 PDF(2144 KB)
PDF(2144 KB)


浙江地区毛竹林根际土壤促生细菌筛选及促生效应研究
杨芾, 王辉, 王琴, 姜春前, 周妍旭, 李潞滨
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 83-90.
 PDF(2144 KB)
PDF(2144 KB)
 PDF(2144 KB)
PDF(2144 KB)
浙江地区毛竹林根际土壤促生细菌筛选及促生效应研究
Screening of growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizosphere soil of Phyllostachys edulis and their growth-promoting effects in Zhejiang Province
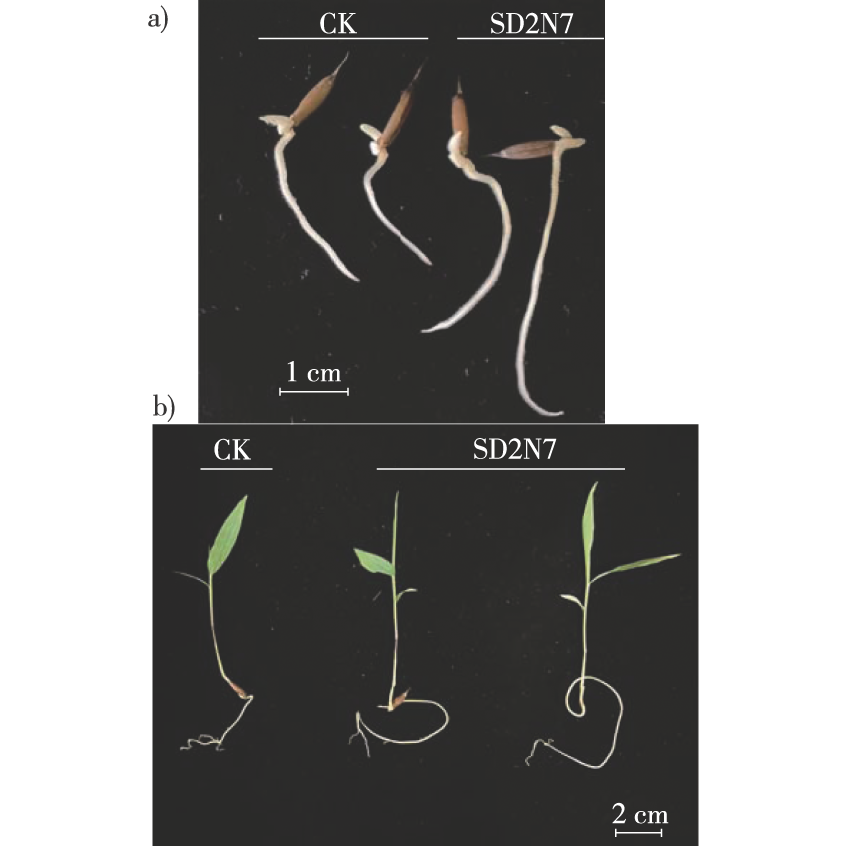
【目的】根际促生菌对促进植物生长发育、改善土壤微生态环境、实现林业可持续发展有重要作用,研究浙江地区毛竹(Phyllostachys edulis)根际土壤功能细菌,考察菌株对毛竹幼苗生长的影响,为开发利用新的竹类植物微生物资源,提升竹林生产力和生态系统服务功能提供依据。【方法】以毛竹根际土壤为对象,利用传统稀释培养的方法分离根际细菌,基于16S rRNA基因序列利用最大似然法构建系统发育树,依托功能平板和特异性颜色变化进行体外功能评价,最后通过回接试验考察功能菌株对毛竹种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响。【结果】①共分离获得根际细菌39株,分属于3门12科23属。其中,放线菌门(Actinomycetota)为优势菌门,占38.5%;优势菌科为芽孢杆菌科(Bacillaceae),占25.6%。②对39株细菌进行功能评价发现,其中20株具有产吲哚乙酸(IAA)的功能,3株具有产铁载体功能,3株具有溶解无机磷能力,7株具有矿化有机磷能力,5株具有解钾能力。③菌株SD2N7同时具有产IAA、无机磷溶解、有机磷矿化以及解钾功能。生理生化指标测定及16s rRNA基因序列比对结果表明,菌株SD2N7为伍尔贝丁拉恩氏菌(Rahnella woolbedingensis)。通过回接试验发现,菌株SD2N7能够显著缩短毛竹种子的萌发时间,并促进毛竹幼苗根和叶片的伸长。【结论】毛竹根际土壤中功能微生物资源丰富,筛选获得了多株具有产IAA和铁载体,以及溶磷和解钾功能的菌株,且回接试验明确了菌株SD2N7对毛竹种子萌发和幼苗生长具有明显的促进作用。
【Objective】 Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria play an important role in promoting plant growth and development, improving the soil microenvironment, and aiding the development of sustainable forestry practices. The functional bacteria in the rhizospheric soil of Phyllostachys edulis, and their effects on seedling growth were investigated to provide a scientific basis for the development and utilization of new microbial resources from bamboo, improving the productivity of bamboo forests, and enhancing the functions of ecosystem services.【Method】The rhizosphere soil of P. edulis was selected as the research object, and the rhizosphere bacteria were isolated using traditional dilution culture methods. A phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene sequences was constructed using the maximum-likelihood method. In vitro functional evaluation was performed based on the functional plates and specific color changes. The effects of the functional strains on the germination of P. edulis seeds and the growth of seedlings were finally investigated with re-inoculation experiments.【Result】 A total of 39 rhizosphere bacterial strains from 23 genera belonging to 12 families under three phyla, were isolated and cultured. Actinomycetota and Bacillaceae were the dominant phylum and family with relative abundances of 41.0% and 25.6%, respectively. Functional analysis of the 39 bacterial strains revealed that 20 and three strains were capable of producing IAA (indole-3-acetic acid) and siderophores, while five and three strains were capable of dissolving potassium and inorganic phosphorus, respectively, and seven strains were capable of mineralizing organic phosphorus. The strain SD2N7 was capable of simultaneously producing IAA, dissolving inorganic phosphorus and potassium, and mineralizing organic phosphorus. Based on the physiological and biochemical characteristics and the 16S rRNA gene alignment, strain SD2N7 was identified as Rahnella woolbedensis. The re-inoculation experiments revealed that strain SD2N7 could significantly shorten the germination period of P. edulis seeds and promote the elongation of the roots and leaves of P. edulis seedlings.【Conclusion】 There were abundant functional microbial resources in the rhizosphere soil of P. edulis, which were capable of producing IAA or siderophores, dissolving phosphorus and potassium, and performing other functions. The back-grafting test additionally demonstrated that strain SD2N7 significantly promoted seed germination and the growth of P. edulis seedlings.
毛竹 / 植物根际促生菌(PGPR) / 分离培养 / 拉恩氏菌属 / 功能评价
Phyllostachys edulis / plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) / isolation and cultivation / Rahnella / function assessment
| [1] |
朱伟垚, 林梦婷, 吴仲义, 等. 不同竹龄毛竹茎干内生细菌多样性与功能预测[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2022, 40(5):766-774.
|
| [2] |
郭丽丽, 张晨洁, 王菲, 等. 牡丹野生种根际土壤细菌群落特征分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(3):45-55.
|
| [3] |
何相玉, 周冠军, 张新洁, 等. 氮磷添加对水曲柳人工林叶片、细根和土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (1): 73-81.
|
| [4] |
张金池, 李翀, 贾赵辉, 等. 功能性微生物在废弃矿山生态修复中的应用[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):146-156.
|
| [5] |
张晓荣, 段广德, 郝龙飞, 等. 氮沉降和接种菌根真菌对灌木铁线莲非结构性碳水化合物及根际土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(1):171-178.
|
| [6] |
邵鹏, 王铮, 钟斯文, 等. 镉胁迫下深色有隔内生真菌对樟子松1年生苗生长及根际土壤环境的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (2): 1-11.
|
| [7] |
曹媛媛, 陈春, 郭婷婷, 等. 亲和性促生菌DW12-L的定殖及其对大豆生长的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2019, 35(4):776-783.
|
| [8] |
冯歌林, 高竞, 严淑娴, 等. 3种竹子内生固氮菌特征及多样性[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(6):1203-1212.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
杨豆, 李广强, 吕永财, 等. 毛竹根系解磷细菌的解磷条件和解磷特性[J]. 经济林研究, 2021, 39(2):115-122.
|
| [11] |
荣良燕, 姚拓, 赵桂琴, 等. 产铁载体PGPR菌筛选及其对病原菌的拮抗作用[J]. 植物保护, 2011, 37(1):59-64.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
戴悦, 张汝军, 张腾月, 等. 红树植物根际土壤细菌分离鉴定及抑菌活性的研究[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2023(3):73-78.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
崔伟国, 尹彦舒, 张方博, 等. 马铃薯细菌多样性解析及促生高产IAA菌株的筛选[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020(1):223-231.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
杨鸿儒, 袁博, 赵霞, 等. 三种荒漠灌木根际可培养固氮细菌类群及其固氮和产铁载体能力[J]. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43(11):2366-2373.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
王义, 余贤美, 郑服丛. 热带土壤解磷细菌PSB26的筛选鉴定及拮抗初探[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2009, 15(7):59-62.
|
| [22] |
东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
夏冬亮, 任玉, 李潞滨, 等. 毛竹内生细菌分离培养基的选择[J]. 北京农学院学报, 2009, 24(1):15-19.
|
| [25] |
潘宇, 刘围, 孟俊, 等. 耐盐促生菌提高盐胁迫下植物生长的研究进展[J]. 生物加工过程, 2024, 22(2):182-188.
|
| [26] |
葛淼淼, 薄永琳, 刘宸, 等. 土壤产铁载体细菌的筛选及其对铁氧化物的活化与利用[J]. 微生物学通报, 2023, 50(3):1062-1072.
|
| [27] |
刘邮洲, 沈佳慧, 乔俊卿, 等. 芽孢杆菌嗜铁素研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2023, 39(1):266-276.
|
| [28] |
陈雅. 竹子内生产铁载体细菌筛选及高活性菌株的全基因组分析[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2020.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
韩烁, 夏冬亮, 李潞滨, 等. 毛竹根部解磷细菌的筛选及多样性研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2010, 33(2):26-31.
|
| [33] |
张扬, 郭春兰, 陈伏生, 等. 毛竹根际2株溶磷解钾促生细菌的筛选鉴定[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2018, 40(4):759-768.
|
| [34] |
陆启帆, 林上平, 刘胜辉, 等. 施肥对毛竹林产量影响的Meta分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1):88-96.
|
| [35] |
焦子伟, 位婉, 李磊, 等. PQQ和IAA促生因子对Rahnella aquatilis HX2菌株促生机理研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(5):907-917.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |