 PDF(2411 KB)
PDF(2411 KB)


南方丘陵区典型混交林树种水分来源对降水的适应性
武文杰, 吴朝明, 朱骊, 王琳棋, 戈禹, 张潭, 刘自强
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6) : 121-128.
 PDF(2411 KB)
PDF(2411 KB)
 PDF(2411 KB)
PDF(2411 KB)
南方丘陵区典型混交林树种水分来源对降水的适应性
Adaptation of typical mixed forest species in the southern hilly region to precipitation variation via water source changes
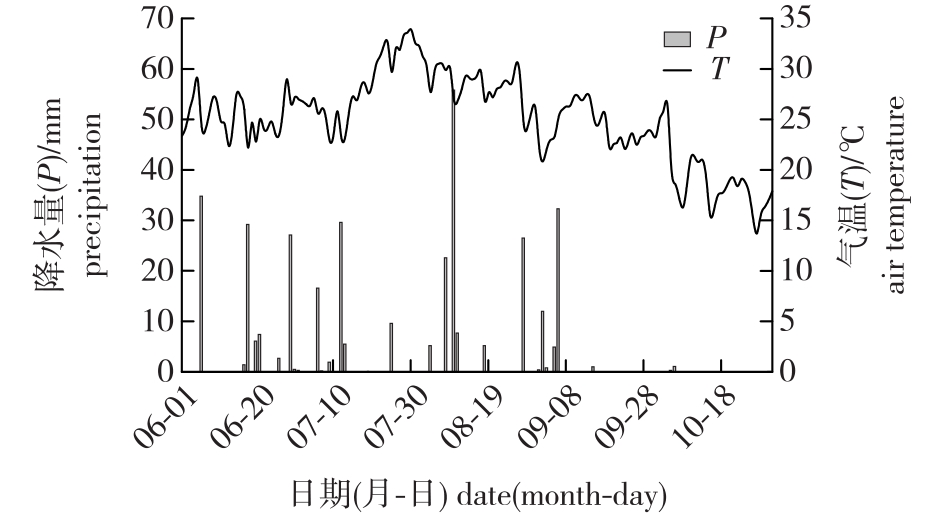
【目的】基于全球气候变化背景下极端天气事件频发对植物水分利用的影响,探讨不同降水条件下南方丘陵区混交林树种对水分来源的适应性变化,为科学实施森林精准经营管理措施提供理论依据。【方法】采集不同降水量梯度下南方丘陵区麻栎(Quercus acutissima)和马尾松(Pinus massoniana)混交林的土壤和植物同位素样品,借助多元线性混合模型,对比分析不同降水梯度下麻栎和马尾松的水分利用来源。【结果】①麻栎在无降水时主要利用[10,30) cm土层的水分,利用率为62.0%;随着降水量的增加,其水源转向[80,100) cm土层的水分和地下水,大雨条件下的利用率分别为34.2%和44.6%。②马尾松在无降水时主要利用地下水和[80,100) cm土层水分,利用率分别为21.2%和21.1%;随降水量增加其水分来源逐渐向(0,10) cm和[10,30) cm土层转移,利用率分别为27.2%和53.3%。【结论】麻栎和马尾松的水分来源对降水的适应性不同,不同降水梯度下两者对土壤水分利用深度能较好地互补。在极端降水频发条件下,不同的水分利用模式有利于减少树种间水分竞争。
【Objective】The frequent extreme weather events that are likely to be associated with global climate change may have an impact on plant water use. The aim of this study was to explore how mixed forest species adapt by accessing different water sources in the southern hilly region of China under different precipitation conditions.【Method】The stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in the xylem, soil, and groundwater from mixed Quercus acutissima and Pinus massoniana forests in the southern hilly region were measured and multi-source linear mixed models (Iso-Source) used to compare and analyze the water use in the forest under different precipitation gradients.【Result】Q. acutissima was found to mainly use soil water from the shallow layer ([10,30) cm) under low precipitation conditions, with a utilization rate of 62.0%; however, under heavier rain the species turns to deep soil water ([80,100) cm) and groundwater, with utilization rates of 34.2% and 44.6%, respectively. P. massoniana mainly uses groundwater and deep soil water ([80,100) cm) with utilization rates of 21.2% and 21.1%, respectively, under low precipitation conditions; however, the species changes to use soil water from depths of (0,10) cm and [10,30) cm layers, with utilization rates of 27.2% and 53.3%, respectively, when precipitation increases.【Conclusion】Q. acutissima and P. massoniana adapt differently to precipitation changes in terms of the water source used, and the depth from which water is sourced changes under different precipitation gradients. The different water use patterns of these species will reduce water competition under the expected frequent extreme precipitation events expected in the future. The results of the study provide a theoretical basis for the implementation of improved forest management.
麻栎 / 马尾松 / 降水梯度 / 水分来源 / 氢氧同位素
Quercus acutissima / Pinus massoniana / precipitation gradient / water source / hydrogen and oxygen isotopes
| [1] |
孙荣卿, 董李勤, 张昆, 等. 四川若尔盖湿地国家级自然保护区水体氢氧同位素与水化学特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2):169-178.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
霍伟杰. 基于氢氧稳定同位素的西南岩溶断陷盆地石漠化地区苹果树水分来源及时空变化特征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
刘文娜, 贾剑波, 余新晓, 等. 北京山区松栎混交群落的植物水分来源研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2018, 26(1):12-22.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
刘自强, 余新晓, 贾国栋, 等. 北京山区侧柏利用水分来源对降水的响应[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(7):16-23.
|
| [18] |
户红红, 陈进豪, 牟洋, 等. 滇东南岩溶山地不同恢复模式云南松水分利用策略的差异[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(1):37-44.
|
| [19] |
王佳敏, 成应杰, 陈金艺, 等. 模拟不同降雨时间格局下喀斯特垂直异质生境对桢楠幼苗光合和生长的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(18):7348-7356.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
周淑贞. 气象学与气候学[M].3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社,1997:74.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
刘自强, 余新晓, 娄源海, 等. 北京山区侧柏水分利用策略[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(11):3697-3705.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
王小明, 周本智, 钟绍柱, 等. 不同降雨条件下天然次生林水文过程动态分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 34(6):57-60.
|
| [27] |
王海燕, 刘廷玺, 王力, 等. 科尔沁沙地坨甸交错区土壤水分的空间变异规律[J]. 干旱区研究, 2013, 30(3):438-443.
|
| [28] |
贾国栋. 基于稳定氢氧同位素技术的植被-土壤系统水分运动机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2013.
|
| [29] |
徐庆, 刘世荣, 安树青, 等. 四川卧龙亚高山暗针叶林土壤水的氢稳定同位素特征[J]. 林业科学, 2007, 43(1):8-14.
|
| [30] |
殷建华. 南方红壤丘陵区不同植被类型土壤不同土层水分对降水的响应[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(11):72-77.
|
| [31] |
崔建国, 崔文山, 邓丽琴, 等. 辽西地区3种落叶栎树抗旱性的初步研究[J]. 辽宁林业科技, 2005(1):10-11,42.
|
| [32] |
蔡鲁, 朱婉芮, 王华田, 等. 鲁中南山地6个造林树种根系形态的比较[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2015, 13(2):83-91.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
徐贵青, 李彦. 共生条件下三种荒漠灌木的根系分布特征及其对降水的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(1):130-137.
|
| [35] |
张治军, 王彦辉, 于澎涛, 等. 不同优势度马尾松的生物量及根系分布特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 32(4):71-75.
|
| [36] |
张成富, 何腾兵, 杨威, 等. 高原山地丘陵区马尾松近成熟林和成熟林细根的垂直分布特征[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 49(6):789-795.
|
| [37] |
邢星, 陈辉, 朱建佳, 等. 柴达木盆地诺木洪地区5种优势荒漠植物水分来源[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(21):6277-6286.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
张鑫, 邢亚娟, 闫国永, 等. 细根对降水变化响应的meta分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(2):164-172.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
孙双峰. 三峡库区岸边植物水分利用研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院(植物研究所), 2006.
|
| [44] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |