 PDF(13758 KB)
PDF(13758 KB)


基于多分类器集成的土地覆盖分类及预测研究
蒋路凡, 苏慧毅, 张银, 刘琴琴, 张小伟, 李明诗
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 255-266.
 PDF(13758 KB)
PDF(13758 KB)
 PDF(13758 KB)
PDF(13758 KB)
基于多分类器集成的土地覆盖分类及预测研究
Land cover classification and prediction based on multiple classifier ensemble learning
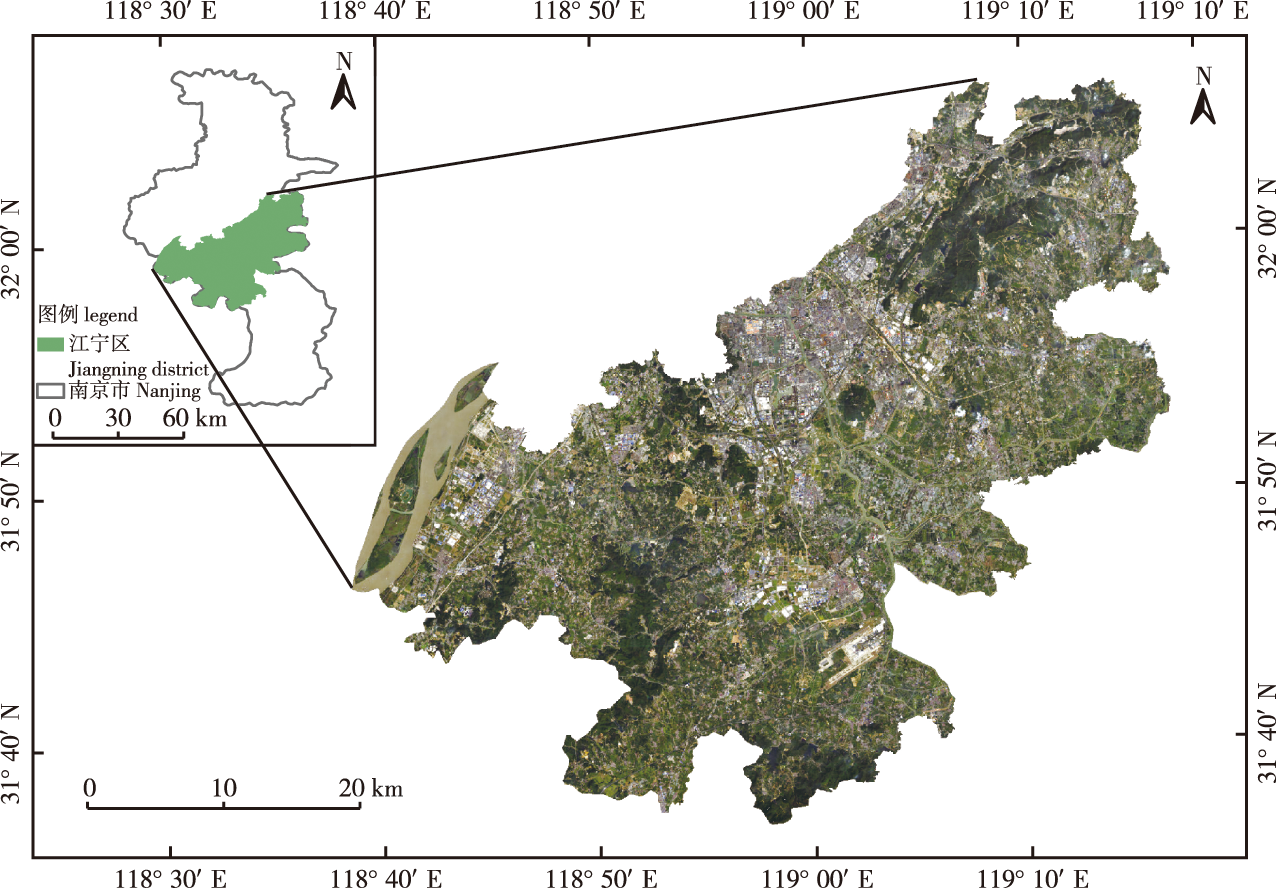
【目的】为发挥不同单分类器各自的优势进而采用集成学习方式提高土地覆盖分类精度,据此比较不同土地覆盖变化模拟模型性能从而执行最优的土地覆盖变化预测,为土地资源合理开发与利用决策制定提供参考。【方法】基于南京市江宁区2000、2010和2020年的Landsat TM/OLI影像,结合研究区实际定义了水体、建筑、林地、草地、耕地和未利用地等6种土地覆盖分类体系,在测试了最大似然法、马氏距离法、最小距离法、神经网络和支持向量机等基分类器性能基础上,采用随机森林和证据理论2种不同的集成学习方法对5种基分类器的分类结果进行集成,比较了集成性能后构建了最终的土地覆盖分类结果。然后,基于2000和2010年的最优集成土地覆盖分类图,运用CA-Markov、PLUS和ANN-CA模型分别对2020年研究区的土地覆盖格局进行模拟,并将不同的模拟结果与2020年真实集成分类结果进行了空间一致性检验,以此确定土地覆盖变化预测的最佳模型并用其预测2030年江宁区的土地覆盖模式。【结果】在单分类器分类结果中,2000年支持向量机算法取得了最佳分类效果,总体精度达到了88.75%,Kappa系数为0.77;2010年神经网络方法表现最佳,总体精度为88.75%,Kappa系数为0.83;2020年最大似然法取得了最佳分类效果,总体精度为82.75%,Kappa系数为0.74。在2种集成方法中,随机森林在2000年取得了最佳集成分类效果,总体精度和Kappa系数分别为91.25%和0.85;证据理论在2010年取得了最佳集成效果,总体精度和Kappa系数分别为90.80%和0.86;随机森林在2020年取得了最佳集成效果,总体精度和Kappa系数分别为93.75%和0.91。就土地覆盖预测而言,PLUS模型获得了98.54%的空间一致性。根据PLUS模型预测2030年土地覆盖结果可知,江宁区各土地覆盖类型变化较小,建设用地略有扩张但范围有限,耕地稍减少但在可控范围内。林地、草地和未利用地变化较小,水体面积相对减少。【结论】恰当的集成策略能明显改进土地覆盖分类精度,合适的、适应局部土地利用状态和政策调控的预测模型可有效预测区域未来土地覆盖分布模式,它们能为区域土地利用、城市管理决策等提供更可靠的方法和数据支持。
【Objective】This study aims to exert the respective advantages of individual base classifiers, different ensemble learning strategies were tested in the present study to improve the final land cover classification accuracy. On this basis, different land cover change simulation models were implemented and compared to obtain more accurate land cover projection results to provide references for formulating decisions of rational development and utilization of land resources in the future.【Method】Based on the Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM)/Operational Land Imager (OLI) images acquired in 2000, 2010 and 2020 covering Jiangning District of Nanjing City, the classification scheme, including water body, built-up land, forest land, grass land, crop land and unused land, was defined by referring to relevant industry standards and the actual conditions of the study area. The land cover classification performances of five base classifiers, including the Maximum Likelihood Classifier, Mahalanobis Distance Classifier, Minimum Distance Classifier, Neural Network, and Support Vector Machine(SVM) Classifiers, were implemented and quantitatively evaluated, followed by an integrated combination of the five individual classification results using the random forest algorithm and Dempster-Shafer (D-S) evidence theory. The final integrated classifications in 2000, 2010 and 2020 with higher overall accuracy were created after comparing the respective ensemble performances of the two algorithms. Based on the optimal integrated land cover classification maps in 2000 and 2010, the cellular automata (CA)-Markov model, PLUS model, and artificial neural network (ANN)-CA model were used to predict the land cover pattern of 2020 in the study area, and the prediction results of different models were compared with the real integrated classification results in 2020 to derive a spatial agreement index, determine the best model for land cover change simulation, and generate the projected land cover pattern of 2030 in Jiangning District.【Result】An independent validation showed that for a single base classifier, SVM algorithm achieved the best classification effect in 2000, with an overall accuracy at 88.75% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.77. In 2010, the neural network algorithm obtained the best classification effect, with an overall accuracy of 88.75% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.83. In 2020, the maximum likelihood algorithm had the best classification effect, with an overall accuracy of 82.75% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.74. Regarding the two ensemble methods, the random forest algorithm achieved the best integrated classification effect in 2000, with an overall accuracy of 91.25% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.85. The evidence theory process achieved the best integrated classification effect in 2010, with an overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient of 90.80% and 0.86, respectively. Moreover, the random forest algorithm achieved the best integrated classification effect in 2020, with an overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient of 93.75% and 0.91, respectively. Regarding land cover prediction, the PLUS model obtained a spatial agreement measure of 98.54%, outperforming the CA-Markov and ANN-CA models.According to the optimal prediction results in 2030 made by the PLUS model, there was a slight expansion of built-up land, but the extent was limited. The areal reduction in cropland was observed but within a controllable range. The changes in forest, grassland, and unused land were slight, while the water body was decreased.【Conclusion】Overall, the present study demonstrated that proper assemble learning strategies produce more accurate land cover classifications in contrast to a single base classifier. In addition, a suitable land cover change prediction or simulation model that adapts to local land use status and policy regulations effectively predicts the future land cover classification pattern. Thus, these strategies provide more reliable methods and data support for the development of land use and urban management decisions.
Landsat 影像 / 地表特征 / 土地覆盖分类 / 集成学习 / 土地覆盖变化模拟
Landsat imagery / surface features / land cover classification / assemble learning / land cover change simulation
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
骆剑承, 周成虎, 杨艳. 遥感地学智能图解模型支持下的土地覆盖/土地利用分类[J]. 自然资源学报, 2001, 16(2):179-183.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
夏玉计. 基于多特征融合支持向量机的土地覆盖类型提取与分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
冯登超, 陈刚, 肖楷乐, 等. 基于最小距离法的遥感图像分类[J]. 北华航天工业学院学报, 2012, 22(3):1-2,5.
|
| [8] |
刘焕军, 杨昊轩, 徐梦园, 等. 基于裸土期多时相遥感影像特征及最大似然法的土壤分类[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(14):132-139.
|
| [9] |
高昂, 唐世浩, 肖萌, 等. 机器学习在遥感影像分类中的应用[J]. 科技导报, 2021, 39(15):67-74.
|
| [10] |
汪靖翔. 决策树算法的原理研究和实际应用[J]. 电脑编程技巧与维护, 2022(8):54-56,72.
|
| [11] |
郑文武, 曾永年. 利用多分类器集成进行遥感影像分类[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2011, 36(11):1290-1293.
|
| [12] |
罗常伟, 王双双, 尹峻松, 等. 集成学习研究现状及展望[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2023, 9(1):1-8.
|
| [13] |
张银辉, 赵庚星. 土地利用/土地覆盖遥感分类方法的研究综述[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2002, 23(3):21-25.
|
| [14] |
李国清, 柏永青, 杨轩, 等. 基于深度学习的高分辨率遥感影像土地覆盖自动分类方法[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(9):1690-1704.
|
| [15] |
崔兆韵, 张承明, 杨晓霞, 等. 基于深度学习的高分遥感影像分类方法研究[J]. 科技与创新, 2021(3):55-57.
|
| [16] |
季顺平, 田思琦, 张驰. 利用全空洞卷积神经元网络进行城市土地覆盖分类与变化检测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(2):233-241.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
雷浩川. 多分类器集成的遥感影像分类研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
|
| [19] |
陈彦冰. 多分类器集成的遥感影像地物分类研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.
|
| [20] |
夏俊士, 杜培军, 张伟. 遥感影像多分类器集成的关键技术与系统实现[J]. 科技导报, 2011, 29(21):22-26.
|
| [21] |
王震. 基于OLI影像的多分类器组合方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
|
| [22] |
龙飞, 任金铜. 基于多分类器集成的GF-2遥感影像分类研究[J]. 科学技术创新, 2023(3):19-24.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
黎云云, 畅建霞, 王义民, 等. 基于CA-Markov模型的黄河流域土地利用模拟预测研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(12):107-116.
|
| [26] |
龚文峰, 袁力, 范文义. 基于CA-Markov的哈尔滨市土地利用变化及预测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(14):216-222.
|
| [27] |
王冬辰, 杜培军, 苏红军, 等. 近20年大同市土地利用/覆盖遥感变化分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(7):68-75.
|
| [28] |
杜培军, 柳思聪. 融合多特征的遥感影像变化检测[J]. 遥感学报, 2012, 16(4):663-677.
|
| [29] |
张辉. 基于多分类器组合的遥感土地利用分类研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(32):389-392.
|
| [30] |
彭正林, 毛先成, 刘文毅, 等. 基于多分类器组合的遥感影像分类方法研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2011, 23(2):19-25.
|
| [31] |
陈洋波, 窦鹏, 张涛. 基于Landsat的多分类器集成遥感影像分类[J]. 测绘科学, 2018, 43(8):97-103,109.
|
| [32] |
周婷, 汪炎, 邹俊, 等. 基于PCA和SVM的遥感影像水体提取方法及验证[J]. 水资源保护, 2023, 39(2):180-189.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
方文, 李朝奎, 梁继, 等. 多分类器组合的遥感影像分类方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2016, 41(10):120-125.
|
| [37] |
鞠琴, 吴金雨, 王兴平, 等. 机器学习算法在降水和气温多模式集成中的应用[J]. 水资源保护, 2024, 40(3):106-115.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
刘宇航. 干旱绿洲区盐碱地遥感影像分类模型及时空变化格局研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2022.
|
| [40] |
李琛, 高彬嫔, 吴映梅, 等. 基于PLUS模型的山区城镇景观生态风险动态模拟[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(1):84-94.
|
| [41] |
梁德强. 基于PLUS模型的齐齐哈尔市土地利用变化与情景模拟[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2022.
|
| [42] |
伍丹, 朱康文, 张晟, 等. 基于PLUS模型和InVEST模型的成渝经济区碳储量演化分析[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 2022, 7(2):85-96.
|
| [43] |
杨文龙. 基于GeoSOS的村镇建设用地扩张分析及规划模拟优化[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016.
|
| [44] |
马婷, 李崇贵, 汤伏全, 等. 基于多分类器集成的落叶松人工林提取[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(11):105-118.
|
| [45] |
吕岳, 施鹏飞, 赵宇明. 多分类器组合的投票表决规则[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2000, 34(5):680-683.
|
| [46] |
张晓羽, 李凤日, 甄贞, 等. 基于随机森林模型的陆地卫星-8遥感影像森林植被分类[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2016, 44(6):53-57,74.
|
| [47] |
张卫春, 刘洪斌, 武伟. 基于随机森林和Sentinel-2影像数据的低山丘陵区土地利用分类:以重庆市江津区李市镇为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(6):1334-1343.
|
| [48] |
张少佳. 多分类器组合及其遥感分类研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010.
|
| [49] |
肖胜杰. 遥感图像多分类器组合方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2017.
|
| [50] |
柏延臣, 王劲峰. 结合多分类器的遥感数据专题分类方法研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2005, 9(5):555-563.
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
凌成星, 鞠洪波, 张怀清, 等. 基于CA-MARKOV模型的北京湿地资源变化预测研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(20):262-269.
|
| [54] |
经阳. 基于CA-Markov模型的佛山市生态用地演变及其模拟[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2016.
|
| [55] |
陈倩. 城市化进程下土地覆盖、森林空间模式及属性变化分析[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2018.
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
谢向东, 林孝松, 王莹, 等. 基于PLUS模型的重庆市南川区土地利用多情景模拟[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2023, 40(6):86-92,113.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |