 PDF(1965 KB)
PDF(1965 KB)


不同林龄水杉人工林地表大型土壤动物群落特征比较研究
曹荔荔, 阮宏华, 李媛媛, 倪娟平, 王国兵, 曹国华, 沈彩芹, 徐亚明
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 91-98.
 PDF(1965 KB)
PDF(1965 KB)
 PDF(1965 KB)
PDF(1965 KB)
不同林龄水杉人工林地表大型土壤动物群落特征比较研究
Variations of surface soil macrofauna in different aged Metasequoia glyptostroboides plantations
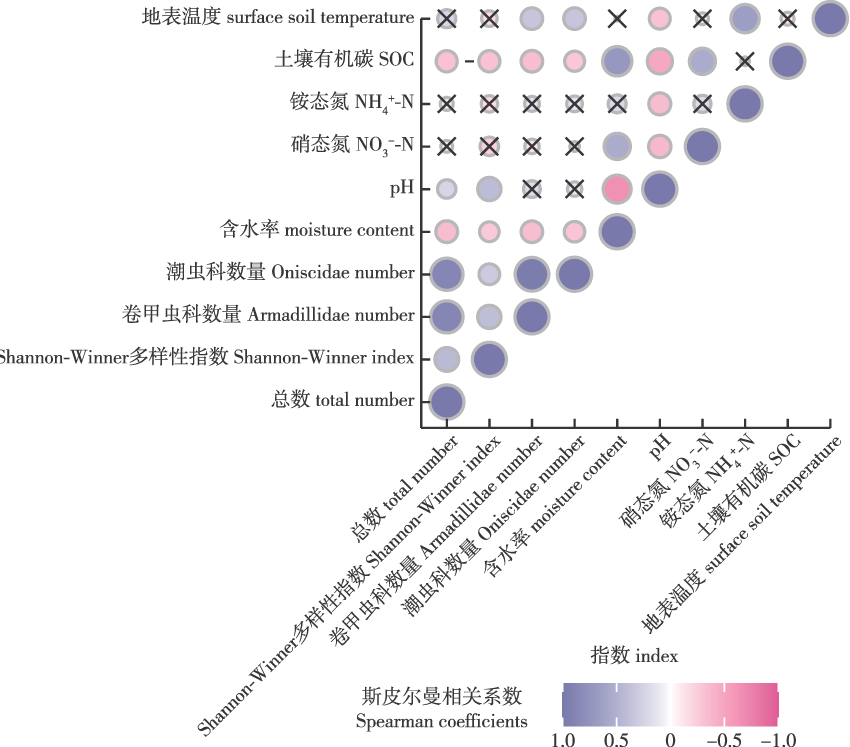
【目的】土壤动物是森林生态系统的重要组成成分,对森林土壤结构和功能具有重要的调控作用。研究不同林龄水杉(Metasequoia glyptostroboides)人工林地表大型土壤动物群落组成和结构的变化,为提高认识土壤生态系统对全球变化的响应和优化水杉人工林科学管理提供参考。【方法】采用野外固定样地调查法,在江苏东台林场选择立地条件和经营措施相对一致的 9 个不同林龄(7、11、16、21、26、31、36、41和 46 年生)水杉人工林,每个年龄林分随机设置 4 个重复样地,分别于 2022 年的生长旺季(8月)和生长末期(11月)采集样品,调查不同林龄水杉人工林地表大型土壤动物群落组成结构及多样性的变化。采用陷阱法对水杉人工林地表大型土壤动物进行采集,土壤动物样品带回实验室后在体视显微镜下进一步分类检索和计数鉴定。此外,用土钻取0~15 cm土层的土壤混合样,带回实验室进行土壤理化性质分析,最后使用SPSS 26和Origin 2021进行统计分析与绘图。【结果】共捕获地表大型土壤动物14 289 只,隶属16目23 科,其优势类群为等足目中的卷甲虫科和潮虫科;不同林龄水杉人工林地表大型土壤动物的优势类群和常见类群差异较大;地表大型土壤动物个体数量在11年生水杉林中最大,36年生中最小;在不同季节中,大型土壤动物个体总数以8月高于11月,而物种丰富度则以11月高于8月。【结论】不同生长发育阶段及季节变化对水杉人工林地表大型土壤动物的群落结构有显著影响,主要呈现出中林龄段的地表大型土壤动物个体总数、类群数量及多样性指数总体上位于较高水平,建议森林经营过程中注重中龄林阶段的地表土壤大型动物的作用和保护。
【Objective】Soil faunas are crucial components of forest ecosystem. This study investigated the distribution characteristics and seasonal variation of soil macrofauna in Metasequoia glyptostroboides plantations of different ages. We analyzed differences in the community structure, seasonal dynamics, and influencing mechanisms of surface soil macrofauna, providing a theoretical basis for future studies on soil fauna community structure in these plantations.【Method】We assessed soil macrofauna community dynamics across nine M. glyptostroboides plantations (seven, 11, 16, 21, 26, 31, 36, 41, and 46 years old) using a randomized block design with four replicate plots per age group, located in a coastal area of northern Jiangsu Province, China. Collections were made in summer (August) and autumn (October) using pitfall traps, and samples were sorted and identified under a stereomicroscope in the laboratory. Additionally, soil samples from the 0-15 cm layer were collected for physicochemical analysis.【Result】We collected a total of 14 289 surface soil macrofauna individuals from 16 orders and 23 families. The dominant groups were Armadillidae and Oniscidae. Significant differences were observed in the dominant and common groups of soil macrofauna among plantations of different ages. The 11-year-old plantation had the highest number of soil macrofauna, while the 36-year-old plantation had the lowest. In terms of seasonal variation, the total number of surface soil macrofauna was higher in August than in November, whereas species richness was greater in November than in August.【Conclusion】The study highlights that both stand development and seasonal variation significantly influence the community structure of surface soil macrofauna in M. glyptostroboides plantations. As the forest matures, the total number, species diversity and diversity index of surface soil macrofauna increase, reaching a high level in middle-aged forests.
地表大型土壤动物 / 生物多样性 / 群落结构 / 林分发育 / 季节变化
surface soil macrofauna / biodiversity / community structure / stand development / seasonal variation
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
朱永恒, 赵春雨, 王宗英, 等. 我国土壤动物群落生态学研究综述[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(12): 1477-1481.
|
| [8] |
王兴松, 李恩星, 杨诗瀚, 等. 根结线虫病对烟草植株根际土壤微生物群落及其功能的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(6): 993-1003.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
刘雨诗, 蒋敏杰, 唐恺阳, 等. 基于大型土壤动物多样性视角的景观驳岸生态学特征研究[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2023, 41(1): 92-100.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
徐昭, 张瑞芝, 王佳楠, 等. Pk-αts高表达提高红松对松材线虫耐病性[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (5): 22-30.
|
| [16] |
问宇翔, 冯坤乔, 童冉, 等. 水杉人工林细根和粗根碳氮磷计量特征对N添加的响应[J]. 林业科学研究, 2022, 35(3): 161-168.
|
| [17] |
程建伟, 刘新民, 郝百惠, 等. 氮沉降对内蒙古典型草原地表节肢动物的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(8):2237-2245.
|
| [18] |
尹文英. 中国土壤动物检索图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1998.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
周泓杨, 张健, 张丹桔, 等. 不同郁闭度控制下马尾松(Pinus massoniana)人工林土壤动物群落特征[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(6): 1939-1955.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
谭艳, 王邵军, 阮宏华, 等. 不同林龄杨树人工林土壤动物群落结构特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(3): 8-12.
|
| [23] |
何相玉, 周冠军, 张新洁, 等. 氮磷添加对水曲柳人工林叶片、细根和土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (1): 73-81.
|
| [24] |
王辉, 陈旭, 吴鹏飞, 等. 白水河国家级自然保护区柳杉(Cryptomeria fortune)人工林大型土壤动物群落特征[J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(7): 1486-1496.
|
| [25] |
彭彩云. 华西雨屏区不同林龄杉木人工林土壤动物群落特征[D]. 四川农业大学, 2021.
|
| [26] |
刘杰, 陈建. 陷阱法调查转Bt棉对棉田地面蜘蛛群落的影响[J]. 植物保护学报, 2015, 42(1): 59-65.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
谭波, 吴福忠, 杨万勤, 等. 不同林龄马尾松人工林土壤节肢动物群落结构[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(4): 1118-1124.
|
| [31] |
肖玖金, 王子豪, 王戈, 等. 三种人工林中小型土壤动物群落季节动态特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2018, 32(10): 167-172.
|
| [32] |
拓向辉, 艾宁, 周永维, 等. 陕北黄土高原典型草地土壤动物群落的基本特征: 以吴起金佛坪小流域为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(8):125-132.
|
| [33] |
李晓东, 史沉鱼, 覃国乐, 等. 濒危植物单性木兰林区土壤动物群落结构与季节动态[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2015, 34(4): 20-26.
|
| [34] |
易兰, 由文辉. 浙江天童栲树林土壤动物群落结构及其季节变化[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006(2): 112-120.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |