 PDF(7578 KB)
PDF(7578 KB)


国土空间视角下长三角城市群自然保护地连通性评估与生态修复重点区域识别
刘琪琪, 刘媛媛, 唐晓岚
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 227-234.
 PDF(7578 KB)
PDF(7578 KB)
 PDF(7578 KB)
PDF(7578 KB)
国土空间视角下长三角城市群自然保护地连通性评估与生态修复重点区域识别
Assessment of natural protected areas connectivity and identification of key ecological restoration areas in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration from the perspective of territorial spatial planning
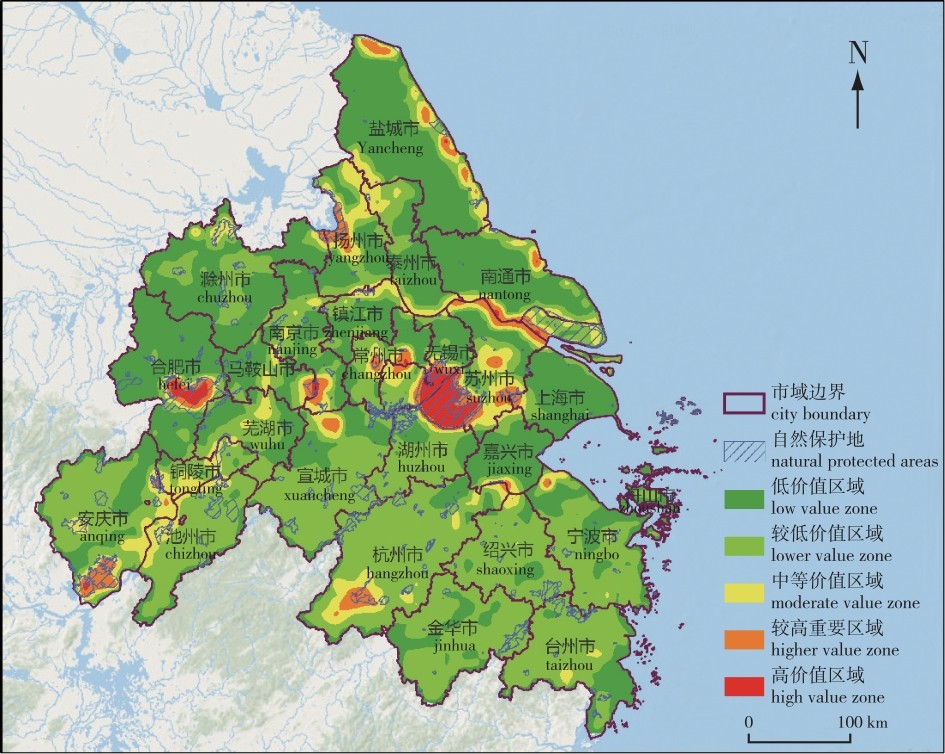
【目的】在城市化进程迅速推进的背景下,构建自然保护地(NPAs)生态安全格局(ESP)对于提升自然保护地的连通性以及推动国土空间生态修复实践具有重要的参考价值。【方法】以长江三角洲(简称长三角)城市群为研究区域,基于生态系统服务价值,结合形态学空间格局分析法(MSPA)与现有自然保护地数据识别生态源地。运用层次分析法(AHP)构建综合阻力面,并利用最小累积阻力模型(MCR)提取生态廊道,从而构建“生态源地-综合阻力面-生态廊道”模式的生态安全格局。系统评估研究区自然保护地的连通性特征,进而识别并划定国土空间生态修复的重点区域。【结果】在长三角城市群自然保护地共识别出145个生态源地,提取323条生态廊道和34条潜在生态廊道;同时,识别出1个低水平生态安全区、179个生态夹点和35个生态障碍点。【结论】研究揭示了长三角城市群自然保护地连通性面临的主要困境,提出了国土空间背景下提升自然保护地连通性与优化生态修复重点区域的策略。具体建议:推动跨区域生态廊道建设,聚焦生态修复重点区域,实施差异化分区修复措施。研究结果可为长三角城市群自然保护地连通性的提升与区域生态修复工作提供科学、可行的参考。
【Objective】In the context of rapid urbanization, establishing an ecological security pattern (ESP) for natural protected areas (NPAs) is crucial for enhancing connectivity and guiding territorial spatial ecological restoration practices.【Method】Taking the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration (YRDUA) as the study area, ecological sources were identified based on ecosystem service value by integrating morphological spatial pattern analysis (MSPA) with data on existing NPAs. A comprehensive resistance surface was constructed using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP), and ecological corridors were extracted via the minimum cumulative resistance (MCR) model. There by constructing an ESP with the model of “Ecological sources-Resistance surface-Ecological corridors”. Connectivity characteristics of NPAs were systematically assessed to pinpoint key areas for territorial spatial ecological restoration. 【Result】The study identified 145 ecological sources, 323 ecological corridors, and 34 potential corridors. Critical restoration targets included one low-security zone, 179 ecological pinch points, and 35 ecological barriers. 【Conclusion】This research reveals significant connectivity challenges among NPAs in the YRDUA and proposes connectivity enhancement strategies within territorial spatial planning: (1) Breaking administrative boundaries to promote cross-regional ecological corridor development. (2) Implementing differentiated restoration in priority zones. These findings provide scientific support for optimizing NPA connectivity and regional ecological restoration.
国土空间规划 / 自然保护地 / 生态安全格局 / 连通性评估 / 生态修复 / 长三角城市群
territorial spatial planning / natural protected areas (NPAs) / ecological security pattern / connectivity assessment / ecological restoration / Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration (YRDUA)
| [1] |
彭建, 吕丹娜, 董建权, 等. 过程耦合与空间集成:国土空间生态修复的景观生态学认知[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(1):3-13.
|
| [2] |
赵智聪, 杨锐. 论国土空间规划中自然保护地规划之定位[J]. 中国园林, 2019, 35(8):5-11.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
姜虹, 彭建. 自然保护地连通网络构建与优化的方法及前瞻[J]. 地理学报, 2024, 79(9):2176-2190.
|
| [6] |
黄俊达, 黄金玲, 陈超劲. 以自然保护地为主体的广州市域生态网络构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(1):247-254.
|
| [7] |
彭建, 赵会娟, 刘焱序, 等. 区域生态安全格局构建研究进展与展望[J]. 地理研究, 2017, 36(3):407-419.
|
| [8] |
杨学龙, 叶秀英, 赵小敏, 等. 基于MSPA与MCR的生态廊道构建及优化研究:以南昌市新建区为例[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2023, 42(3):85-91.
|
| [9] |
唐晓岚, 王忆梅, 周孔飞. 基于生态安全格局的山岳型风景区景观资源保护利用研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(2):178-186.
|
| [10] |
范春苗, 王志泰, 汤娜, 等. 基于形态学空间格局和空间主成分的贵阳市中心城区生态网络构建[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(16):6620-6632.
|
| [11] |
贾艳艳, 唐晓岚, 任宇杰. 长江流域安徽段生态系统服务价值与景观生态风险时空演变及其关联分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(3):31-40.
|
| [12] |
赵同谦, 欧阳志云, 王效科, 等. 中国陆地地表水生态系统服务功能及其生态经济价值评价[J]. 自然资源学报, 2003, 18(4):443-452.
|
| [14] |
谢高地, 甄霖, 鲁春霞, 等. 一个基于专家知识的生态系统服务价值化方法[J]. 自然资源学报, 2008, 23(5):911-919.
|
| [15] |
赵永华, 张玲玲, 王晓峰. 陕西省生态系统服务价值评估及时空差异[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(10):2662-2672.
|
| [16] |
杨立焜, 周婧楠, 孙道成, 等. 基于面向未来生态保护的全域生态安全格局构建:以开封为例[J]. 城市发展研究, 2022, 29(9):33-39.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
杨青, 刘耕源, 杨志峰. 气候变化和土地利用变化驱动下的生物多样性系统分析新框架[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(3):871-884.
|
| [19] |
马坤, 陈颖晖, 唐晓岚, 等. 基于受威胁物种保护的长江中游流域自然保护地空间优化研究[J]. 地理研究, 2023, 42(12):3115-3129.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
孙丽慧, 刘浩, 汪丁, 等. 基于生态系统服务与生态环境敏感性评价的生态安全格局构建研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(11):2508-2517.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
赵广英, 宋聚生. “三区三线” 划定中的规划逻辑思辨[J]. 城市发展研究, 2020, 27(8):13-19,58.
|
| [25] |
杨文越, 徐子豪, 叶泓妤, 等. 粤港澳大湾区道路基础设施对生态网络的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(6): 1653-1660.
|
| [26] |
付励强, 邹红菲, 马建章, 等. 中国自然保护地的区域性联合保护机制和发展策略分析[J]. 林业资源管理, 2019(5):1-6,156.
|
| [27] |
姚鸿文, 王世红, 朱程昊, 等. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园生态补偿机制与标准研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(5):21-27.
|
| [28] |
于文轩, 冯瀚元. 生态文明视域下自然保护地法治体系的完善[J]. 城市与环境研究, 2024, 11(1):41-51.
|
| [29] |
李笑兰. 推动国家公园模式与社会组织的实践案例[J]. 旅游学刊, 2018, 33(8): 12-14.
|
| [30] |
刘琪琪, 唐晓岚, 刘媛媛. 韩国国立公园管理经验对中国国家公园制度的启示与借鉴[J]. 自然保护地, 2024, 4(3): 26-40.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |