. 基于SSR的刺槐无性系遗传多样性分析和指纹图谱构建[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(10): 80-89.
|
| [15] |
姚俊修, 李善文, 任飞, 等. 西洋接骨木转录组SSR挖掘及荧光标记开发[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(12):123-129,147.
|
| [16] |
姚俊修, 毛秀红, 李善文, 等. 基于荧光SSR标记的白杨派种质资源遗传多样性研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(6):92-100.
|
| [17] |
沈植国, 汤正辉, 袁德义, 等. 接骨木种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2019, 47(10):8-11,15.
|
| [18] |
郭宇兰, 刘克武, 宗宪春. 接骨木概况及遗传多样性研究进展[J]. 中国林副特产, 2019(4):82-86.
|
| [19] |
李金英, 赵春莉, 刘树英, 等. 忍冬科3属植物种质资源研究进展[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(1):143-148,154.
|
| [20] |
何其芳, 李荣华, 郭培国, 等. 利用SSR荧光标记技术分析烟草种质的遗传多样性[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(10):95-102.
|
| [21] |
郝晨阳, 王兰芬, 贾继增, 等. SSR荧光标记和银染技术的比较分析[J]. 作物学报, 2005, 31(2):144-149.
|
| [22] |
王瑞云, 季煦, 陆平, 等. 利用荧光SSR分析中国糜子遗传多样性[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(4):530-548.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
王明庥. 林木遗传育种学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社,2001:57-64.
|
| [26] |
朱其卫, 李火根. 鹅掌楸不同交配组合子代遗传多样性分析[J]. 遗传, 2010, 32(2):183-188.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
陈立强, 师尚礼. 42份紫花苜蓿种质资源遗传多样性的SSR分析[J]. 草业科学, 2015, 32(3):372-381.
|
| [29] |
吕锋, 解孝满, 韩彪, 等. 基于SSR标记的麻栎天然群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(3):109-116.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |