 PDF(1823 KB)
PDF(1823 KB)


 PDF(1823 KB)
PDF(1823 KB)
 PDF(1823 KB)
PDF(1823 KB)
氮沉降对滇中高原地带性森林土壤呼吸的影响
Effects of nitrogen deposition on soil respiration in zonal forests in the central Yunnan Plateau
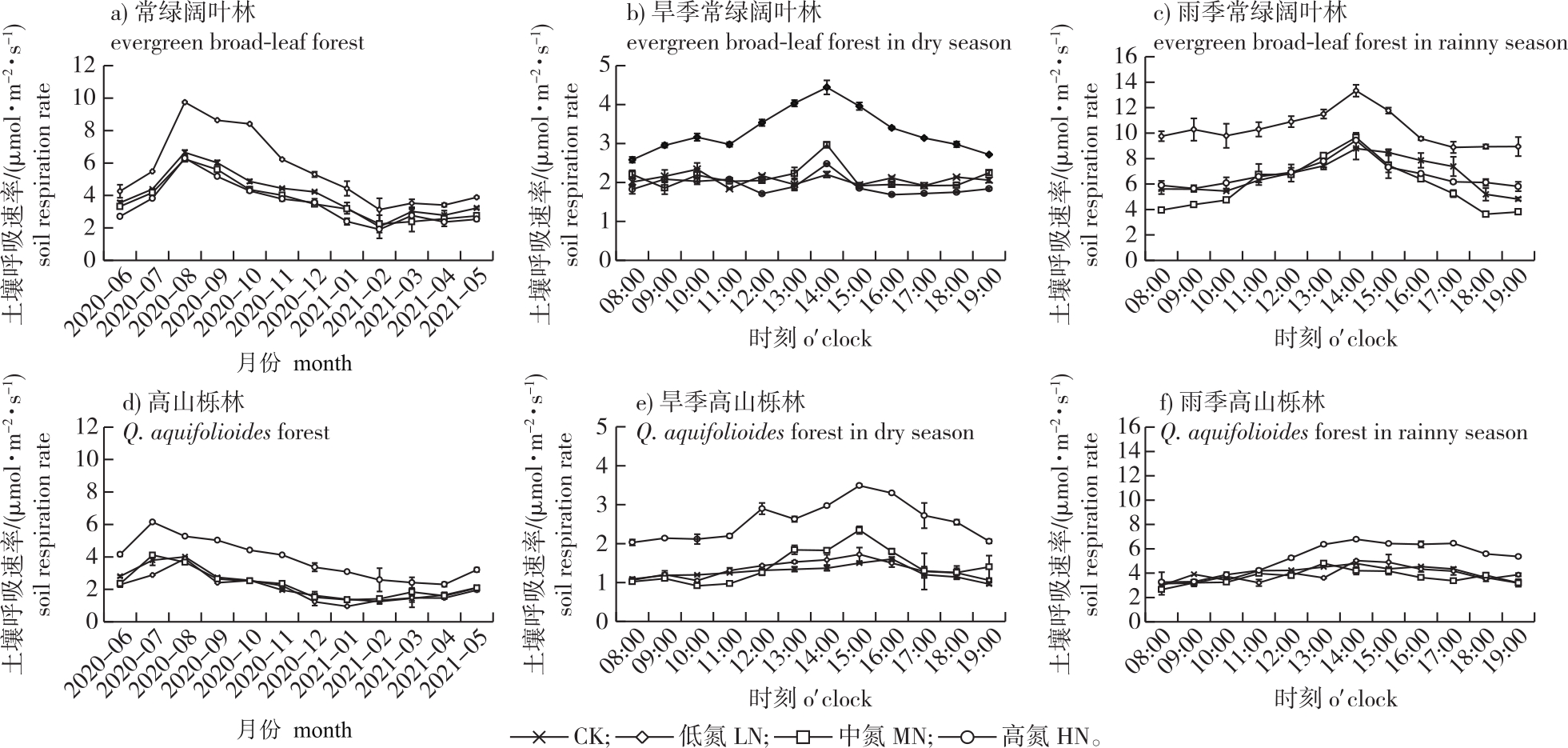
【目的】探究氮沉降下滇中高原地带性森林土壤特性的改变对土壤呼吸的影响,阐明滇中高原地带性森林土壤呼吸对氮沉降的响应机制,为准确评估亚热带森林生态系统碳含量收支及物质循环提供理论依据。【方法】以滇中高原常绿阔叶林和高山栎林两种地带性森林土壤为研究对象,设置4个氮处理梯度:对照[施氮量0 g/(m2·a),CK]、低氮[施氮量10 g/(m2·a),LN]、中氮[施氮量20 g/(m2·a),MN]和高氮[施氮量25 g/(m2·a),HN],研究施氮后土壤呼吸(RS)、温度(T)、湿度(W)和有机碳(TOC)、全氮(TN)、全磷(TP)、硝态氮($\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$)、铵态氮($\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$)含量及微生物生物量碳、氮(MBC、MBN)的动态变化特征,分析氮沉降对土壤呼吸的影响。【结果】①与CK处理相比,常绿阔叶林土壤呼吸在LN处理下增加,在MN、HN处理下降低;高山栎林土壤呼吸随施氮量增加而增大。②旱季时两种林分土壤呼吸低于雨季,雨季较旱季分别增长了155.15%(高山栎林)和181.78%(常绿阔叶林)。③不同季节两种林分土壤TOC、TN、$\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$、$\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$含量均随施氮量增加而增加,雨季时两种林分土壤MBC在各施氮处理下均低于CK。④旱季和雨季常绿阔叶林土壤呼吸与pH、TP含量、MBN存在一定的正相关(P>0.05不显著,下同);高山栎林土壤呼吸与TOC、TN、$\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$ 和$\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$含量存在一定正相关关系(P>0.05),与TP含量、MBC和MBN呈现一定的负相关关系(P>0.05),并与pH显著负相关(P<0.05)。【结论】氮沉降可通过影响土壤TOC、TN、TP、$\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$、$\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$含量及MBC和MBN使土壤呼吸发生改变,适量的氮沉降对土壤呼吸具有促进作用,过量的氮添加会抑制土壤呼吸。
【Objective】The study explored effects of changes in soil characteristics in zonal forests on soil respiration under nitrogen deposition in the central Yunnan Plateau. The study aimed to elucidate the mechanism underlying the response of soil respiration to nitrogen deposition in zonal forests, and provide a theoretical basis for the accurate assessment of the carbon budget and material cycle of subtropical forest ecosystems. 【Method】This study focused on two types of zonal forest soils, namely, evergreen broad-leaved forests and Quercus aquifolioides forests, in the central Yunnan Plateau. The soils were treated with different gradients of nitrogen, control [0 g/(m2·a) nitrogen, CK], low nitrogen [10 g/(m2·a) nitrogen, LN], medium nitrogen [20 g/(m2·a) nitrogen, MN], and high nitrogen [25 g/(m2·a) nitrogen, HN]. The variations in the characteristics of soil respiration (RS), temperature (T), humidity (W), organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), nitrate nitrogen ($\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$), ammonium nitrogen ($\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$) content, microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) were determined under nitrogen deposition. Additionally, the correlation between soil respiration and soil characteristics were determined to elucidate the mechanism underlying the effect of nitrogen deposition on soil respiration. 【Result】Compared to the CK group, soil respiration increased in the LN treatment group and decreased in the MN and HN treatment groups in the evergreen broad-leaf forests. Compared with the CK group, soil respiration increased with an increase in nitrogen application for all the treatment groups in the Q. aquifolioides forests. Soil respiration was lower in the dry season than that in the rainy season in both stands, and increased by 155.15% and 181.78% in the Q. aquifolioides and evergreen broad-leaf forests, respectively, in the rainy season compared to those in the dry season. The TOC, TN, $\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$, and $\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$ contents in the soil increased with the gradient of applied nitrogen in different seasons in both stands. Additionally, the contents of soil MBC in both stands were lower than that of the CK group in the rainy season at the different concentrations of nitrogen. The soil respiration of the evergreen broad-leaved forests exhibited a non-significant positive correlation with the pH, TP content and MBN (P > 0.05) in the dry and rainy seasons. Soil respiration in the Q. aquifolioides forests exhibited a non-significant positive correlation with the TOC, TN, $\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$, and $\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$ content, non-significant negative correlation with the TP content, MBC and MBN, and a significant negative correlation with the pH (P < 0.05) during the dry and rainy seasons. 【Conclusion】Nitrogen deposition can alter soil respiration by affecting the soil chemical indicators, including the TOC, TN, TP, $\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$, $\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$ content, MBC, and MBN. The findings revealed that moderate nitrogen deposition can promote soil respiration, while excessive nitrogen addition can inhibit soil respiration.
nitrogen deposition / soil respiration / soil charcteristics / the central Yunnan Plateau
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
杨赛兰, 耿庆宏, 许崇华, 等. 加拿大一枝黄花入侵对杨树人工林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(5):117-124.
|
| [3] |
江原, 甘小玲, 曹丰丰, 等. 短期氮磷添加对祁连山亚高山草地土壤呼吸组分的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(4):2283-2292.
|
| [4] |
高伟峰, 史宝库, 金光泽. 模拟氮沉降对典型阔叶红松林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(1):8-14.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
叶彦辉, 刘云龙, 韩艳英, 等. 氮沉降对西藏高山灌丛草甸土壤理化性质的短期影响[J]. 草地学报, 2017, 25(5):973-981.
|
| [8] |
张雨鉴, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 等. 模拟氮沉降对滇中高山栎林凋落物碳氮磷释放和生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(11):70-80,92.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
王泽西, 陈倩妹, 黄尤优, 等. 川西亚高山森林土壤呼吸和微生物生物量碳氮对施氮的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(19):7197-7207.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
周世兴, 黄从德, 向元彬, 等. 氮沉降和降水变化对华西雨屏区天然常绿阔叶林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(4):94-101,110.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
李超, 刘苑秋, 王翰琨, 等. 庐山毛竹扩张及模拟氮沉降对土壤N2O和CO2排放的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(1):146-155.
|
| [15] |
邢进梅, 王克勤, 宋娅丽, 等. 常绿阔叶林凋落叶、枝分解过程对模拟N沉降的响应[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(4):123-133.
|
| [16] |
陆姣云, 张鹤山, 田宏, 等. 氮沉降影响草地生态系统土壤氮循环过程的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6):221-234.
|
| [17] |
肖春艳, 胡情情, 陈晓舒, 等. 基于文献计量的大气氮沉降研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(3):1294-1307.
|
| [18] |
铁烈华, 张仕斌, 熊梓岑, 等. 华西雨屏区常绿阔叶林凋落叶分解过程中木质素降解对模拟氮、硫沉降的响应[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(2):25-31.
|
| [19] |
黄幸然, 郭萍萍, 吴旺旺, 等. 模拟氮沉降增加对不同树种土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(6):1420-1426.
|
| [20] |
水新利, 白云玉, 张英洁, 等. 氮沉降对长白山3种苔原类型凋落物早期分解的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 2021, 39(6):580-591.
|
| [21] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [22] |
潘禹, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 等. 模拟N沉降对滇中亚高山典型森林凋落物分解及土壤微生物的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(3):88-97.
|
| [23] |
孙海燕, 赵俊平, 肖艳玲, 等. 模拟氮沉降对武夷山亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(9):1632-1638.
|
| [24] |
武倩, 韩国栋, 王瑞珍, 等. 模拟增温对草地植物、土壤和生态系统碳交换的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(4):105-114.
|
| [25] |
王红, 王邵军, 李霁航, 等. 森林土壤呼吸及其主要调控因素研究进展[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2017, 32(1):92-97.
|
| [26] |
余景松, 付若仙, 俞元春, 等. 氮沉降对北亚热带麻栎林土壤呼吸及其温湿度敏感性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(4):1029-1037.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
林雨萱, 哀建国, 宋新章, 等. 模拟氮沉降和磷添加对杉木林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(3):494-501.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
曾清苹, 何丙辉, 毛巧芝, 等. 重庆缙云山两种林分土壤呼吸对模拟氮沉降的季节响应差异性[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(11):3244-3252.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
张婷, 周金蓉, 冯廉洁, 等. 土壤生化特性在模拟氮沉降条件下对土壤呼吸和N2O排放的影响[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 14(1):88-97.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
张克胜, 尚晴, 刘彦春, 等. 中国不同气候带人工林与天然林的土壤呼吸差异[J]. 生态科学, 2017, 36(6):49-56.
|
| [37] |
张俞, 熊康宁, 喻阳华, 等. 中国南方喀斯特石漠化地区3种经济林土壤呼吸日动态特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(1):92-99.
|
| [38] |
王楠, 潘小承, 白尚斌. 模拟酸雨对我国亚热带毛竹林土壤呼吸及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(10):3420-3430.
|
| [39] |
陈小平. 科尔沁沙丘-草甸湿地水热碳通量变化及响应机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2018.
|
| [40] |
白英辰, 陈晶, 康峰峰, 等. 模拟氮沉降下不同凋落物处理对太岳山华北落叶松林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2017, 37(4):92-99.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
张雨鉴, 宋娅丽, 王克勤. 滇中亚高山森林乔木层各器官生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(6):1669-1678.
|
| [44] |
张建华, 唐志尧, 沈海花, 等. 氮添加对北京东灵山地区灌丛土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(1):81-94.
|
| [45] |
涂利华, 戴洪忠, 胡庭兴, 等. 模拟氮沉降对华西雨屏区撑绿杂交竹林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(4):829-836.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
张雪, 梅莉, 宋利豪, 等. 模拟氮沉降对马尾松土壤微生物群落结构及温室气体释放的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(6):1917-1925.
|
| [48] |
付若仙, 余景松, 张云彬, 等. 氮添加下城市森林土壤呼吸动态变化及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(3):744-752.
|
| [49] |
王铭, 刘兴土, 李秀军, 等. 松嫩平原西部草甸草原典型植物群落土壤呼吸动态及影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(1):45-52.
|
| [50] |
陈书涛, 刘巧辉, 胡正华, 等. 不同土地利用方式下土壤呼吸空间变异的影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(3):1017-1025.
|
| [51] |
苏梓锐, 曾发旭, 郑成洋. 氮添加对亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤有机碳及土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(3):517-525.
|
| [52] |
于辉, 陈燕, 张欢, 等. 添加无机氮对山西太岳山油松林土壤氮素及温室气体通量的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(3):85-91.
|
| [53] |
赵凯歌, 周正虎, 金鹰, 等. 长期氮添加对落叶松和水曲柳人工林土壤碳、氮、磷含量和胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5):177-184.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |