 PDF(1768 KB)
PDF(1768 KB)


南京市地下车库地表尘重金属源解析及风险评估
蓝洋, 李岩, 董珍, 冯笛珂, 刘科, 贾振毅, 范庆斌, 李柠, 程新宇, 温佳乐, 黄浩然, 叶子, 虞叶
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 203-211.
 PDF(1768 KB)
PDF(1768 KB)
 PDF(1768 KB)
PDF(1768 KB)
南京市地下车库地表尘重金属源解析及风险评估
Analysis of heavy metal sources and risk assessment of surface dust in underground parking garages in Nanjing City
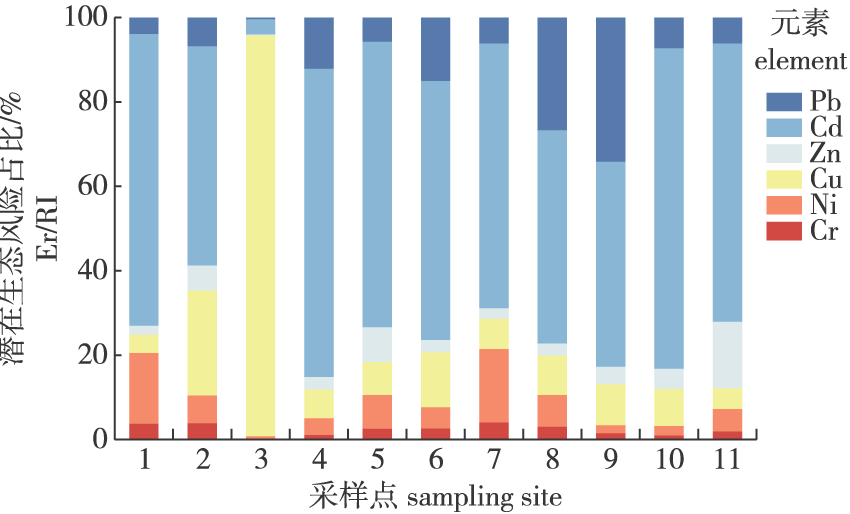
【目的】通过对南京市地下车库中地表尘重金属的来源解析和生态风险及人体健康风险的评估,提高公众对地下车库风险危害的认知。【方法】采集了南京市不同区域内地下车库中地表尘作为样本进行重金属检测,通过绝对因子分析-多元线性回归(APCS-MLR)受体模型进行源解析;生态风险方面运用地累积指数法、潜在生态风险指数法评估;运用人体健康风险评估模型进行人体健康风险评估。【结果】①南京市地下车库中地表尘重金属来源有4个因子,分别为燃料燃烧源、工业源、道路和工业降尘源、机动车排放源。②研究区Zn和Cu的平均地累积指数都达到了中至强度污染,潜在生态风险指数综合表现为较强风险。③对于人体健康来说,6种重金属的总非致癌风险对于儿童大于1,处于安全阈值之外;对于成人小于1,处于可控范围;而对于人体致癌风险来说,两种重金属元素Ni、Cr的值都大于相对安全标准的1×10-4。【结论】南京市地下车库中地表尘重金属无论对于生态还是人体健康都有负面影响,需要采取防治措施。
【Objective】This study aims to raise public awareness about the risks associated with underground parking garages in Nanjing City by analyzing heavy metals in surface dust and evaluating both ecological and human health risks. 【Method】Surface dust samples were collected from underground parking garages in different regions of Nanjing for heavy metal analysis. Source apportionment analysis was performed using the absolute principal component scores-multiple linear regression (APCS-MLR) receptor model. Ecological risk was assessed using the geo-accumulation index method and the potential ecological risk index method. Human health risks were evaluated using the human health risk index. 【Result】(1) Four sources of heavy metals in surface dust were identified: fuel combustion, industrial emissions, road and industrial dust deposition, and vehicle exhaust emissions. (2) In the study area, average geo-accumulation index values for Zn and Cu indicated moderate to strong pollution, while the potential ecological risk index suggested a relatively high ecological risk. (3) For human health, cumulative non-carcinogenic risks for the six heavy metals exceeded the safe threshold for children (>1) but remained within a manageable range for adults (<1). Carcinogenic risks associated with Ni and Cr exceeded acceptable levels, with value standards (1×10-4). 【Conclusion】The presence of heavy metals in surface dust from underground parking garages in Nanjing negatively impacts both the ecosystem and human health, underscoring the need for preventive and control measures.
地下车库 / 地表灰尘 / 重金属 / 源解析 / 生态风险 / 人体健康风险评估
underground garage / surface dust / heavy metals / source apportionment / ecological risk / human healthy risk assessment
| [1] |
徐铭焓, 林涛, 余爱华, 等. 南京市不同功能区路域表土重金属污染评价及相关性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(6):65-71.
|
| [2] |
常静, 刘敏, 侯立军, 等. 城市地表灰尘的概念、污染特征与环境效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(5):1155-1160.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
余美娟, 付庆龙, 刘永林, 等. 植物性产品重金属污染状况及其健康风险评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(3):96-100.
|
| [6] |
石文广, 李靖, 张玉红, 等. 7种杨树铅抗性和积累能力的比较研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(3):61-70.
|
| [7] |
薛红琴, 赵尘, 孔思达. 城市道路路面沉积物重金属污染程度评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(6):121-124.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
李琦路, 吴锦涛, 张颖, 等. 新乡市机动车排放对道路灰尘中重金属与多环芳烃污染的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(12):5258-5264.
|
| [10] |
李宏艳, 赵志新, 何秋生, 等. 山西介休焦化区PM2.5重金属污染特征、 关键毒性组分与来源[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(4):1528-1538.
|
| [11] |
楚芳婕, 孙爽, 李令军, 等. 2018—2020年北京市交通监测站点大气污染特征分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(12):5548-5560.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
柴育红, 王明新, 赵兴青. 重工业区户外灰尘重金属含量水平及其生态和健康风险评估[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6):1375-1384.
|
| [15] |
耿雅妮, 梁青芳, 杨宁宁, 等. 宝鸡市城区灰尘重金属空间分布、来源及健康风险[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(5):696-706.
|
| [16] |
杜曼曼, 丁庆玲, 王倩. 宜兴市典型道路灰尘(<150 μm)组分中重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(6): 1689-1698. DOI: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019041202.
|
| [17] |
李军, 李开明, 位静, 等. 兰州BRT沿线站台灰尘及其两侧绿化带土壤重金属污染及健康风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(2):228-240.
|
| [18] |
李晓燕, 汪浪, 张舒婷. 城市室内灰尘重金属水平、影响因素及健康风险:以贵阳市为例[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(8):2889-2896.
|
| [19] |
南京市统计局国家统计局南京调查队. 南京市2023年国民经济和社会发展统计公报:2024年3月[N]. 南京日报,2024-03-31(A03).
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
孙宗斌, 刘百桥, 周俊, 等. 天津城市道路灰尘重金属污染及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(8):244-250.
|
| [24] |
弓晓峰, 陈春丽, 周文斌, 等. 鄱阳湖底泥中重金属污染现状评价[J]. 环境科学, 2006, 27(4):732-736.
|
| [25] |
唐阵武, 程家丽, 岳勇, 等. 武汉典型湖泊沉积物中重金属累积特征及其环境风险[J]. 湖泊科学, 2009, 21(1):61-68.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
蔡艳洁, 张恩楼, 刘恩峰, 等. 云南阳宗海沉积物重金属污染时空特征及潜在生态风险[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(5):1121-1133.
|
| [28] |
韩琳, 徐夕博. 基于PMF模型及地统计的土壤重金属健康风险定量评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(11):5114-5124.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
中华人民共和国生态环境部.建设用地土壤污染风险评估技术导则:HJ 25.3—2019[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2019.
|
| [31] |
刘海, 魏伟, 黄健敏, 等. 长江流域(安徽段)土壤-作物系统重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(3):1686-1697.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
韦新东, 王誉洁, 贺梓健. 长春市某地下停车场PM2.5中重金属健康风险研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(3):1154-1161.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
张利瑞, 彭鑫波, 马延龙, 等. 兰州市耕地“五毒” 重金属的风险评价与归因分析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(9):4767-4778.
|
| [37] |
孙变变, 赵银鑫, 常丹, 等. 银川市城市绿地土壤重金属分布特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(6):262-268,277.
|
| [38] |
管孝艳, 王少丽, 高占义, 等. 盐渍化灌区土壤盐分的时空变异特征及其与地下水埋深的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(4):198-206.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
袁宏, 钟红梅, 赵利, 等. 基于PCA/APCS受体模型的崇州市典型农田土壤重金属污染源解析[J]. 四川环境, 2019, 38(6):35-43.
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
罗燃燃, 戴海夏, 张蕴晖, 等. 上海郊区家庭妇女PM2.5重金属组分暴露水平、来源与健康风险[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(12):5224-5233.
|
| [45] |
周亚龙, 杨志斌, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区农田土壤-农作物系统重金属潜在生态风险评估及其源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4):2003-2015.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
孙昂, 曹景丽, 王明仕, 等. 典型工业城市中小学降尘重金属风险评估和源解析研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(6):655-664.
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
王萌, 李杉杉, 李晓越, 等. 我国土壤中铜的污染现状与修复研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(5):305-313.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |