 PDF(2548 KB)
PDF(2548 KB)


施钾肥对闽楠幼树枝叶挥发性次生代谢物组分及含量的影响
罗家琦, 文仕知, 刘沛书, 彭晓锋, 周瑾瑾, 何功秀
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 75-86.
 PDF(2548 KB)
PDF(2548 KB)
 PDF(2548 KB)
PDF(2548 KB)
施钾肥对闽楠幼树枝叶挥发性次生代谢物组分及含量的影响
Effect of potassium fertilization on the composition and content of volatile secondary metabolites in leaves and twigs of young Phoebe bournei
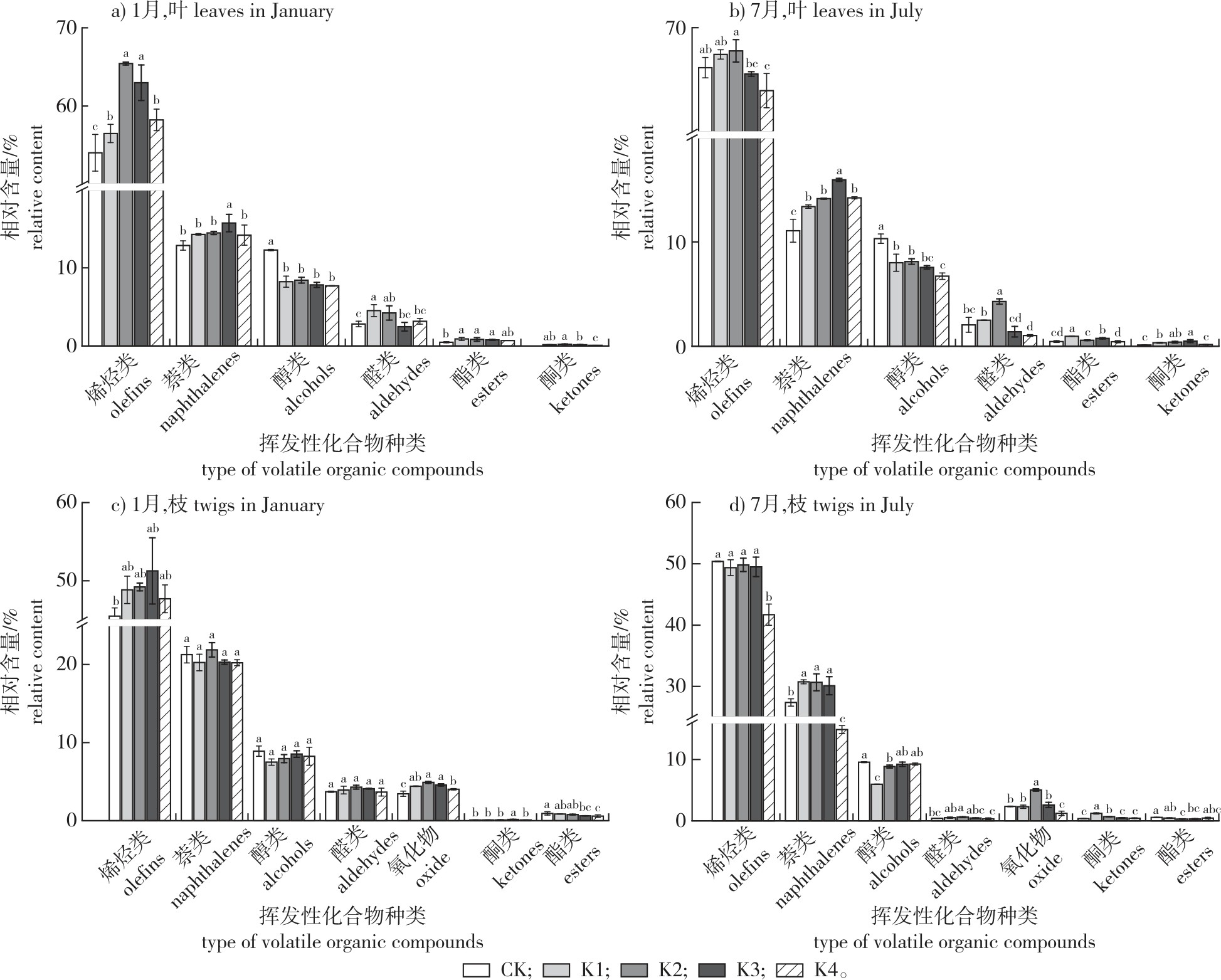
【目的】研究不同钾(K)添加量对闽楠幼树枝、叶挥发性次生代谢物(volatile secondary metabolites,VOCs)总含量、组分及其相对含量的影响,为闽楠人工林的多功能经营提供参考。【方法】对金洞林场10 年生闽楠人工林设置5种钾肥(K2O>52%)施用浓度梯度(CK. 0 g/株;K1.60 g/株;K2. 120 g/株;K3.180 g/株;K4.240 g/株),于施肥后次年1(夏季)和7月(冬季)分别采样,用水蒸气蒸馏法提取枝叶VOCs,采用气相色谱-质谱联用技术(GC-MS)测定组分与相对含量。【结果】施钾量对闽楠VOCs的含量有显著影响,枝、叶VOCs含量均呈先升后降的趋势,1月枝叶VOCs在K2处理下总质量分数最高(叶0.48‰、枝0.55‰),7月枝叶VOCs在K1处理下最高(叶0.47‰、枝0.34‰)。叶主要特征挥发性成分为白菖烯、香树烯、(-)-Alpha-蒎烯等,枝的主要特征成分为β-石竹烯、(-)-Alpha-蒎烯、(-)-Alpha-荜澄茄油烯等。闽楠的VOCs以烯烃类、萘类和醇类为主,叶两季烯烃类、萘类的相对含量在K2处理下显著提升,醇类在施肥后相对含量显著下降。叶养分元素正向影响枝VOCs含量且路径系数极显著,枝养分元素正向影响叶VOCs各种类的相对含量。【结论】施钾肥显著影响闽楠枝叶VOCs的总含量、种类、组分的相对含量和养分元素含量,添加量在60~180 g/株时,闽楠枝叶VOCs总含量达到最高。综合而言,1月K3为最佳处理,7月最佳处理为K2。模型证明养分元素对叶VOCs中萘类和枝VOCs中含氧化物的影响权重较高。
【Objective】Deciphering the effects of different potassium (K) additions on the total amount and main components of volatile secondary metabolites (VOCs) in the leaves and twigs can provide guidance for the multifunctional management of Phoebe bournei. 【Method】Here, the 10-year-old P. bournei monoculture plantations in Jindong Forestry Farm were selected as research objects, and five potassium fertilizer (K2O>52%) levels (CK, 0 g/individual; K1, 60 g/individual; K2, 120 g/individual; K3, 180 g/individual; K4, 240 g/individual) were employed and conducted. The samples were collected in January and July after the amendment of potassium fertilizer (in summer). The determinations and extractions of plant VOCs were using hydro distillation and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). 【Result】The potassium fertilization level had a significant effect on the content of VOCs in P. bournei. The VOCs content in leaves and twigs showed a trend of initially increasing and then decreasing. In January, the highest extraction rate (mass fraction) was observed in the K2 treatment (in leaves 0.48‰, in twigs 0.55‰), while the highest extraction rate (mass fraction) was observed in the K1 treatment (in leaves 0.47‰, in twigs 0.34‰) in July. Alloaroma dendrene, caryophyllene and (-)-alpha-pinene in leaves was the feature components in leaves of P. bournei VOCs, and beta-caryophyllene, (-)-alpha-pinene and (-)-alpha-bisabolene were the characteristic components of VOCs in twigs. The VOCs were mainly composed of olefins, naphthalenes, and alcohols. The relative content of olefins and naphthalenes in the leaves increased significantly under the K2 treatment in both seasons, while the relative content of alcohols decreased significantly after fertilization. In addition, leaf nutrients had a positive effect on the content of VOCs in twigs, and the path coefficient was extremely significant. Twig nutrients had a positive effect on the relative content of various types of VOCs in the leaves. 【Conclusion】The application of potassium fertilizer significantly affects the amount and components of VOCs and nutrient content in the leaves and twigs of P. bournei, when the application is 60-180 g/individual, the total content of VOCs in the leaves and twigs of P. bournei reaches its highest level. Overall, K3 is the optimal treatment in January, while K2 is the optimal treatment in July. The model demonstrates that nutrient elements have a positive impact on the synthesis of sesquiterpenes such as alkenes and naphthalenes in the VOCs found in leaves and twigs.
Phoebe bournei / potassium fertilizer / volatile secondary metabolites / nutrient
| [1] |
郝龙飞, 王庆成, 刘婷岩, 等. 指数施肥对斑叶稠李苗木生物量分配、光合作用及根系形态的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2014, 50(11):175-181.
|
| [2] |
周维. 氮磷钾配比施肥对格木幼苗生长及光合特性影响的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2016.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
陆潭, 陈华涛, 沈振国, 等. 植物钾通道与钾转运体研究进展[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(S1):372-379.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
郭满, 杨博超, 王凤娇, 等. 供钾水平对核桃幼苗生长及光合作用的影响[J]. 中国果树, 2023(2):25-30.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
扶巧梅. 五种柏科植物精油对蚊虫的生物活性[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2012.
|
| [13] |
毛运芝, 冯璐璐, 冉慧, 等. 缙云山5种乡土楠木资源叶片精油挥发性成分GC-MS鉴定与组成差异分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(2):182-196.
|
| [14] |
郑炳松, 程晓建, 蒋德安, 等. 钾元素对植物光合速率、Rubisco和RCA的影响[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 2002, 19(1):104-108.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
何金明, 肖艳辉, 王羽梅, 等. 钾浓度对茴香植株生长发育、精油含量和组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(3):417-422.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
胡文杰. 樟树不同化学型精油主成分时空变异规律及优良单株选择[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2013.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
周全发, 谢柯香. 闽楠苗木培育技术[J]. 林业与生态, 2019(9):36-37.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
谢亚斌. 不同配方施肥对闽楠幼林影响的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2019.
|
| [25] |
赵姣. 芳樟枝叶精油含量与营养元素含量的动态变化及其相关性[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(12):57-67.
|
| [26] |
张薇, 付昀, 李季芳, 等. 基于凯氏定氮法与杜马斯燃烧法测定土壤全氮的比较研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(35):172-175.
|
| [27] |
邹映雪, 黄安香, 杨守禄, 等. 森林植物全钾测定两种消煮法比较[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2016, 44(4):32-35.
|
| [28] |
董翔, 何功秀, 文仕知, 等. 不同施肥处理条件下闽楠叶片精油组分GC/MS鉴定分析[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2020, 35(12):156-163.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
刘沛书, 文仕知, 李智华, 等. 施氮对闽楠挥发性次生代谢物组分和含量的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(5):16-26,48.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
陈大华, 叶和春, 李国凤, 等. 植物类异戊二烯代谢途径的分子生物学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2000, 42(6):551-558.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
王金祥, 李玲, 潘瑞炽. 高等植物中赤霉素的生物合成及其调控[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2002, 38(1):1-8.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
冉慧, 冯璐璐, 毛运芝, 等. 重庆4种野生樟科植物叶片精油GC-MS鉴定及挥发性成分分析[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(7):91-103.
|
| [46] |
曾祥谓. 我国多功能森林经营中的珍贵树种问题研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2010.
|
| [47] |
段博莉. 樟树叶片精油及其主要成分的遗传变异规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2006.
|
| [48] |
郭淑红, 薛立, 张柔, 等. 华南地区4种林分改造树种的叶片养分季节动态[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2011, 32(3):77-81.
|
| [49] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |