 PDF(1523 KB)
PDF(1523 KB)


基于模糊层次分析的栗子坪国家级自然保护区生态健康评价
冯婷婷, 郑阳, 骆伟, 代勤龙, 李健威, 王飞, 脱云飞
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 212-220.
 PDF(1523 KB)
PDF(1523 KB)
 PDF(1523 KB)
PDF(1523 KB)
基于模糊层次分析的栗子坪国家级自然保护区生态健康评价
Ecological health assessment based on fuzzy analytic hierarchy process: a case study of Liziping National Nature Reserve
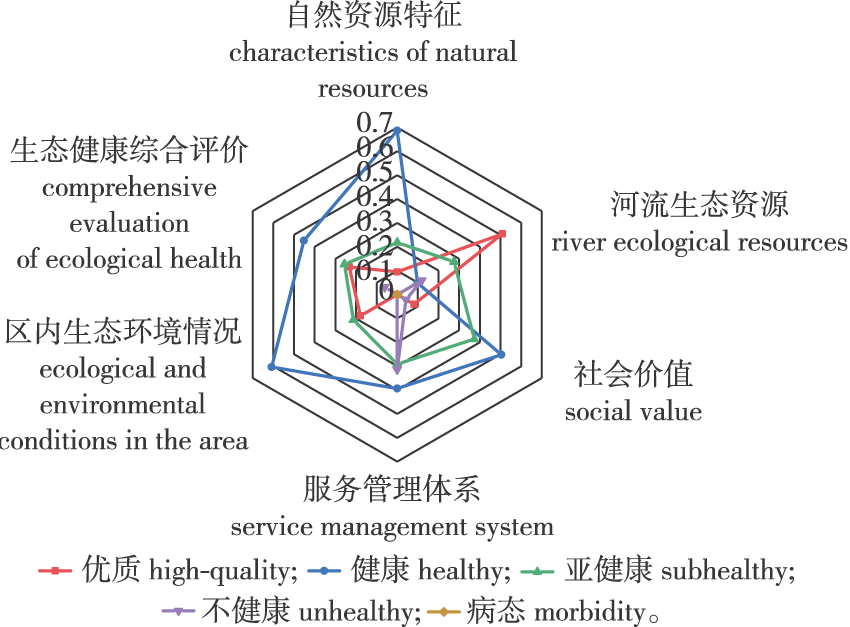
【目的】明确生态健康评价体系建立及其指标选取是自然保护区生态健康评价的关键问题,通过生态健康评价了解自然保护区生态健康状况,为改善区域生态环境提供依据。【方法】选取四川栗子坪国家级自然保护区的自然资源特性、河流生态资源、社会价值、服务管理体系和生态环境情况5个准则层,以及31个指标层建立生态健康综合评价指标体系,基于模糊层次分析法生态健康综合评价模型对自然保护区生态健康进行评价。【结果】栗子坪国家级自然保护区自然资源特性、河流生态资源、社会价值、服务管理体系和生态环境指标权重分别为0.157、0.277、0.124、0.073和0.370,其最大特征根和一致性指标分别为5.158和0.040。自然资源特性、社会价值、生态环境情况处于健康和亚健康状态的隶属度得分分别为0.687和0.218、0.504和0.373、0.608和0.212,河流生态资源处于优质和亚健康状态的隶属度分别为0.509和0.275,服务管理体系处于健康状态的隶属度为0.394。栗子坪国家级自然保护区生态健康在优质、健康、亚健康、不健康和病态隶属度评价得分分别为0.232、0.452、0.255、0.061和0,生态健康隶属度综合得分为0.452,生态健康评价结果为健康。【结论】该研究可为栗子坪国家级自然保护区生态保护及其生态环境综合治理提供科学依据与技术支撑。
【Objective】The critical challenges in ecological health assessment involve establishing a comprehensive assessment system and selecting appropriate indicators. This study aims to evaluate the ecological health status of nature reserves to provide a scientific basis for improving the regional ecological environment. 【Method】This study established a comprehensive ecological health evaluation index system for the Sichuan Liziping National Nature Reserve. The system encompasses five criteria: natural resource characteristics, river ecological resources, social value, service management system, and ecological environment conditions, further subdivided into 31 specific indicators. A fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (AHP) model was employed to evaluate the reserve’s ecological health. 【Result】The evaluation revealed the relative weights of the criteria as follows: natural resource characteristics (0.157), river ecological resources (0.277), social value (0.124), service management system (0.073), and ecological environment conditions (0.370). The maximum eigenvalue and consistency index were calculated as 5.158 and 0.040. Membership scores for natural resources, social value, and ecological environment conditions in “healthy” and “sub-healthy” states were 0.687 and 0.218, 0.504 and 0.373, 0.608 and 0.212, respectively. River ecological resources showed membership scores of 0.509 in “high quality” and 0.275 in “sub-healthy” states, while the service management system exhibited a “healthy” state membership score of 0.394. Overall, the ecological health evaluation yielded scores for “high quality” (0.232), “healthy” (0.452), “sub-healthy” (0.255), “unhealthy” (0.061), and “sick” (0) membership states. The comprehensive membership score was 0.452, categorizing the reserve’s ecological health as “healthy.” 【Conclusion】 This study offers a scientific foundation and technical guidance for ecological conservation and the integrated management of the ecological environment in the Liziping National Nature Reserve.
生态健康 / 模糊层次分析法 / 隶属度 / 栗子坪国家级自然保护区
ecological health / fuzzy analytic hierarchy process / membership degree / Liziping National Nature Reserve
| [1] |
刘春青, 张韬, 刘佳慧, 等. 辉腾锡勒风电场草地生态系统健康评价[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(2):213-221.
|
| [2] |
易浪, 孙颖, 尹少华, 等. 生态安全格局构建:概念、框架与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4):845-856.
|
| [3] |
樊贤璐, 徐国宾. 基于生态—社会服务功能协调发展度的湖泊健康评价方法[J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(5):1225-1234.
|
| [4] |
游清徽, 刘玲玲, 方娜, 等. 基于大型底栖无脊椎动物完整性指数的鄱阳湖湿地生态健康评价[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(18):6631-6641.
|
| [5] |
徐菲, 王永刚, 张楠, 等. 北京市白河和潮河流域生态健康评价[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(3):932-942.
|
| [6] |
燕琳, 马岚, 潘成忠, 等. 基于模糊综合评价与灰色关联分析的河流自然性评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(3):480-488.
|
| [7] |
李勇, 丛怡, 贾佳. 基于熵权法的汾渭平原城市空气质量模糊综合评价[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(8):236-243,206.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
朱佳玮, 孙文章, 岳秀峰. 基于滨海环境资源特点的大连旅游承载状态评价[J]. 地理科学, 2021, 41(4):664-673.
|
| [10] |
王慧杰, 毕粉粉, 董战峰. 基于AHP-模糊综合评价法的新安江流域生态补偿政策绩效评估[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(20):7493-7506.
|
| [11] |
王晓艳, 章四龙, 刘磊. 基于AHP-熵权法的水环境承载力模糊综合评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(9):206-212.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
席健, 朱玉东, 何可, 等. 四川栗子坪国家级自然保护区林麝野化培训个体的生境选择[J]. 四川林业科技, 2023, 44(2):51-57.
|
| [17] |
王大勇, 李华静, 刘翠, 等. 冶勒自然保护区大熊猫及其栖息地保护现状与管理对策[J]. 四川林业科技, 2011, 32(6):113-115.
|
| [18] |
王秋燕, 陈鹏飞, 李学东, 等. 森林健康评价方法综述[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(2):177-183.
|
| [19] |
康文辉. 永定河上游太子城河流域土壤养分空间分布及其影响因素[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2021.
|
| [20] |
陈红. 小相岭山系大中型兽类多样性调查评估[D]. 南充: 西华师范大学, 2021.
|
| [21] |
燕琳. 河流自然性评价指标体系与评价方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020.
|
| [22] |
徐香勤, 蔡文倩, 雷坤, 等. 天津市河流生态完整性评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(10):2308-2317.
|
| [23] |
苏辉东, 贾仰文, 牛存稳, 等. 河流健康评价指标与权重分配的统计分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2019, 35(6):138-144.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
王同达, 曹锦雪, 赵永华, 等. 基于PSR模型的陕西省土地生态系统健康评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(5):1563-1572.
|
| [32] |
陈歆, 靳甜甜, 苏辉东, 等. 拉萨河河流健康评价指标体系构建及应用[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(3):799-809.
|
| [33] |
张月琪, 张志, 江鎞倩, 等. 城市红树林生态系统健康评价与管理对策:以粤港澳大湾区为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(5):2352-2369.
|
| [34] |
曹小玉, 赵文菲, 李际平, 等. 中亚热带几种典型森林土壤养分含量分析及综合评价[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(9):3525-3535.
|
| [35] |
舒远琴, 宋维峰, 马建刚. 哈尼梯田湿地生态系统健康评价指标体系构建[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(23):9292-9304.
|
| [36] |
田耀武, 黄志霖, 肖文发, 等. 基于物元模型和小班尺度的兰陵溪流域森林生态系统健康评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(5):1458-1464.
|
| [37] |
袁瑞强, 钟钰翔, 龙西亭. 洞庭湖上游平原浅层地下水水质综合评价[J]. 水资源保护, 2021, 37(6):121-127.
|
| [38] |
胡威, 李卫明, 王丽, 等. 基于GA-BP优化模型的中小河流健康评价研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(5):1786-1797.
|
| [39] |
罗腾峰, 叶茂, 殷锡凯, 等. 人为干扰对阿尔泰山林地和草地生态系统健康影响分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(6):18-25.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |